Volcanoes
... – Sticky, very viscous lava clogs up the vent. Gas (CO2 and H2O) that come out of solution and make bubbles. Gas pressure builds up and the volcano explodes. – Result is a cloud of ash that blankets countryside or an ash flow that rushes down the volcano side at speeds up to 100 km/h, incinerating e ...
... – Sticky, very viscous lava clogs up the vent. Gas (CO2 and H2O) that come out of solution and make bubbles. Gas pressure builds up and the volcano explodes. – Result is a cloud of ash that blankets countryside or an ash flow that rushes down the volcano side at speeds up to 100 km/h, incinerating e ...
_____ 1. What happens to the atmosphere after large
... _____ 5. made of pyroclastic material usually produced from moderately explosive eruptions _____ 6. formed from explosive eruptions of pyroclastic material followed by quieter flows of lava; also called stratovolcanoes ...
... _____ 5. made of pyroclastic material usually produced from moderately explosive eruptions _____ 6. formed from explosive eruptions of pyroclastic material followed by quieter flows of lava; also called stratovolcanoes ...
Volcanic and Plutonic
... Dike: A sheet of magma that cuts vertically through other layers of rock. Sill: A sheet of magma that cuts horizontally between other layers of rock. Laccolith: A magmatic body formed horizontally between layers of rock, exerting pressure upwards so as to cause a bulge. Lopolith: A magmatic body for ...
... Dike: A sheet of magma that cuts vertically through other layers of rock. Sill: A sheet of magma that cuts horizontally between other layers of rock. Laccolith: A magmatic body formed horizontally between layers of rock, exerting pressure upwards so as to cause a bulge. Lopolith: A magmatic body for ...
Volcanic Landforms
... surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes, composite volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, and lava plateaus. At some places on Earth’s surface, thin layers of lava pour out of a vent. More layers of such lava harden on ...
... surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes, composite volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, and lava plateaus. At some places on Earth’s surface, thin layers of lava pour out of a vent. More layers of such lava harden on ...
EandV_Exam2_StudyGui..
... What is its plate tectonic cause? What type of eruption was it? What was it’s magma composition? (Study Hint: the last three are closely related to each other) What was the impact of this eruption (i.e. approx. deaths/hazards)? What is notable about this volcano? Why do you think this volcano was me ...
... What is its plate tectonic cause? What type of eruption was it? What was it’s magma composition? (Study Hint: the last three are closely related to each other) What was the impact of this eruption (i.e. approx. deaths/hazards)? What is notable about this volcano? Why do you think this volcano was me ...
Topic 8 Volcanoes
... The photograph above shows a dike composed of a dark band of basaltic rock which cuts across the lighter layers of gneiss. This dike is located on the west side of the Palisades Interstate Parkway in New Jersey. ...
... The photograph above shows a dike composed of a dark band of basaltic rock which cuts across the lighter layers of gneiss. This dike is located on the west side of the Palisades Interstate Parkway in New Jersey. ...
VOLCANOES STUDY GUIDE Test 1/14/15 Key Words • Volcano
... Shield Volcano-built by thinner, fluid lava that spreads over a large area Cinder-Cone Volcanoes-built by thick lava, cone shape mountain, steep sides Composite Volcanoes-built by layers of ash and cinders sandwiched between layers of hardened lava Need to know Most of Earth’s volcanoes are loca ...
... Shield Volcano-built by thinner, fluid lava that spreads over a large area Cinder-Cone Volcanoes-built by thick lava, cone shape mountain, steep sides Composite Volcanoes-built by layers of ash and cinders sandwiched between layers of hardened lava Need to know Most of Earth’s volcanoes are loca ...
Notes 13.2 Studying the composition of rocks, scientists determine
... Studying the composition of rocks, scientists determine there are 2 types of magma o Mafic- rich in mg/fe and dark in color (commonly makes up oceanic crust) o Felsic- rich in silicate minerals and light in color (more common in continental crust) What determines the force of eruptions? o Viscosity ...
... Studying the composition of rocks, scientists determine there are 2 types of magma o Mafic- rich in mg/fe and dark in color (commonly makes up oceanic crust) o Felsic- rich in silicate minerals and light in color (more common in continental crust) What determines the force of eruptions? o Viscosity ...
Mount Kilauea, HI
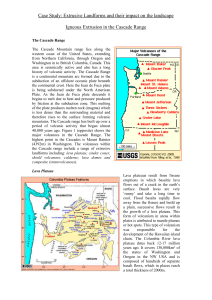
... The Columbia Plateau is located across Washington, Oregon and Idaho. It is in between the Cascade Range and the Rocky Mountains. A long time ago, the fissure of the Columbia Plateau spread out about 63,000 square miles over the Pacific Northwest. This formed a large igneous province. The lava flowed ...
... The Columbia Plateau is located across Washington, Oregon and Idaho. It is in between the Cascade Range and the Rocky Mountains. A long time ago, the fissure of the Columbia Plateau spread out about 63,000 square miles over the Pacific Northwest. This formed a large igneous province. The lava flowed ...
Shasta/Lava Beds/Lassen
... Mt. Shasta • prominent landmark at an elevation of 4,317 meters (14,162 feet) • volume of nearly 500 cubic kilometers makes it the largest of the Cascade stratovolcanoes ...
... Mt. Shasta • prominent landmark at an elevation of 4,317 meters (14,162 feet) • volume of nearly 500 cubic kilometers makes it the largest of the Cascade stratovolcanoes ...
