brochure for DermaLife pH 5.5-7
... When moisture on the skin evaporates, it draws heat out of the body to keep the internal temperature constant. The more humid the air (i.e., the more moisture the air contains), the harder it is for the body to achieve this cooling effect through the evaporation of sweat. In the DermaLifeTM System, ...
... When moisture on the skin evaporates, it draws heat out of the body to keep the internal temperature constant. The more humid the air (i.e., the more moisture the air contains), the harder it is for the body to achieve this cooling effect through the evaporation of sweat. In the DermaLifeTM System, ...
Heat wave: Caring for babies and young children
... Heat wave: Caring for babies and young children .Babies and young children (up to 4 years of age) are particularly sensitive to the effects of high temperatures and can quickly get stressed by heat. They may not always show signs or symptoms as quickly as an adult, even though they have been affecte ...
... Heat wave: Caring for babies and young children .Babies and young children (up to 4 years of age) are particularly sensitive to the effects of high temperatures and can quickly get stressed by heat. They may not always show signs or symptoms as quickly as an adult, even though they have been affecte ...
Ch 44 Lecture
... 2.Conformers: Allow for internal environment to change over a range of external conditions. ...
... 2.Conformers: Allow for internal environment to change over a range of external conditions. ...
Eastern Blue Tongued Skink
... the original tail. Further, until regeneration, the lizard must cope with the loss of other tail functions such as locomotion, competing for mates, etc. Diurnal, day active. They tend to fight over territory. Lizards regulate their body temperature by basking in the sun’s warm rays and during mid-da ...
... the original tail. Further, until regeneration, the lizard must cope with the loss of other tail functions such as locomotion, competing for mates, etc. Diurnal, day active. They tend to fight over territory. Lizards regulate their body temperature by basking in the sun’s warm rays and during mid-da ...
Chapter 16 notes
... Thermal Energy and Matter Heat: is the transfer of thermal energy from one object to another due to a difference in temperature Heat flows from: ...
... Thermal Energy and Matter Heat: is the transfer of thermal energy from one object to another due to a difference in temperature Heat flows from: ...
Humidity Ratio - SNS Courseware
... • When designing an air conditioning system, the temperature and moisture content of the air to be conditioned, and the same properties of the air needed to produce the desired air conditioning effect. • In other words, we can say that Psychrometry is the study of MOIST AIR or mixture of dry air and ...
... • When designing an air conditioning system, the temperature and moisture content of the air to be conditioned, and the same properties of the air needed to produce the desired air conditioning effect. • In other words, we can say that Psychrometry is the study of MOIST AIR or mixture of dry air and ...
Too Hot to Handle, Too Cold to Hold
... http://t0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcRY6ldjvFdbNv1yzHxQODUdh2Bl-FXF_Qo2nA4r9X3Ix27PEeqd ...
... http://t0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcRY6ldjvFdbNv1yzHxQODUdh2Bl-FXF_Qo2nA4r9X3Ix27PEeqd ...
Ch. 40 Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function note
... o Endotherms are warmed by their metabolism (“warm-blooded”) o Ectotherms are warmed by their environment (“cold-blooded”) ...
... o Endotherms are warmed by their metabolism (“warm-blooded”) o Ectotherms are warmed by their environment (“cold-blooded”) ...
Specific Heat Capacity of an Unknown Metal
... Chemists identify substances on the basis of their chemical and physical properties. One physical property of a substance is the amount of energy it will absorb per unit of mass. This property can be measured quite accurately and is called specific heat (cp)Specific heat is the amount of energy meas ...
... Chemists identify substances on the basis of their chemical and physical properties. One physical property of a substance is the amount of energy it will absorb per unit of mass. This property can be measured quite accurately and is called specific heat (cp)Specific heat is the amount of energy meas ...
