Lecture 4: 09.16.05 Temperature, heat, and entropy
... •� Work and heat are not state functions; they are path dependent- what does this mean? In most physical situations, we are concerned with a quantity of heat or work transferred into or out of a material, which causes a change from one state of the material to another. Path dependence implies that t ...
... •� Work and heat are not state functions; they are path dependent- what does this mean? In most physical situations, we are concerned with a quantity of heat or work transferred into or out of a material, which causes a change from one state of the material to another. Path dependence implies that t ...
Q = mcAT - nnhsrasetti
... units for c are consistent with your units for Q. ΔT, change in temperature, can be measured in K, °C, or °F. Just make sure that your units for c are consistent with your units for ΔT. Always start a problem by listing the given information (with units) and writing down the specific heat capaci ...
... units for c are consistent with your units for Q. ΔT, change in temperature, can be measured in K, °C, or °F. Just make sure that your units for c are consistent with your units for ΔT. Always start a problem by listing the given information (with units) and writing down the specific heat capaci ...
Experiment 5
... where L is the latent heat of transformation appropriate for the type of phase change taking place. In using eq. 2, the sign must be chosen appropriately according to the sign convention discussed above. As an example, if the object is melting, heat is being added so that the plus sign is correct. T ...
... where L is the latent heat of transformation appropriate for the type of phase change taking place. In using eq. 2, the sign must be chosen appropriately according to the sign convention discussed above. As an example, if the object is melting, heat is being added so that the plus sign is correct. T ...
Thermochemistry Calculations
... Molar Heat of Condensation The energy that must be removed in order to convert one mole of gas to liquid at its condensation point. ...
... Molar Heat of Condensation The energy that must be removed in order to convert one mole of gas to liquid at its condensation point. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch.40 Animal structure and function
... An animal is a regulator for a particular environmental variable if it uses internal control mechanisms to moderate internal change while external conditions fluctuate. ...
... An animal is a regulator for a particular environmental variable if it uses internal control mechanisms to moderate internal change while external conditions fluctuate. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch.40 Animal structure and function
... An animal is a regulator for a particular environmental variable if it uses internal control mechanisms to moderate internal change while external conditions fluctuate. ...
... An animal is a regulator for a particular environmental variable if it uses internal control mechanisms to moderate internal change while external conditions fluctuate. ...
Heat transfer in a photovoltaic panel
... Heat transfer coefficient of convection in glass surface, W/m2K Heat transfer coefficient of radiation in glass surface, W/m2K Heat transfer coefficient of convection in frame surface, W/m2K Heat transfer coefficient of radiation in frame surface, W/m2K Initial temperature, K Internal heat absorptio ...
... Heat transfer coefficient of convection in glass surface, W/m2K Heat transfer coefficient of radiation in glass surface, W/m2K Heat transfer coefficient of convection in frame surface, W/m2K Heat transfer coefficient of radiation in frame surface, W/m2K Initial temperature, K Internal heat absorptio ...
Chemistry 30
... Your hand would feel warmer. Exothermic reactions release heat to the surroundings. ...
... Your hand would feel warmer. Exothermic reactions release heat to the surroundings. ...
Chemistry 30
... Your hand would feel warmer. Exothermic reactions release heat to the surroundings. ...
... Your hand would feel warmer. Exothermic reactions release heat to the surroundings. ...
Dry heat - Grainchain
... Foods which are baked, grilled or roasted undergo colour, odour and flavour changes. The process is called dextrinisation. ...
... Foods which are baked, grilled or roasted undergo colour, odour and flavour changes. The process is called dextrinisation. ...
1aIntro to Weather
... controlling temperature, but it is not the only factor: Differential heating of land and water: land heats up more rapidly and to higher temperatures and cools more rapidly and to cooler temperatures than water Altitude: higher elevations generally experience lower temperatures than lower elevations ...
... controlling temperature, but it is not the only factor: Differential heating of land and water: land heats up more rapidly and to higher temperatures and cools more rapidly and to cooler temperatures than water Altitude: higher elevations generally experience lower temperatures than lower elevations ...
Ch 223 — The Meaning of Free Energy
... Since Suniv is always greater than zero, the term on the left is "negative energy", or energy that will be lost by the system after a reaction, for example (again, Suniv is equal to zero when the system is at equilibrium). To be more precise, the terms on the right represent the maximum amount of ...
... Since Suniv is always greater than zero, the term on the left is "negative energy", or energy that will be lost by the system after a reaction, for example (again, Suniv is equal to zero when the system is at equilibrium). To be more precise, the terms on the right represent the maximum amount of ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... Explain how heat is being transferred in the stove-pot-water system. A. Heat is being transferred from the stove to the pot through convection and from the pot to the water through conduction. B. Heat is being transferred from the stove to the pot through conduction and from the pot to the water thr ...
... Explain how heat is being transferred in the stove-pot-water system. A. Heat is being transferred from the stove to the pot through convection and from the pot to the water through conduction. B. Heat is being transferred from the stove to the pot through conduction and from the pot to the water thr ...
