Introduction to Thermal Circuits for Steady-State, One
... Thermal conduction and convection are often phenomenologically introduced in firstsemester optomechanical courses. Respective expressions governing the relation between heat flux, in W/ m 2 , to either a linear material’s temperature gradient (conduction) or the difference in surface and ambient tem ...
... Thermal conduction and convection are often phenomenologically introduced in firstsemester optomechanical courses. Respective expressions governing the relation between heat flux, in W/ m 2 , to either a linear material’s temperature gradient (conduction) or the difference in surface and ambient tem ...
Lecture 3 Water balance, Respiration and cardio
... • Heat energy gained – Qabs = radiation absorbed by the surface – M = metabolic heat production – R = infrared radiation received/emitted – C = Heat gained/lost by convection – LE = Heat gained by condensation or lost by evaporation – G = Heat gained/lost by conduction ...
... • Heat energy gained – Qabs = radiation absorbed by the surface – M = metabolic heat production – R = infrared radiation received/emitted – C = Heat gained/lost by convection – LE = Heat gained by condensation or lost by evaporation – G = Heat gained/lost by conduction ...
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
... In cold climates their efficiency drops considerably when temperatures are below the freezing point. In such cases, geothermal (ground-source) HP that use the ground as the heat source can be used. Such heat pumps are more expensive to install, but they are also more efficient. Air conditioners are ...
... In cold climates their efficiency drops considerably when temperatures are below the freezing point. In such cases, geothermal (ground-source) HP that use the ground as the heat source can be used. Such heat pumps are more expensive to install, but they are also more efficient. Air conditioners are ...
Heat Transfer and Friction Characteristics in Turbulent
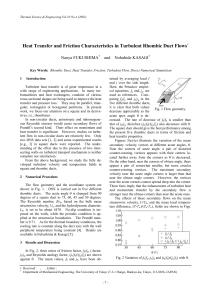
... The square duct should give the best performance among the present five rhombic ducts in terms of friction and heat transfer properties. Figures 3(a)-(e) illustrate the variation of the mean secondary velocity vectors at different acute angles, θ. Near the corners of acute angle, a pair of distorted ...
... The square duct should give the best performance among the present five rhombic ducts in terms of friction and heat transfer properties. Figures 3(a)-(e) illustrate the variation of the mean secondary velocity vectors at different acute angles, θ. Near the corners of acute angle, a pair of distorted ...
intro to physics - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Substances with low specific heat don’t store much heat, most of the heat increases translational speed (KE) of particles Substances with high specific heat store a large quantity heat as PE first, and then increase in temperature What happens to the thermal (internal) energy of a substance when it ...
... Substances with low specific heat don’t store much heat, most of the heat increases translational speed (KE) of particles Substances with high specific heat store a large quantity heat as PE first, and then increase in temperature What happens to the thermal (internal) energy of a substance when it ...
Enthalpy of combustion
... The enthalpy of combustion of a substance is the amount of energy given out when one mole of a substance burns in excess oxygen. ...
... The enthalpy of combustion of a substance is the amount of energy given out when one mole of a substance burns in excess oxygen. ...
Homeostasis Across Body Systems
... likely to see a question centered on a theme like “transport of amterials” via the digestive, respiratory, and circulatory systems than a pure question on the excretory system for example. This rule is not iron-clad as 2 pure immune questions have been asked recently (2007 form B and 2005). The AP e ...
... likely to see a question centered on a theme like “transport of amterials” via the digestive, respiratory, and circulatory systems than a pure question on the excretory system for example. This rule is not iron-clad as 2 pure immune questions have been asked recently (2007 form B and 2005). The AP e ...
Physics, Chapter 18: Transfer of Heat
... As an example, consider the case of a jar of water which is heated by applying a flame at one side A, as shown in Figure 18-2. Heat is conducted through the glass to the water. As the water in contact with the glass is heated by conduction, its density decreases, and it floats to the top. Colder wat ...
... As an example, consider the case of a jar of water which is heated by applying a flame at one side A, as shown in Figure 18-2. Heat is conducted through the glass to the water. As the water in contact with the glass is heated by conduction, its density decreases, and it floats to the top. Colder wat ...