Introduction to homeostasis
... assimilated under the control of insulin. Normally, fluctuations are kept within 70 to 110 mg cm−3. In type 1 diabetes cells in the pancreas stop making insulin. Consequently, blood glucose levels rise, causing symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss and frequent urination. Biochemists and biotechnolo ...
... assimilated under the control of insulin. Normally, fluctuations are kept within 70 to 110 mg cm−3. In type 1 diabetes cells in the pancreas stop making insulin. Consequently, blood glucose levels rise, causing symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss and frequent urination. Biochemists and biotechnolo ...
Name: Introduction to Meteorology Homework #1 (Chapters 1 and 2
... 31. Low latitudes (tropics) tend to gain more energy than they lose (heat surplus) since they receive more direct sunlight and high latitudes lose more energy to space than they gain (deficit). So that the temperature imbalance does not become extreme (unstable), _________________________and _______ ...
... 31. Low latitudes (tropics) tend to gain more energy than they lose (heat surplus) since they receive more direct sunlight and high latitudes lose more energy to space than they gain (deficit). So that the temperature imbalance does not become extreme (unstable), _________________________and _______ ...
Procedure
... aqueous NH3 with aqueous HCl to form aqueous ammonium chloride. 2. To use calorimetry to measure the heat of solution of ammonium chloride. 3. To calculate the heat of formation of solid ammonium chloride using these data and the known heats of formation of NH3 and HCl solutions. Discussion: When a ...
... aqueous NH3 with aqueous HCl to form aqueous ammonium chloride. 2. To use calorimetry to measure the heat of solution of ammonium chloride. 3. To calculate the heat of formation of solid ammonium chloride using these data and the known heats of formation of NH3 and HCl solutions. Discussion: When a ...
Mechanisms of Heat Transfer
... • The classical curves closely match the quantum mechanical view at radio frequencies • Radio astronomers equate the energy coming from a radio source with a temperature • NOTE: The object is not necessarily a blackbody at that temperature! Scientists would use other spectral information to determin ...
... • The classical curves closely match the quantum mechanical view at radio frequencies • Radio astronomers equate the energy coming from a radio source with a temperature • NOTE: The object is not necessarily a blackbody at that temperature! Scientists would use other spectral information to determin ...
5.1 The Nature of Heat
... Oceans store thermal energy (heat) Water can absorb heat on a hot day Water can release heat on a cool day Water’s specific heat capacity is larger than that of oil, sand, or metal ...
... Oceans store thermal energy (heat) Water can absorb heat on a hot day Water can release heat on a cool day Water’s specific heat capacity is larger than that of oil, sand, or metal ...
Mechanisms of Heat Transfer
... • The classical curves closely match the quantum mechanical view at radio frequencies • Radio astronomers equate the energy coming from a radio source with a temperature • NOTE: The object is not necessarily a blackbody at that temperature! Scientists would use other spectral information to determin ...
... • The classical curves closely match the quantum mechanical view at radio frequencies • Radio astronomers equate the energy coming from a radio source with a temperature • NOTE: The object is not necessarily a blackbody at that temperature! Scientists would use other spectral information to determin ...
CHAPTER 14: Heat Answers to Questions 1. The work goes
... convective currents to be able to completely circulate. If the flow of air is blocked, then the convective currents and the heating process will be interrupted. Heating will be less efficient and less uniform if the convective currents are prevented from circulating. 16. A ceiling fan makes more of ...
... convective currents to be able to completely circulate. If the flow of air is blocked, then the convective currents and the heating process will be interrupted. Heating will be less efficient and less uniform if the convective currents are prevented from circulating. 16. A ceiling fan makes more of ...
Heat - Haiku
... Convection currents. Convection occurs because an area with warm molecules expands and becomes less dense than the cooler areas nearby. Hence the warm area rises. Cooler molecules fall into the space left by the warm molecules and a convection current is set up. ...
... Convection currents. Convection occurs because an area with warm molecules expands and becomes less dense than the cooler areas nearby. Hence the warm area rises. Cooler molecules fall into the space left by the warm molecules and a convection current is set up. ...
