Thermal Conductivity
... Figure 2: The Heat Conduction Apparatus allows comparing the heat conduction properties of four conducting bars. One end of the bars is heated by a Peltier device. Temperature readings are taking with thermistors at locations T1 through T8. ...
... Figure 2: The Heat Conduction Apparatus allows comparing the heat conduction properties of four conducting bars. One end of the bars is heated by a Peltier device. Temperature readings are taking with thermistors at locations T1 through T8. ...
Lecture 2 - Richard Grotjahn
... • T of air inside decreases • Mass M of air inside does not change. • P outside, pushing on jug does not change • So, V decreases to match decrease of T ...
... • T of air inside decreases • Mass M of air inside does not change. • P outside, pushing on jug does not change • So, V decreases to match decrease of T ...
Energy
... • For a system whose exact description is unknown, its entropy is defined as the amount of information needed to exactly specify the state of the system ...
... • For a system whose exact description is unknown, its entropy is defined as the amount of information needed to exactly specify the state of the system ...
heated bar method
... aluminum blocks. Four flexible heaters are attached to the aluminum blocks that supply heat to the base of the sample. Heat is transferred by the sample via two pathways: 1. conduction through the solid sample 2. convection from the surface to the surroundings The temperature profile of the sample i ...
... aluminum blocks. Four flexible heaters are attached to the aluminum blocks that supply heat to the base of the sample. Heat is transferred by the sample via two pathways: 1. conduction through the solid sample 2. convection from the surface to the surroundings The temperature profile of the sample i ...
Quiz-1_MA
... The volume of an iron cube, 5 cm on edge, will increase by what amount if it is heated from 10°C to 60°C? A) ...
... The volume of an iron cube, 5 cm on edge, will increase by what amount if it is heated from 10°C to 60°C? A) ...
Heat Transfer
... the geotherm look like? If there's nonzero net heat flow per unit area out of the slab, this heat must be generated internally in the slab. In that case: d 2T dq q(y y) q(y) y yk 2 yH, dy dy ...
... the geotherm look like? If there's nonzero net heat flow per unit area out of the slab, this heat must be generated internally in the slab. In that case: d 2T dq q(y y) q(y) y yk 2 yH, dy dy ...
ppt
... the geotherm look like? If there's nonzero net heat flow per unit area out of the slab, this heat must be generated internally in the slab. In that case: d 2T dq q(y y) q(y) y yk 2 yH, dy dy ...
... the geotherm look like? If there's nonzero net heat flow per unit area out of the slab, this heat must be generated internally in the slab. In that case: d 2T dq q(y y) q(y) y yk 2 yH, dy dy ...
CH3080_reportsample_formaterrors
... To design a heat pipe - heat exchanger system for recovering about 80% of the thermal energy from exhaust air of the ventilator of a commercial building. The air flow in the ventilator is 6800 m3/hr (standard conditions) at an air velocity of 9100 m3/hr. The temperature of the exhaust air is 297 K a ...
... To design a heat pipe - heat exchanger system for recovering about 80% of the thermal energy from exhaust air of the ventilator of a commercial building. The air flow in the ventilator is 6800 m3/hr (standard conditions) at an air velocity of 9100 m3/hr. The temperature of the exhaust air is 297 K a ...
Document
... currents, you must first understand how heat t________ ransfers from one object to another. Fill in the blanks on your worksheet as you progress through this PowerPoint presentation in order to understand heat transfer. Save and use these notes to study for a test on this unit. ...
... currents, you must first understand how heat t________ ransfers from one object to another. Fill in the blanks on your worksheet as you progress through this PowerPoint presentation in order to understand heat transfer. Save and use these notes to study for a test on this unit. ...
Chapter 18
... The Celsius and Fahrenheit scales Celsius scale. Celsius degree has the same size as the Kelvin, but the zero point is different TC = (TK –273.15)oC Fahrenheit scale. Fahrenheit degree is smaller than Celsius degree, the zero point is also different TF = ((9/5) TC + 32)oF Boiling point of water: TC ...
... The Celsius and Fahrenheit scales Celsius scale. Celsius degree has the same size as the Kelvin, but the zero point is different TC = (TK –273.15)oC Fahrenheit scale. Fahrenheit degree is smaller than Celsius degree, the zero point is also different TF = ((9/5) TC + 32)oF Boiling point of water: TC ...
ASU Chain Reaction - Volume 2
... Animals with sweat glands perspire to cool large areas of skin. Water is secreted through pores in the skin. When it evaporates, the water vapor carries away heat from the skin. Lizards, snakes, and other cold-blooded animals cannot generate body heat from the energy in their food. To stay warm, the ...
... Animals with sweat glands perspire to cool large areas of skin. Water is secreted through pores in the skin. When it evaporates, the water vapor carries away heat from the skin. Lizards, snakes, and other cold-blooded animals cannot generate body heat from the energy in their food. To stay warm, the ...
Concepts for specific heat
... The results is plotted in Fig. 1. In the case β~ω ≫ 1 (i.e. kB T ≪ ~ω) this becomes vanishingly small, while for β~ω ≪ 1 (i.e. kB T ≫ ~ω) we obtain the classical result kB . One says, that the degree of freedom freezes in around a temperature where kB T = ~ω. As the energies of the phonons for solid ...
... The results is plotted in Fig. 1. In the case β~ω ≫ 1 (i.e. kB T ≪ ~ω) this becomes vanishingly small, while for β~ω ≪ 1 (i.e. kB T ≫ ~ω) we obtain the classical result kB . One says, that the degree of freedom freezes in around a temperature where kB T = ~ω. As the energies of the phonons for solid ...
Sec. 15.1 - Midland Park School District
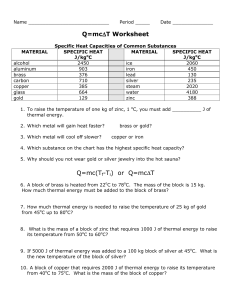
... The specific heat of any substance is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of the substance by 1 0C. Recall that 1 calorie or 4.184 J is required to raise the temperature of one gram of pure water by 1 degree Celsius. The specific heat (C) of water, then, is 1cal or 4.184 J. g ...
... The specific heat of any substance is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of the substance by 1 0C. Recall that 1 calorie or 4.184 J is required to raise the temperature of one gram of pure water by 1 degree Celsius. The specific heat (C) of water, then, is 1cal or 4.184 J. g ...
Potential energy - Midland Park School District
... The specific heat of any substance is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of the substance by 1 0C. Recall that one calorie or 4.184 J is required to raise the temperature of one gram of pure water by 1 degree Celsius. The specific heat (C) of water, then, is 1cal or 4.184 J. ...
... The specific heat of any substance is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of the substance by 1 0C. Recall that one calorie or 4.184 J is required to raise the temperature of one gram of pure water by 1 degree Celsius. The specific heat (C) of water, then, is 1cal or 4.184 J. ...
Document
... • A 5.00 gram sample of a metal is initially at 55.0 ºC. When the metal is allowed to cool for a certain time, 98.8 Joules of energy are lost and the temperature decreases to 11.0º C. What is the specific heat of the metal? What metal is it? ...
... • A 5.00 gram sample of a metal is initially at 55.0 ºC. When the metal is allowed to cool for a certain time, 98.8 Joules of energy are lost and the temperature decreases to 11.0º C. What is the specific heat of the metal? What metal is it? ...
Heat Sinks and Component Temperature Control
... Apply recommended torque on mounting bolts and nuts and use thermal grease between component and heat sink. ...
... Apply recommended torque on mounting bolts and nuts and use thermal grease between component and heat sink. ...
Document
... equilibrium with C. After this has happened if the adiabatic wall between A and B is replaced by a conducting wall and C is insulated from A and B by an adiabatic wall . It is found that the states of A and B change no further i.e. they are found to be in thermal equilibrium with each other. ...
... equilibrium with C. After this has happened if the adiabatic wall between A and B is replaced by a conducting wall and C is insulated from A and B by an adiabatic wall . It is found that the states of A and B change no further i.e. they are found to be in thermal equilibrium with each other. ...
doc heat conversion
... substance becomes hotter. Similarly, when heat energy if withdrawn from a substance the particles move slower and becomes colder. The Relationship between Heat and Temperature When a substance is heated, its temperature rises. Heat decreases or increases the temperature of a body. For instance, when ...
... substance becomes hotter. Similarly, when heat energy if withdrawn from a substance the particles move slower and becomes colder. The Relationship between Heat and Temperature When a substance is heated, its temperature rises. Heat decreases or increases the temperature of a body. For instance, when ...
Energy - Montana State University Billings
... Density of air ρ=mass/volume Density can be determined via its relationship to pressure and temperature: Equation of State (Ideal Gas Law: P = ρ R T (Pressure equals the product of the density, Universal gas constant and absolute temperature) ...
... Density of air ρ=mass/volume Density can be determined via its relationship to pressure and temperature: Equation of State (Ideal Gas Law: P = ρ R T (Pressure equals the product of the density, Universal gas constant and absolute temperature) ...
Heat and Thermal Energy Word Problems
... 13. A 500 g block of metal absorbs 5016 J of heat when its temperature changes from 20.0oC to 30.0oC. Calculate the specific heat of the metal. 14. A copper wire has a mass of 165 g. An electric current runs through the wire for a short time and its temperature rises from 21oC to 39oC. What minimum ...
... 13. A 500 g block of metal absorbs 5016 J of heat when its temperature changes from 20.0oC to 30.0oC. Calculate the specific heat of the metal. 14. A copper wire has a mass of 165 g. An electric current runs through the wire for a short time and its temperature rises from 21oC to 39oC. What minimum ...
Unit 3:Tectonic Processes
... Sial (i.e. light granitic rock): major component of the continents Sima (i.e. dense basaltic rock): major component of the ocean basins ...
... Sial (i.e. light granitic rock): major component of the continents Sima (i.e. dense basaltic rock): major component of the ocean basins ...
Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical
... When energy is transferred from one object to another, it appears as work and/or heat ∆E = Efinal – Einitial = Eproducts – Ereactants ∆ – refers to the final state of the system minus the initial state Because the total energy must be conserved, a change in the energy of the system is always accompa ...
... When energy is transferred from one object to another, it appears as work and/or heat ∆E = Efinal – Einitial = Eproducts – Ereactants ∆ – refers to the final state of the system minus the initial state Because the total energy must be conserved, a change in the energy of the system is always accompa ...
solutions
... Much of thermodynamics concerns the transformation of heat into mechanical energy. At the heart of this transformation is the heat engine, a device that converts heat into mechanical energy (think about trying to convert heat to work directly). Regardless of whether the heat engine is a spark igniti ...
... Much of thermodynamics concerns the transformation of heat into mechanical energy. At the heart of this transformation is the heat engine, a device that converts heat into mechanical energy (think about trying to convert heat to work directly). Regardless of whether the heat engine is a spark igniti ...
Heat wave

A heat wave is a prolonged period of excessively hot weather, which may be accompanied by high humidity, especially in oceanic climate countries. While definitions vary, a heat wave is measured relative to the usual weather in the area and relative to normal temperatures for the season. Temperatures that people from a hotter climate consider normal can be termed a heat wave in a cooler area if they are outside the normal climate pattern for that area.The term is applied both to routine weather variations and to extraordinary spells of heat which may occur only once a century. Severe heat waves have caused catastrophic crop failures, thousands of deaths from hyperthermia, and widespread power outages due to increased use of air conditioning. A heat wave is considered extreme weather, and a danger because heat and sunlight may overheat the human body.