Lesson
... Lesson Background Concepts for Teachers: Explain the concept that heat flows from a hot source to a cold source, and the equation that describes how much heat is lost or gained. Explain each term. Explain that in a calorimeter, the heat gained is equal to the heat lost so we can setup an energy bala ...
... Lesson Background Concepts for Teachers: Explain the concept that heat flows from a hot source to a cold source, and the equation that describes how much heat is lost or gained. Explain each term. Explain that in a calorimeter, the heat gained is equal to the heat lost so we can setup an energy bala ...
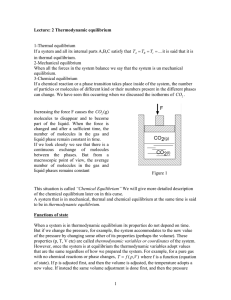
First Law of Thermodynamics
... as well as mechanically. This occurs near the surface (thermal conduction and turbulen mixing) or inside clouds due to the release of latent heat. The potential temperature of an air parcel is then no longer conserved, but now θ changes in proportion to heat transferred into the system. The increase ...
... as well as mechanically. This occurs near the surface (thermal conduction and turbulen mixing) or inside clouds due to the release of latent heat. The potential temperature of an air parcel is then no longer conserved, but now θ changes in proportion to heat transferred into the system. The increase ...
Bacon¹s inductive method, example of heat.
... From the SEP: http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/francis-bacon/ “Forms, as the final result of the methodical procedure, are: nothing more than those laws and determinations of absolute actuality which govern and constitute any simple nature, as heat, light, weight, in every kind of matter and subjec ...
... From the SEP: http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/francis-bacon/ “Forms, as the final result of the methodical procedure, are: nothing more than those laws and determinations of absolute actuality which govern and constitute any simple nature, as heat, light, weight, in every kind of matter and subjec ...
Thermal Energy - Cloudfront.net
... made of particles and atoms that constantly and randomly move. All atoms are in constant, random motion, ALL the time---even in your body! The faster they move, the more KE they have. Hot object’s particles move faster than an object that is cold. ...
... made of particles and atoms that constantly and randomly move. All atoms are in constant, random motion, ALL the time---even in your body! The faster they move, the more KE they have. Hot object’s particles move faster than an object that is cold. ...
File - Ms. A Science Online
... Radiated heat energy travels through empty space. Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light, which is 300,000,000 meters per second. Sometimes these waves are visible, like when something is “red hot.” You can see how hot it is, but you can also feel it from a distance, as your skin absorbs ...
... Radiated heat energy travels through empty space. Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light, which is 300,000,000 meters per second. Sometimes these waves are visible, like when something is “red hot.” You can see how hot it is, but you can also feel it from a distance, as your skin absorbs ...
Note Guide 7-4
... •Potential energy = energy of position/stored energy. But in chemistry we have chemical potential energy = energy stored in the chemical bonds of a substance --how much energy stored is determined by kinds of atoms and how they are arranged. •Heat(q) = energy that transfers from one object to anothe ...
... •Potential energy = energy of position/stored energy. But in chemistry we have chemical potential energy = energy stored in the chemical bonds of a substance --how much energy stored is determined by kinds of atoms and how they are arranged. •Heat(q) = energy that transfers from one object to anothe ...
Thermodynamics - Bowles Physics
... Is there an IDEAL engine model? Our goal is to figure out just how efficient such a heat engine can be: what’s the most work we can possibly get for a given amount of fuel? The efficiency question was first posed—and solved—by Sadi Carnot in 1820, not long after steam engines had become efficient e ...
... Is there an IDEAL engine model? Our goal is to figure out just how efficient such a heat engine can be: what’s the most work we can possibly get for a given amount of fuel? The efficiency question was first posed—and solved—by Sadi Carnot in 1820, not long after steam engines had become efficient e ...
Examination Heat Transfer
... a) Consider a long cylinder submerged in a flowing fluid with a constant heat transfer coefficient hc (no variations in length and circumferential direction). At time t = 0 the cylinder temperature equals T = Ti and an internal heat source q’’’ is switched on. 1) Give the describing differential equ ...
... a) Consider a long cylinder submerged in a flowing fluid with a constant heat transfer coefficient hc (no variations in length and circumferential direction). At time t = 0 the cylinder temperature equals T = Ti and an internal heat source q’’’ is switched on. 1) Give the describing differential equ ...
Heat equation

The heat equation is a parabolic partial differential equation that describes the distribution of heat (or variation in temperature) in a given region over time.