File
... hardens beneath Earth’s surface creates landforms. F.3.4.3. Analyze other distinct features that occur in volcanic areas. ...
... hardens beneath Earth’s surface creates landforms. F.3.4.3. Analyze other distinct features that occur in volcanic areas. ...
Crustal Deformation
... 27. How are volcanoes formed in subduction zones? What is the magma composed of in these regions? Give an example of this type of volcano on Earth. ...
... 27. How are volcanoes formed in subduction zones? What is the magma composed of in these regions? Give an example of this type of volcano on Earth. ...
Lecture 12
... Large Igneous Province Fed by massive mantle plumes Caused by flood basalts (especially fluid basaltic lavas) Discharge over time through long fissures (cracks) Create large plateaus ...
... Large Igneous Province Fed by massive mantle plumes Caused by flood basalts (especially fluid basaltic lavas) Discharge over time through long fissures (cracks) Create large plateaus ...
What mainly controls eruptive style? Viscosity in magma 2. Eruptive
... Tom Sisson of USGS estimates its age at ~100 ka ...
... Tom Sisson of USGS estimates its age at ~100 ka ...
File
... 4. Rocks are classified by what they are made of and how they form. Igneous rocks always begin as magma. What are the two main types of igneous rocks, and what is the main difference between them? How does each type form into solid rock? ...
... 4. Rocks are classified by what they are made of and how they form. Igneous rocks always begin as magma. What are the two main types of igneous rocks, and what is the main difference between them? How does each type form into solid rock? ...
Haystack Rock - City of Cannon Beach
... Height: 71.62 meters or 235 feet - comprised of about 1 million tons of rock Comprised of basalt, feldspar, silica, olivine and pyroxene “How did the Rock get here?” Around 15 million years ago molten lava flowed from the “Yellowstone Hotspot”. Of the 300 flows that happened, Haystack Rock arrived v ...
... Height: 71.62 meters or 235 feet - comprised of about 1 million tons of rock Comprised of basalt, feldspar, silica, olivine and pyroxene “How did the Rock get here?” Around 15 million years ago molten lava flowed from the “Yellowstone Hotspot”. Of the 300 flows that happened, Haystack Rock arrived v ...
Slide 1
... A volcano is a mountain formed of lava and/or pyroclastic material (hot fragment of preexisting rocks that are blown from the vent of a volcano). ...
... A volcano is a mountain formed of lava and/or pyroclastic material (hot fragment of preexisting rocks that are blown from the vent of a volcano). ...
Chapter 6 Study Guide
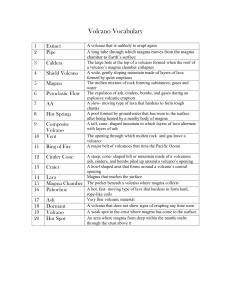
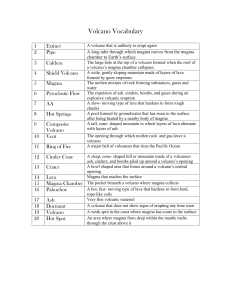
... A _______ is a mass of rock that formed when a large body of magma cooled inside the Earth’s crust. An are where magma melts through the crust in the middle of a plate is called a(n) ________________. Inside a volcano, magma collects in a pocket called a ________________. Magma from and explosive er ...
... A _______ is a mass of rock that formed when a large body of magma cooled inside the Earth’s crust. An are where magma melts through the crust in the middle of a plate is called a(n) ________________. Inside a volcano, magma collects in a pocket called a ________________. Magma from and explosive er ...
5volcano notes chapter
... 2. Landforms created by magma include: Volcanic neck-magma hardens in volcanoes pipe. Batholiths-mass of rock formed when a large body of magma cools inside the ...
... 2. Landforms created by magma include: Volcanic neck-magma hardens in volcanoes pipe. Batholiths-mass of rock formed when a large body of magma cools inside the ...
Volcano - watertown.k12.wi.us
... greater depths may have a coarse grained texture. Often dikes will be ___________________ resistant to erosion and leave a walllike protrusion on the surface. An example is Ship Rock (New Mexico). There also dikes in Wisconsin. 3. ___________________ - is a relatively horizontal structure that is pa ...
... greater depths may have a coarse grained texture. Often dikes will be ___________________ resistant to erosion and leave a walllike protrusion on the surface. An example is Ship Rock (New Mexico). There also dikes in Wisconsin. 3. ___________________ - is a relatively horizontal structure that is pa ...
clozevolcanonotes
... greater depths may have a coarse grained texture. Often dikes will be ___________________ resistant to erosion and leave a walllike protrusion on the surface. An example is Ship Rock (New Mexico). There also dikes in Wisconsin. 3. ___________________ - is a relatively horizontal structure that is pa ...
... greater depths may have a coarse grained texture. Often dikes will be ___________________ resistant to erosion and leave a walllike protrusion on the surface. An example is Ship Rock (New Mexico). There also dikes in Wisconsin. 3. ___________________ - is a relatively horizontal structure that is pa ...
Volcanoes
... likely to do so. Mt. St Helens was dormant for 123 years before it erupted in 1980. ...
... likely to do so. Mt. St Helens was dormant for 123 years before it erupted in 1980. ...