Thermodynamics
... All thermodynamic systems generate waste heat. This waste results in an increase in entropy, which for a closed system is a quantitative measure of the amount of thermal energy not available to do work. Entropy in any closed system always increases; it never decreases. Additionally, moving parts pro ...
... All thermodynamic systems generate waste heat. This waste results in an increase in entropy, which for a closed system is a quantitative measure of the amount of thermal energy not available to do work. Entropy in any closed system always increases; it never decreases. Additionally, moving parts pro ...
contents - UET Mechanical 09
... Spot cooling for components or medical applications Perfect for temperature calibration in precision detection systems Rapid response times Instantaneous temperature change Reduced power consumption Dehumidification Efficient condensation of atmospheric water vapor ...
... Spot cooling for components or medical applications Perfect for temperature calibration in precision detection systems Rapid response times Instantaneous temperature change Reduced power consumption Dehumidification Efficient condensation of atmospheric water vapor ...
SUMMARY
... needed to increase the temperature of 1 gram of a substance 1 degree Celsius. The specific heat of various substances is not the same because the molecular structure of each substance is different. Energy transfer that takes place because of a temperature difference does so through conduction, conve ...
... needed to increase the temperature of 1 gram of a substance 1 degree Celsius. The specific heat of various substances is not the same because the molecular structure of each substance is different. Energy transfer that takes place because of a temperature difference does so through conduction, conve ...
heat vs temp student sheet
... Specific Heat (C) is the amount of heat it takes to raise the temperature of 1 g of a substance 1oC. The symbol for specific heat is C. It has units of joules / g oC or calories / g oC. Every substance has its own unique specific heat that can be found in reference books. The formula used to ...
... Specific Heat (C) is the amount of heat it takes to raise the temperature of 1 g of a substance 1oC. The symbol for specific heat is C. It has units of joules / g oC or calories / g oC. Every substance has its own unique specific heat that can be found in reference books. The formula used to ...
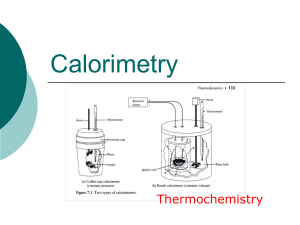
Thermochemistry - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... one another (insulation), then filled with a specific quantity of water and covered with another cup as a cover. A chemical reaction or phase change takes place inside and a thermometer is placed within to measure any change in temperature that occurs to the system. ...
... one another (insulation), then filled with a specific quantity of water and covered with another cup as a cover. A chemical reaction or phase change takes place inside and a thermometer is placed within to measure any change in temperature that occurs to the system. ...
Section 2.3 Day 2
... Finish 2.3: “Measurements and Calculations in Chemistry” Specific heat, scientific notation Homework: Pg. 63: #1-8, 10, 11 “Scientific Notation/Significant Figures” WS Concept review: “Measurements and Calculations in Chemistry” ...
... Finish 2.3: “Measurements and Calculations in Chemistry” Specific heat, scientific notation Homework: Pg. 63: #1-8, 10, 11 “Scientific Notation/Significant Figures” WS Concept review: “Measurements and Calculations in Chemistry” ...
Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia is elevated body temperature due to failed thermoregulation that occurs when a body produces or absorbs more heat than it dissipates. Extreme temperature elevation then becomes a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment to prevent disability or death.The most common causes include heat stroke and adverse reactions to drugs. The former is an acute temperature elevation caused by exposure to excessive heat, or combination of heat and humidity, that overwhelms the heat-regulating mechanisms. The latter is a relatively rare side effect of many drugs, particularly those that affect the central nervous system. Malignant hyperthermia is a rare complication of some types of general anesthesia.Hyperthermia differs from fever in that the body's temperature set point remains unchanged. The opposite is hypothermia, which occurs when the temperature drops below that required to maintain normal metabolism.