CHM112 Lab – Heat of Neutralization – Grading Rubric
... Followed procedure correctly without depending too much on instructor or lab partner ...
... Followed procedure correctly without depending too much on instructor or lab partner ...
3-10-09 Thermodynamics
... In 1824, Sadi Carnot analyzed the cycles of compression and expansion and discovered that the heat converted to useful work depends on the temperature difference between the high and low temperature reservoirs. ...
... In 1824, Sadi Carnot analyzed the cycles of compression and expansion and discovered that the heat converted to useful work depends on the temperature difference between the high and low temperature reservoirs. ...
Enthalpy of Neutralization
... Calorimetry will be employed to determine the amount of heat lost by the reaction and gained by the salt water solution. A calorimeter is simply a container used to measure the heat change. Coffee Cup Calorimetry just means that we will be measuring heat at constant pressure, H. The heat lost by th ...
... Calorimetry will be employed to determine the amount of heat lost by the reaction and gained by the salt water solution. A calorimeter is simply a container used to measure the heat change. Coffee Cup Calorimetry just means that we will be measuring heat at constant pressure, H. The heat lost by th ...
WS F: Phase Change Problems Worksheet
... or steam? How much heat is released by the one which releases the most? Water will release the most energy since the specific heat of liquid water is the ...
... or steam? How much heat is released by the one which releases the most? Water will release the most energy since the specific heat of liquid water is the ...
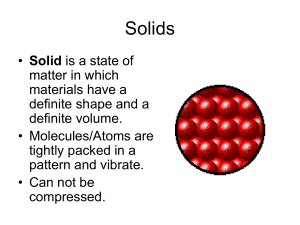
Phase Changes
... solid changes into a liquid. • Boiling Point: The temperature at which a liquid changes into a gas. • What is a Freezing point? Compare the freezing and melting points of water. ...
... solid changes into a liquid. • Boiling Point: The temperature at which a liquid changes into a gas. • What is a Freezing point? Compare the freezing and melting points of water. ...
Thermal Energy - WordPress.com
... • What do we see? