Chapter 6
... • Some energy can be lost as heat (ex: frictional heating), represented by q • Heat vs. Temperature: TEMPERATURE reflects movement of particles. HEAT deals with transfer of energy between two objects due to a temperature difference. • Energy can also be transferred through work (force activing over ...
... • Some energy can be lost as heat (ex: frictional heating), represented by q • Heat vs. Temperature: TEMPERATURE reflects movement of particles. HEAT deals with transfer of energy between two objects due to a temperature difference. • Energy can also be transferred through work (force activing over ...
Thermal Barrier Coatings
... This is a coating system whose function is to reduce component temperature and thereby increase life. Thermal Barrier Coatings are generally a combination of multiple layers of coatings, with each layer having a specific function and requirement. The topmost layer provides thermal insulation and con ...
... This is a coating system whose function is to reduce component temperature and thereby increase life. Thermal Barrier Coatings are generally a combination of multiple layers of coatings, with each layer having a specific function and requirement. The topmost layer provides thermal insulation and con ...
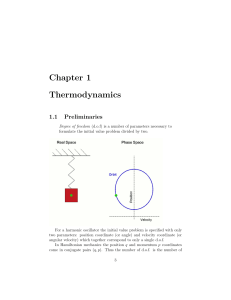
Chapter 1 Thermodynamics
... According to Carnot’s theorem the efficiency of reversible process between any two temperatures is a universal number, i.e. ÷(T1 , T2 ). This allows us to define not only relative, but also absolute temperature scale. Consider three Carnot cycles 1-2, 2-3 and 1-3 operating between different temperat ...
... According to Carnot’s theorem the efficiency of reversible process between any two temperatures is a universal number, i.e. ÷(T1 , T2 ). This allows us to define not only relative, but also absolute temperature scale. Consider three Carnot cycles 1-2, 2-3 and 1-3 operating between different temperat ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... Since ice absorbs energy as it melts, we can measure this energy. Melting energy is called the heat of fusion,Hfus, for ice. (The name comes from the fact that to fuse two pieces of metal you must melt them.) You will melt a known amount of ice and see how much heat it absorbs. Heat of fusion is re ...
... Since ice absorbs energy as it melts, we can measure this energy. Melting energy is called the heat of fusion,Hfus, for ice. (The name comes from the fact that to fuse two pieces of metal you must melt them.) You will melt a known amount of ice and see how much heat it absorbs. Heat of fusion is re ...
THE NEW DIGITAL GEOTHERMAL ATLAS OF CATALONIA FOR
... Catalonia is located in the NE of the Iberian peninsula (Figure 1). With 7.5 million people and 32.100 Km2, its territory has a great geographic variability with an altitude range that covers from sea level in the Mediterranean up to 3.100 m in the Pyrenees. The climate is predominantly Mediterranea ...
... Catalonia is located in the NE of the Iberian peninsula (Figure 1). With 7.5 million people and 32.100 Km2, its territory has a great geographic variability with an altitude range that covers from sea level in the Mediterranean up to 3.100 m in the Pyrenees. The climate is predominantly Mediterranea ...
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
... 1‐2 Reversible isothermal expansion: The gas expands slowly, doing work on the surroundings. Reversible heat transfer from the heat source at TH to the gas which is also at TH. 2‐3 Reversible adiabatic expansion: The cylinder‐piston is now insulated (adiabatic) and gas co ...
... 1‐2 Reversible isothermal expansion: The gas expands slowly, doing work on the surroundings. Reversible heat transfer from the heat source at TH to the gas which is also at TH. 2‐3 Reversible adiabatic expansion: The cylinder‐piston is now insulated (adiabatic) and gas co ...
Chapter 7: Energy and Chemical Change
... the average kinetic energy of its atoms and molecules The temperature for curve (1) is lower than for curve (2) because the average kinetic energy is lower. ...
... the average kinetic energy of its atoms and molecules The temperature for curve (1) is lower than for curve (2) because the average kinetic energy is lower. ...
WBL6_Lecture_Ch10-2djgx21
... A higher temperature does not necessarily mean that one object has more internal energy than another; the size of the object matters as well. When heat is transferred from one object to another, they are said to be in thermal contact. Two objects in thermal contact without heat transfer are in therm ...
... A higher temperature does not necessarily mean that one object has more internal energy than another; the size of the object matters as well. When heat is transferred from one object to another, they are said to be in thermal contact. Two objects in thermal contact without heat transfer are in therm ...
2.0 - Edquest
... Storm windows were used in the past to prevent heat from leaving the inside of the house in the winter. They weren’t very efficient, because the space between the two panes of glass allowed convection current to take heat out even more. The new energy efficient windows prevent this from happening by ...
... Storm windows were used in the past to prevent heat from leaving the inside of the house in the winter. They weren’t very efficient, because the space between the two panes of glass allowed convection current to take heat out even more. The new energy efficient windows prevent this from happening by ...
Electrical Properties
... Narrower energy band gap i.e. size < 2 eV, is found in semiconductors, while the broader energy band gap i.e. size > 4 eV, is found in insulators. Fermi energy for the last two band structures lies within the band gap near its center. Metals have high conductivities because of the large number ...
... Narrower energy band gap i.e. size < 2 eV, is found in semiconductors, while the broader energy band gap i.e. size > 4 eV, is found in insulators. Fermi energy for the last two band structures lies within the band gap near its center. Metals have high conductivities because of the large number ...
PY2P10 Finn Problems Chap 1
... 4.1 Heat is suppliedto an engineat the rate of 106J minute-r What is the effrciency and theenginehasan output of 10horsepower. per minute? heat output is the of the engineand what 4.2 A storage battery delivers a current into an external circuit and performs electrical work. The battery remains at a ...
... 4.1 Heat is suppliedto an engineat the rate of 106J minute-r What is the effrciency and theenginehasan output of 10horsepower. per minute? heat output is the of the engineand what 4.2 A storage battery delivers a current into an external circuit and performs electrical work. The battery remains at a ...
WS Specific Heat 2
... WS Specific Heat 2 1. How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 19.68 g of calcium from 18.00 °C to 82.40 °C? The specific heat of calcium is 0.647 J/g°C. 2. 400.0 J of heat are applied to a sample of beryllium. Its temperature increases from 22.00 °C to 50.00 °C. What is the sample’s ma ...
... WS Specific Heat 2 1. How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 19.68 g of calcium from 18.00 °C to 82.40 °C? The specific heat of calcium is 0.647 J/g°C. 2. 400.0 J of heat are applied to a sample of beryllium. Its temperature increases from 22.00 °C to 50.00 °C. What is the sample’s ma ...
Heat of Reaction
... energy is converted to kinetic energy. But, some of the kinetic energy may also be converted into random molecular motion (U, internal energy) of the water. Does this sound familiar ? It should. It is the 1st law of Thermodynamics. ...
... energy is converted to kinetic energy. But, some of the kinetic energy may also be converted into random molecular motion (U, internal energy) of the water. Does this sound familiar ? It should. It is the 1st law of Thermodynamics. ...
Chapter 04: Heat and Temperature
... • As our ball drops from the top of the Tower of Pisa, all of its molecules are falling; the whole ball loses PE as it gains KE • Internal: The total KE and PE of the molecules comprising the object • As our ball drops, friction with the air causes some of its molecules to move faster, slightly incr ...
... • As our ball drops from the top of the Tower of Pisa, all of its molecules are falling; the whole ball loses PE as it gains KE • Internal: The total KE and PE of the molecules comprising the object • As our ball drops, friction with the air causes some of its molecules to move faster, slightly incr ...
(Chapter 9 - Temperature)
... IV. Phase Changes – Latent Heat We know (from last chapter) that the state of matter depends on the (general) arrangement of its molecules. More specifically, the state depends on the temperature* of the material and the pressure exerted on it. * recall that molecules at higher temperatures move mor ...
... IV. Phase Changes – Latent Heat We know (from last chapter) that the state of matter depends on the (general) arrangement of its molecules. More specifically, the state depends on the temperature* of the material and the pressure exerted on it. * recall that molecules at higher temperatures move mor ...
Activity 63: Measuring Calories
... Next class we are reviewing for the test and working on our project. ◦ Bring any materials you would need to work on the project! ...
... Next class we are reviewing for the test and working on our project. ◦ Bring any materials you would need to work on the project! ...
Тепломассообмен
... to our physical problems in the most straightforward manner. 2. In elementary solid mechanics the lagrangian method of analysis is used. It describes the behavior of discrete particles, or point masses, as they move in space. Fundamental laws, such as Newton’s second law, apply directly to the discr ...
... to our physical problems in the most straightforward manner. 2. In elementary solid mechanics the lagrangian method of analysis is used. It describes the behavior of discrete particles, or point masses, as they move in space. Fundamental laws, such as Newton’s second law, apply directly to the discr ...
Thermal Energy Storage Capacity of some Phase changing
... increase in its temperature. This energy is generally stored in translational, vibrational and rotational modes. Thus materials with greater number of atoms in its composition are expected to have higher heat capacity. Modulated differential scanning caloriemetry (MDSC) imposes time varying heat rat ...
... increase in its temperature. This energy is generally stored in translational, vibrational and rotational modes. Thus materials with greater number of atoms in its composition are expected to have higher heat capacity. Modulated differential scanning caloriemetry (MDSC) imposes time varying heat rat ...