Assignment #21 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... - Mount Fuji, Mt. St. Helens, Mount Vesuvius, Mt. Etna, Krakatoa - can erupt for lengthy periods of time Lava Flows: - mafic lava: flows like wate, very low in silicate material, does not build domes but spreads over large areas – produce plateau basalts (fig. 4.27 p. 96) can build up to several tho ...
... - Mount Fuji, Mt. St. Helens, Mount Vesuvius, Mt. Etna, Krakatoa - can erupt for lengthy periods of time Lava Flows: - mafic lava: flows like wate, very low in silicate material, does not build domes but spreads over large areas – produce plateau basalts (fig. 4.27 p. 96) can build up to several tho ...
Lab 5 Lecture
... The magma chamber below is (partially or completely) emptied after an eruption The emptied magma chamber can no longer support the weight of the overlying rock The overlying rock collapses into itself, forming a circular basin ...
... The magma chamber below is (partially or completely) emptied after an eruption The emptied magma chamber can no longer support the weight of the overlying rock The overlying rock collapses into itself, forming a circular basin ...
Hawaii Volcanoes National Park
... changed over time so they can predict where the best place would be to plant new plants in an area where they predict might not be damaged by lava. ...
... changed over time so they can predict where the best place would be to plant new plants in an area where they predict might not be damaged by lava. ...
Volcanoes - Helena High School
... • An active volcano is one that is currently erupting or has erupted recently (in geological terms). • A dormant volcano is one that has not erupted lately but is considered likely to do so in the future. ...
... • An active volcano is one that is currently erupting or has erupted recently (in geological terms). • A dormant volcano is one that has not erupted lately but is considered likely to do so in the future. ...
Classifying Volcanoes
... a. Magma Chamber- area where magma pools and builds up pressure before being released as an eruption b. Magma- liquid rock that is beneath the surface of the Earth c. Lava- liquid rock that is above the surface of the Earth d. Central Pipe- main tube that magma flows through from the magma chamber e ...
... a. Magma Chamber- area where magma pools and builds up pressure before being released as an eruption b. Magma- liquid rock that is beneath the surface of the Earth c. Lava- liquid rock that is above the surface of the Earth d. Central Pipe- main tube that magma flows through from the magma chamber e ...
Chapter 6 study guide
... 11. Give an example of an igneous rock with fine texture and coarse texture? 12. What is a hot spot? 13. How do hot spots form volcanoes? 14. What is the main “thing” magma needs to contain in order to rise to the surface? 15. What is silica? 16. What does silica do to magma? 17. Magma that does not ...
... 11. Give an example of an igneous rock with fine texture and coarse texture? 12. What is a hot spot? 13. How do hot spots form volcanoes? 14. What is the main “thing” magma needs to contain in order to rise to the surface? 15. What is silica? 16. What does silica do to magma? 17. Magma that does not ...
Case Study: Extrusive Landforms and their impact on the
... gas blast from the exposed magma (which had been contained at pressure) devastated an area 30km wide and extending 20km northwards, flattening trees within the surrounding zone. A vertical ash cloud was sent 25km into the atmosphere causing periods of darkness and circled around the earth in just ov ...
... gas blast from the exposed magma (which had been contained at pressure) devastated an area 30km wide and extending 20km northwards, flattening trees within the surrounding zone. A vertical ash cloud was sent 25km into the atmosphere causing periods of darkness and circled around the earth in just ov ...
Force of Volcanoes
... Types of Eruptions and Volcanoes (video) ______________ volcanoes form from long, gradual lava flows, pouring out in all directions. The ___________ ______________ are short and built from these ejected materials, mainly ash and rocks that fall near the summit or crate of the volcano. ______________ ...
... Types of Eruptions and Volcanoes (video) ______________ volcanoes form from long, gradual lava flows, pouring out in all directions. The ___________ ______________ are short and built from these ejected materials, mainly ash and rocks that fall near the summit or crate of the volcano. ______________ ...
Inside Earth 3-2 Worksheets 2013
... Monitoring volcanoes – easier for geologists than earthquakes – because there are usually signs/warnings that a volcano will erupt -pimples What are some changes or clues that geologists look for when they are monitoring volcanoes? _________________________________________________________________ _ ...
... Monitoring volcanoes – easier for geologists than earthquakes – because there are usually signs/warnings that a volcano will erupt -pimples What are some changes or clues that geologists look for when they are monitoring volcanoes? _________________________________________________________________ _ ...
Ch 7 S 4 Volcanic Landforms
... i. Some eruptions of lava form high, level areas ii. Lava flows out of several long cracks in an area, the thin lava flows a long way before cooling and solidifying, and the layers flow on top of each other forming a high plateau iii.Columbia Plateau in Washington, Oregon, and Idaho ...
... i. Some eruptions of lava form high, level areas ii. Lava flows out of several long cracks in an area, the thin lava flows a long way before cooling and solidifying, and the layers flow on top of each other forming a high plateau iii.Columbia Plateau in Washington, Oregon, and Idaho ...
Level Mountain

Level Mountain is a massive shield volcano in Cassiar Country, northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located just southeast of Callison Ranch, southwest of Dease Lake and about 50 km (31 mi) north of Mount Edziza. It lies on the Nahlin Plateau, comprising a series of buttes and ridges. The shield is lightly glaciated, as compared to the Coast Mountains just to the west. The only named summit of Level Mountain is Meszah Peak on the north side of the shield with an elevation of 2,190 m (7,185 ft), making it the highest point of Level Mountain. Immediately to the west, however, are the Heart Peaks, a related volcanic range just east of the Sheslay River, which is the edge of the Nahlin Plateau.Level Mountain rises above adjacent forested lowlands and undulating alpine areas surround the steeper central peaks. Streams that originate from these peaks drain across the Nahlin Plateau.