Volcanoes/REVIEW
... 4. What types of lava are produced by quiet eruptions? _____________________________________________ 5. What other eruption is there besides a quiet eruption and how is it different than a quiet eruption? _________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 4. What types of lava are produced by quiet eruptions? _____________________________________________ 5. What other eruption is there besides a quiet eruption and how is it different than a quiet eruption? _________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ ...
VOLCANOES form where molten rock is vented at Earth`s surface.
... • Ancient people from the area believed that Vulcano was the chimney of the forge of Vulcan (blacksmith of the Roman gods) • They thought hot lava fragments and clouds of dust erupting from Vulcano came from Vulcan's forge as he beat out thunderbolts for Jupiter (king of the gods) and weapons for Ma ...
... • Ancient people from the area believed that Vulcano was the chimney of the forge of Vulcan (blacksmith of the Roman gods) • They thought hot lava fragments and clouds of dust erupting from Vulcano came from Vulcan's forge as he beat out thunderbolts for Jupiter (king of the gods) and weapons for Ma ...
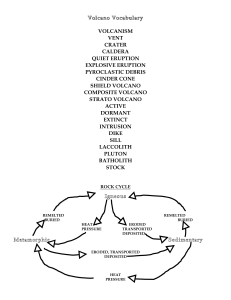
The Rock cycle: Initially proposed by James Hutton
... Describe the processes that change the composition of magma Bowen’s Reaction Series: Minerals crystallize at different temps. Mafic mineras crystalize at hotter temps. Felsic at cooler. So the mafic minerals crystallize and settle to the bottom of the magma chamber, leaving the rest of the magma mo ...
... Describe the processes that change the composition of magma Bowen’s Reaction Series: Minerals crystallize at different temps. Mafic mineras crystalize at hotter temps. Felsic at cooler. So the mafic minerals crystallize and settle to the bottom of the magma chamber, leaving the rest of the magma mo ...
Igneous Rocks - Occurrence and Classification
... Hawaiian – fluid basaltic lava is thrown into the air in jets from a vent or line of vents (a fissure) at the summit or on the flank of a volcano. Strombolian – distinct bursts of fluid lava (usually basalt or basaltic andesite) from the mouth of a magma-filled summit conduit. Vulcanian - short, vio ...
... Hawaiian – fluid basaltic lava is thrown into the air in jets from a vent or line of vents (a fissure) at the summit or on the flank of a volcano. Strombolian – distinct bursts of fluid lava (usually basalt or basaltic andesite) from the mouth of a magma-filled summit conduit. Vulcanian - short, vio ...
Unit 4 Chapter
... form steep sided volcanoes with a lot of activity Most famous volcanoes Mt St Helen's & Mt Vesuvius The Aleutian Islands, island arcs, by the North Pacific Ocean, ...
... form steep sided volcanoes with a lot of activity Most famous volcanoes Mt St Helen's & Mt Vesuvius The Aleutian Islands, island arcs, by the North Pacific Ocean, ...
Vocano (Lecture 2)
... Olympus Mons is the largest volcano on Mars. This shield volcano, similar to volcanoes in Hawaii, measures 624 km (374 mi) in diameter by 25 km (16 mi) high. It is 100 times larger than Mauna Loa on Earth. Located on the Tharsis Plateau near the equator, Olympus Mons is bordered by an escarpment. Th ...
... Olympus Mons is the largest volcano on Mars. This shield volcano, similar to volcanoes in Hawaii, measures 624 km (374 mi) in diameter by 25 km (16 mi) high. It is 100 times larger than Mauna Loa on Earth. Located on the Tharsis Plateau near the equator, Olympus Mons is bordered by an escarpment. Th ...
Volcano Report
... Shield volcanoes are formed from quiet (non-explosive) eruptions. The eruptions usually consist of flowing lava along a large area. After numerous eruptions, a dome-shaped volcanic mountain is formed from the built-up lava flows. Composite Volcanoes Composite volcanoes are very large and are formed ...
... Shield volcanoes are formed from quiet (non-explosive) eruptions. The eruptions usually consist of flowing lava along a large area. After numerous eruptions, a dome-shaped volcanic mountain is formed from the built-up lava flows. Composite Volcanoes Composite volcanoes are very large and are formed ...
What do we expect in a volcanic eruption?
... • Lava flows from from others (called some pyroclastics. Better • Range from mafic than fireworks? (e.g. basalt) to • You bet!!! felsic, like all ign rx • Rocks may form from ...
... • Lava flows from from others (called some pyroclastics. Better • Range from mafic than fireworks? (e.g. basalt) to • You bet!!! felsic, like all ign rx • Rocks may form from ...
Level Mountain

Level Mountain is a massive shield volcano in Cassiar Country, northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located just southeast of Callison Ranch, southwest of Dease Lake and about 50 km (31 mi) north of Mount Edziza. It lies on the Nahlin Plateau, comprising a series of buttes and ridges. The shield is lightly glaciated, as compared to the Coast Mountains just to the west. The only named summit of Level Mountain is Meszah Peak on the north side of the shield with an elevation of 2,190 m (7,185 ft), making it the highest point of Level Mountain. Immediately to the west, however, are the Heart Peaks, a related volcanic range just east of the Sheslay River, which is the edge of the Nahlin Plateau.Level Mountain rises above adjacent forested lowlands and undulating alpine areas surround the steeper central peaks. Streams that originate from these peaks drain across the Nahlin Plateau.