L 17 - Thermodynamics [2] Thermal Expansion Coefficients of linear
... • thermal expansion of metals is put to good use in a bi-metallic strip. • this is two strips of different metals bonded ...
... • thermal expansion of metals is put to good use in a bi-metallic strip. • this is two strips of different metals bonded ...
CH 105 -- TAKE-HOME LAB The Vapor Pressure and Heat of
... 2. Write out the Clausius-Clapeyron Equation and label the factors that correspond to the factors in the point-slope formula. State directly what the slope of the graph represents. 3. How is it possible for the Ideal Gas Constant to have different values? 4. The molecular weights of water and methan ...
... 2. Write out the Clausius-Clapeyron Equation and label the factors that correspond to the factors in the point-slope formula. State directly what the slope of the graph represents. 3. How is it possible for the Ideal Gas Constant to have different values? 4. The molecular weights of water and methan ...
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTORY REMARKS 1.1 Introduction
... The “calories” that nutritionists quote when talking about the calorific value of foods, is actually the kilocalorie and it is sometimes (but by no means always) written Calorie, with a capital C. How much simpler it would all be if all of us just used joules! There is yet another problem associated ...
... The “calories” that nutritionists quote when talking about the calorific value of foods, is actually the kilocalorie and it is sometimes (but by no means always) written Calorie, with a capital C. How much simpler it would all be if all of us just used joules! There is yet another problem associated ...
heat
... system is allowed to reach a final intermediate temperature. Heat lost by hot object = Heat gained by cold water Cs material (mass)material (Tfinal-Tinitial)material = Cs water (mass)water (Tfinal-Tinitial)water ...
... system is allowed to reach a final intermediate temperature. Heat lost by hot object = Heat gained by cold water Cs material (mass)material (Tfinal-Tinitial)material = Cs water (mass)water (Tfinal-Tinitial)water ...
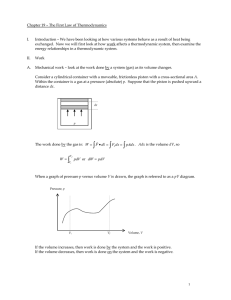
Chapter 19 – The First Law of Thermodynamics
... What is the molar heat capacity of the gas when heat is added isobarically? Add heat while keeping the pressure constant. In this case the added heat energy goes into increasing the kinetic energy (internal energy) of the molecules and in doing work on the environment ...
... What is the molar heat capacity of the gas when heat is added isobarically? Add heat while keeping the pressure constant. In this case the added heat energy goes into increasing the kinetic energy (internal energy) of the molecules and in doing work on the environment ...
February 21
... casing are attached on one side of a 1.2-cmthick 20-cm by 30-cm copper plate (k = 386 W/m·oC) by screws that exert an average pressure of 10 MPa. The base area of each transistor is 9 cm2, and each transistor is placed at the center of a 10-cm by 10-cm section of the plate. The interface roughness i ...
... casing are attached on one side of a 1.2-cmthick 20-cm by 30-cm copper plate (k = 386 W/m·oC) by screws that exert an average pressure of 10 MPa. The base area of each transistor is 9 cm2, and each transistor is placed at the center of a 10-cm by 10-cm section of the plate. The interface roughness i ...
Unit 2.7: Periodic Table Group1 Group2 Li Be Na Mg K Ca Rb Sr Cs
... Light the burner and measure the time taken for the gas evolved to reach the mark on the test tube in the water bath Repeat the experiments by changing the salts. Titrations If the accurate concentration of the one solution is known, a titration can be used to determine the concentration of anot ...
... Light the burner and measure the time taken for the gas evolved to reach the mark on the test tube in the water bath Repeat the experiments by changing the salts. Titrations If the accurate concentration of the one solution is known, a titration can be used to determine the concentration of anot ...
Lecture 14 - UMD Physics
... and system due to difference in temperatures QH, C (> 0) = heat transferred to/from a hot/cold reservoir Q = −QC in 1st law (heat transferred from system...) 1st law: Q = Ws + ∆Eth refers to system Q = QH − QC ; Ws = 0; ∆Eth = 0 (steady state) ⇒ QH = QC (system provides route for energy transfer fro ...
... and system due to difference in temperatures QH, C (> 0) = heat transferred to/from a hot/cold reservoir Q = −QC in 1st law (heat transferred from system...) 1st law: Q = Ws + ∆Eth refers to system Q = QH − QC ; Ws = 0; ∆Eth = 0 (steady state) ⇒ QH = QC (system provides route for energy transfer fro ...
LECTURE NOTES ON PHS 222 (THERMAL PHYSICS) BY DR. V.C.
... Where Pext = external pressure applied in order to perform work, which causes a change in volume dV. The negative sign implies compression (dV<0) when dw should be positive ...
... Where Pext = external pressure applied in order to perform work, which causes a change in volume dV. The negative sign implies compression (dV<0) when dw should be positive ...
AA2 - U of L Class Index
... Heat flows from an area of high temperature to an area of low temperature QG = -HsCS T/z Hs is the soil thermal diffusivity (m2s-1) (Hs and CS refer to the ability to transfer heat energy) ...
... Heat flows from an area of high temperature to an area of low temperature QG = -HsCS T/z Hs is the soil thermal diffusivity (m2s-1) (Hs and CS refer to the ability to transfer heat energy) ...
Precalculus: Graphs of Tangent, Cotangent, Secant, and Cosecant
... The adjacent side has length zero! This isn’t one of our special triangles, it is a quadrantal angle! So we can still solve this, but it isn’t one of our special triangles after all. The cosecant equal to one means the sine is equal to one. The angle with sine equal to one is π/2, so x = π/2. Howeve ...
... The adjacent side has length zero! This isn’t one of our special triangles, it is a quadrantal angle! So we can still solve this, but it isn’t one of our special triangles after all. The cosecant equal to one means the sine is equal to one. The angle with sine equal to one is π/2, so x = π/2. Howeve ...
29naude
... • Formulate an equation for the shell with tensorial analysis using the Mooney Rivlin hyperelastic model. • Determine the parametric relations • Solve the equation to predict the behaviour of the system ...
... • Formulate an equation for the shell with tensorial analysis using the Mooney Rivlin hyperelastic model. • Determine the parametric relations • Solve the equation to predict the behaviour of the system ...
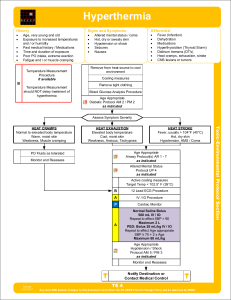
Hyperthermia
... Heat Stroke: Consists of dehydration, tachycardia, hypotension, temperature 104°F (40°C), and an altered mental status. Sweating generally disappears as body temperature rises above 104°F (40°C). The young and elderly are more prone to be dry with no sweating. Exertional Heat Stroke: In exertional h ...
... Heat Stroke: Consists of dehydration, tachycardia, hypotension, temperature 104°F (40°C), and an altered mental status. Sweating generally disappears as body temperature rises above 104°F (40°C). The young and elderly are more prone to be dry with no sweating. Exertional Heat Stroke: In exertional h ...
Heat equation

The heat equation is a parabolic partial differential equation that describes the distribution of heat (or variation in temperature) in a given region over time.



![L 17 - Thermodynamics [2] Thermal Expansion Coefficients of linear](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014728078_1-e88e92f3857e030978e2ede6a9072797-300x300.png)