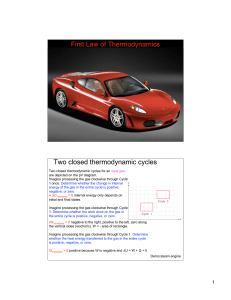
6-First Law
... 1. Increase the temperature of the solid until it reaches its melting temperature. 2. Melt the solid to form a liquid, maintaining a constant temperature. 3. Increase the temperature of the liquid until it reaches its boiling temperature. 4. Boil away all the liquid to form a gas, maintaining a cons ...
... 1. Increase the temperature of the solid until it reaches its melting temperature. 2. Melt the solid to form a liquid, maintaining a constant temperature. 3. Increase the temperature of the liquid until it reaches its boiling temperature. 4. Boil away all the liquid to form a gas, maintaining a cons ...
BUOYANCY-DRIVEN TURBULENT CONVECTION IN A BUNDLE
... As experimental velocity and temperature profiles are not available in the literature, a preliminary validation of the method employed is performed by the comparison of the global quantities like f and Nu against results in Ref. [4] and [2]. The time averaged velocity and temperature fields are repo ...
... As experimental velocity and temperature profiles are not available in the literature, a preliminary validation of the method employed is performed by the comparison of the global quantities like f and Nu against results in Ref. [4] and [2]. The time averaged velocity and temperature fields are repo ...
Cold Plate - L.D.S. System
... water, in virtue of a specific heat much higher than air, it is far more effective as a vector fluid in removing heat from a warm body. A small pump allows the circulation of fluid which must be cooled through a heat exchanger, a remote heat sink or air-cooled by means of a refrigerating unit. The h ...
... water, in virtue of a specific heat much higher than air, it is far more effective as a vector fluid in removing heat from a warm body. A small pump allows the circulation of fluid which must be cooled through a heat exchanger, a remote heat sink or air-cooled by means of a refrigerating unit. The h ...
U3 S1 L2 q=mct
... 1. Calculate the heat change involved when 2.00 L of water is heated from 20.0°C to 99.7°C in an electric kettle. 2. Calculate the heat change associated with cooling a 350.0 g aluminum bar from 70.0°C to 25.0°C. Is the change endothermic or exothermic? Why? (Hint: what is the sign of your answer?) ...
... 1. Calculate the heat change involved when 2.00 L of water is heated from 20.0°C to 99.7°C in an electric kettle. 2. Calculate the heat change associated with cooling a 350.0 g aluminum bar from 70.0°C to 25.0°C. Is the change endothermic or exothermic? Why? (Hint: what is the sign of your answer?) ...
Electronic properties of CeNi Si compound M. F
... on the valence of the Ce ion. It is believed that the hybridization between the conduction electrons and 4f Ce electrons should be responsible for the valence state of Ce. A strong hybridization will decrease the localization of the 4f Ce electrons and result in a non-magnetic intermediate valence s ...
... on the valence of the Ce ion. It is believed that the hybridization between the conduction electrons and 4f Ce electrons should be responsible for the valence state of Ce. A strong hybridization will decrease the localization of the 4f Ce electrons and result in a non-magnetic intermediate valence s ...
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTORY REMARKS 1.1 Introduction
... Prepositions play an important part in thermodynamics! Heat may be supplied to a system or lost from it. Work may be done on a gas or by it. An answer to a question in thermodynamics of “5 joules” is meaningless unless you make it clear and unambiguous whether the system lost 5 joules of heat or gai ...
... Prepositions play an important part in thermodynamics! Heat may be supplied to a system or lost from it. Work may be done on a gas or by it. An answer to a question in thermodynamics of “5 joules” is meaningless unless you make it clear and unambiguous whether the system lost 5 joules of heat or gai ...
Glossary of Terms - NJR Home Services
... HVAC - This stands for Heating, Ventilating and Air Conditioning and are the initials often used to describe the industry that produces the equipment that brings comfort to your home. Split System - This describes an air conditioning or heat pump system that is split into two sections - an outdoor s ...
... HVAC - This stands for Heating, Ventilating and Air Conditioning and are the initials often used to describe the industry that produces the equipment that brings comfort to your home. Split System - This describes an air conditioning or heat pump system that is split into two sections - an outdoor s ...
Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia is elevated body temperature due to failed thermoregulation that occurs when a body produces or absorbs more heat than it dissipates. Extreme temperature elevation then becomes a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment to prevent disability or death.The most common causes include heat stroke and adverse reactions to drugs. The former is an acute temperature elevation caused by exposure to excessive heat, or combination of heat and humidity, that overwhelms the heat-regulating mechanisms. The latter is a relatively rare side effect of many drugs, particularly those that affect the central nervous system. Malignant hyperthermia is a rare complication of some types of general anesthesia.Hyperthermia differs from fever in that the body's temperature set point remains unchanged. The opposite is hypothermia, which occurs when the temperature drops below that required to maintain normal metabolism.