Radiant Cooling: Thermally Active Floors
... lower occupied regions. Stratification of high spaces during heating is inefficient, because the excessive temperature of the upper unoccupied regions of the space created as a byproduct of maintaining comfort conditions in the lower occupied region, resulting in excessive heat loss. Radiant cooling ...
... lower occupied regions. Stratification of high spaces during heating is inefficient, because the excessive temperature of the upper unoccupied regions of the space created as a byproduct of maintaining comfort conditions in the lower occupied region, resulting in excessive heat loss. Radiant cooling ...
new energy-efficient building concepts affecting human thermal
... losses depending on indoor air temperature estimated by Eq. 4. (Metabolic rate is 100 W m-2, total skin area 1.87 m2, and relative air humidity 50%.) Figure 2 presents values for evaporative heat losses from skin through moisture diffusion and sweating (Esk = Edif+ Esw). In the base case, human meta ...
... losses depending on indoor air temperature estimated by Eq. 4. (Metabolic rate is 100 W m-2, total skin area 1.87 m2, and relative air humidity 50%.) Figure 2 presents values for evaporative heat losses from skin through moisture diffusion and sweating (Esk = Edif+ Esw). In the base case, human meta ...
Meteorology Part 1
... Vancouver is near the large ocean, which heats/cools slower than land. It holds that heat easily, keeping Vancouver’s air from ...
... Vancouver is near the large ocean, which heats/cools slower than land. It holds that heat easily, keeping Vancouver’s air from ...
Thermochemistry
... absolute heat contents of hydrogen, oxygen or water. But if we have defined the H of any free element (hydrogen and oxygen) to be zero then ∆H = H (2 moles of water) We see that the ∆H that we measure for this experiment is equal to the heat content of 2 moles of water. This ∆H is thus a measure of ...
... absolute heat contents of hydrogen, oxygen or water. But if we have defined the H of any free element (hydrogen and oxygen) to be zero then ∆H = H (2 moles of water) We see that the ∆H that we measure for this experiment is equal to the heat content of 2 moles of water. This ∆H is thus a measure of ...
Chapter 12
... • So the internal energy could be transferred as mechanical energy in the form of work. • Recall that work required some displacement to exist, we also need that fluid to create a displacement. • So work can only be done when there is a change in volume. – The pressure should remain constant. – If n ...
... • So the internal energy could be transferred as mechanical energy in the form of work. • Recall that work required some displacement to exist, we also need that fluid to create a displacement. • So work can only be done when there is a change in volume. – The pressure should remain constant. – If n ...
Solutions Student Handout
... chemical reaction from 30˚C to 50˚C. Specific heat capacity of water is 4.18J/˚C g. q= mc∆T = 100g (4.18J/˚C g) (50˚C− 30˚C) = 8360 J Ex. 2 Water and chemical 80g of sodium hydroxide dissolves in 120g of water and causes an increase in temperature from 20˚C to 30˚C. Calculate the heat of the reactio ...
... chemical reaction from 30˚C to 50˚C. Specific heat capacity of water is 4.18J/˚C g. q= mc∆T = 100g (4.18J/˚C g) (50˚C− 30˚C) = 8360 J Ex. 2 Water and chemical 80g of sodium hydroxide dissolves in 120g of water and causes an increase in temperature from 20˚C to 30˚C. Calculate the heat of the reactio ...
15 Thermodynamics
... Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that is built upon the fundamental laws that heat and work obey. ...
... Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that is built upon the fundamental laws that heat and work obey. ...
Experiment 6 ~ Joule Heating of a Resistor
... When a resistor absorbs electrical energy, it dissipates this energy in the form of heat Q. If the resistor is placed in the calorimeter, the amount of heat produced can be measured when it is absorbed in the calorimeter. Consider the experimental arrangement shown in Figure 5.1, which a resistor co ...
... When a resistor absorbs electrical energy, it dissipates this energy in the form of heat Q. If the resistor is placed in the calorimeter, the amount of heat produced can be measured when it is absorbed in the calorimeter. Consider the experimental arrangement shown in Figure 5.1, which a resistor co ...
Low velocity zones in the Earth`s crust
... In the resent years fragmentary crustal low velocity zones were revealed by DSS profiles at depths of 5—22 km around the Earth. However, their nature remains not quite clear. Interdisciplinary interpretation of DSS data including petrophysical thermobaric modelling the ithospheric composition brings ...
... In the resent years fragmentary crustal low velocity zones were revealed by DSS profiles at depths of 5—22 km around the Earth. However, their nature remains not quite clear. Interdisciplinary interpretation of DSS data including petrophysical thermobaric modelling the ithospheric composition brings ...
The Integumentary System
... One of the body’s primary ways of cooling itself is through the evaporation of moisture from the surface of the skin. Which structure in the dermis is responsible for this cooling? F ...
... One of the body’s primary ways of cooling itself is through the evaporation of moisture from the surface of the skin. Which structure in the dermis is responsible for this cooling? F ...
vertebrates - Bishop Ireton
... according to environmental temperature • Frogs and toads secrete chemical so they are bad tasting so predator won’t eat them • Frogs have vocal chords to communicate ...
... according to environmental temperature • Frogs and toads secrete chemical so they are bad tasting so predator won’t eat them • Frogs have vocal chords to communicate ...
95HE-4
... 6. A gas at a pressure P0 is contained in a vessel . If the masses of all the molecules are halved and their velocities doubled, the resulting pressure P would be equal to A. 4 P0 B. 2 P0 C. P0 D. P0 / 2 7. A length of steel wire 2.5mm diameter is heated from 13OC to 113OC and its ends are securely ...
... 6. A gas at a pressure P0 is contained in a vessel . If the masses of all the molecules are halved and their velocities doubled, the resulting pressure P would be equal to A. 4 P0 B. 2 P0 C. P0 D. P0 / 2 7. A length of steel wire 2.5mm diameter is heated from 13OC to 113OC and its ends are securely ...
CHEMISTRY
... called a vapor. • Vaporization is the process by which a liquid changes into a gas or vapor. • As temperature increases, water molecules gain kinetic energy – At Boiling point, molecules throughout the liquid have the energy to enter the gas or vapor phase. ...
... called a vapor. • Vaporization is the process by which a liquid changes into a gas or vapor. • As temperature increases, water molecules gain kinetic energy – At Boiling point, molecules throughout the liquid have the energy to enter the gas or vapor phase. ...
As body temperature increasesàmuscle tissue in
... The name of our course is Anatomy and Physiology. Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body. It includes not only its form and structure but also how those structures relate to each other. Anatomy literally means cutting open and was first studied by dissection. Physiology is the science o ...
... The name of our course is Anatomy and Physiology. Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body. It includes not only its form and structure but also how those structures relate to each other. Anatomy literally means cutting open and was first studied by dissection. Physiology is the science o ...
2010 MULTIPHYSICS MODELING OF INDUCTION HARDENING OF RING GEARS A.Candeo HES
... Although these concepts usually hold true for conventional hardening processes (e.g., casehardening by carburizing or nitriding), they must be carefully extended to induction hardening. In fact, this process is characterized by a very fast electromagnetic heating which originates directly within the ...
... Although these concepts usually hold true for conventional hardening processes (e.g., casehardening by carburizing or nitriding), they must be carefully extended to induction hardening. In fact, this process is characterized by a very fast electromagnetic heating which originates directly within the ...
Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia is elevated body temperature due to failed thermoregulation that occurs when a body produces or absorbs more heat than it dissipates. Extreme temperature elevation then becomes a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment to prevent disability or death.The most common causes include heat stroke and adverse reactions to drugs. The former is an acute temperature elevation caused by exposure to excessive heat, or combination of heat and humidity, that overwhelms the heat-regulating mechanisms. The latter is a relatively rare side effect of many drugs, particularly those that affect the central nervous system. Malignant hyperthermia is a rare complication of some types of general anesthesia.Hyperthermia differs from fever in that the body's temperature set point remains unchanged. The opposite is hypothermia, which occurs when the temperature drops below that required to maintain normal metabolism.