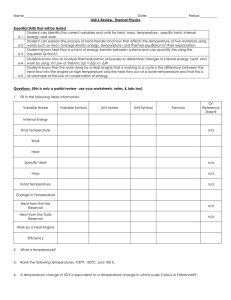
Chem 1010 Tutorials Tutorial 9A – Heat and Work Fall 2013
... 105 kJ of work is performed on a system during compression as it releases 625 kJ of heat. What is the change in internal energy of the system? ...
... 105 kJ of work is performed on a system during compression as it releases 625 kJ of heat. What is the change in internal energy of the system? ...
Heat Transfer Conduction, Convection, and Radiation
... • Thermal energy transfer is heat moving from a warmer object to a cooler object. This is known as thermal energy transfer. ...
... • Thermal energy transfer is heat moving from a warmer object to a cooler object. This is known as thermal energy transfer. ...
First, there are several issues regarding this course need to be
... (The calculated result is slightly larger than the experimental value). Quite often, we do not have to go through the above process in order to know the standard Gibbs energy of formation or standard reaction Gibbs energy, which could be employed for further calculations such as calculating equilibr ...
... (The calculated result is slightly larger than the experimental value). Quite often, we do not have to go through the above process in order to know the standard Gibbs energy of formation or standard reaction Gibbs energy, which could be employed for further calculations such as calculating equilibr ...
Introduction
... Read Chapter 23 through. You may be somewhat acquainted with the first half or so of this chapter because the material is covered in CE212. The equation development of particular importance to us is on Pages 757 through 760. It is built around Figure 23-8(a). Thus, there is a temperature gradient in ...
... Read Chapter 23 through. You may be somewhat acquainted with the first half or so of this chapter because the material is covered in CE212. The equation development of particular importance to us is on Pages 757 through 760. It is built around Figure 23-8(a). Thus, there is a temperature gradient in ...
ME 435: Thermal Energy Systems Design
... In past lectures we found that the power draw (Wc) and the capacity (Qe) are important performance parameters for a compressor. If we can develop heat exchanger models that describe the heat transfer rate, we have a set of equations that are coupled together. For example, the evaporator heat transfe ...
... In past lectures we found that the power draw (Wc) and the capacity (Qe) are important performance parameters for a compressor. If we can develop heat exchanger models that describe the heat transfer rate, we have a set of equations that are coupled together. For example, the evaporator heat transfe ...
Chapter 6 Thermodynamics and the Equations of Motion
... (6.1.35a) is normally negligible. We can estimate its size with respect to the term involving the rate of change of temperature as, (using δp for the pressure variation and δT for the temperature variation): ...
... (6.1.35a) is normally negligible. We can estimate its size with respect to the term involving the rate of change of temperature as, (using δp for the pressure variation and δT for the temperature variation): ...
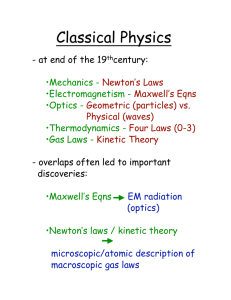
Classical Physics
... Thermal Radiation. The Rate at which an object radiates is given by the Stefan-Boltzman Law: Prad = ε σ A T4 where Prad : Power radiated in Watts A : Area of emitter (or absorber!) T : Temperature of emitter in K σ : Universal constant ( S-B’s constant) σ = 5.6703 x 10-8 W/(m2K4) ε : the emissivity ...
... Thermal Radiation. The Rate at which an object radiates is given by the Stefan-Boltzman Law: Prad = ε σ A T4 where Prad : Power radiated in Watts A : Area of emitter (or absorber!) T : Temperature of emitter in K σ : Universal constant ( S-B’s constant) σ = 5.6703 x 10-8 W/(m2K4) ε : the emissivity ...
Temperature
... • Stores more energy when raising Temp; • Releases more energy when lowering Temp ...
... • Stores more energy when raising Temp; • Releases more energy when lowering Temp ...
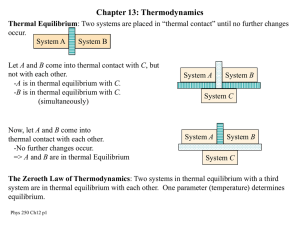
Chapters 12-15 Thermodynamics
... temperature, pressure, volume • The macroscopic parameters reflect the average behavior of the microscopic constituents of the system, for example, the velocities of the molecules which cannot be directly measured • Newton’s laws cannot be used to solve problems involving 1023 particles ...
... temperature, pressure, volume • The macroscopic parameters reflect the average behavior of the microscopic constituents of the system, for example, the velocities of the molecules which cannot be directly measured • Newton’s laws cannot be used to solve problems involving 1023 particles ...
Ch. 5: Thermochemistry
... (P ΔV is the amount of work done by expanding gases, but in most reactions, there is a very small volume change, so ΔE ~ ΔH in many cases.) ...
... (P ΔV is the amount of work done by expanding gases, but in most reactions, there is a very small volume change, so ΔE ~ ΔH in many cases.) ...
Summary of lesson - TI Education
... Answer: Agree because 3 + 5 = 8 and 3 – 2(5) = –7, and we know that the system is graphed as two distinct lines that intersect at only one point. Teacher Tip: Some students might also note that the equations are different so the lines are distinct, and because they have one point in common they are ...
... Answer: Agree because 3 + 5 = 8 and 3 – 2(5) = –7, and we know that the system is graphed as two distinct lines that intersect at only one point. Teacher Tip: Some students might also note that the equations are different so the lines are distinct, and because they have one point in common they are ...
Heat equation

The heat equation is a parabolic partial differential equation that describes the distribution of heat (or variation in temperature) in a given region over time.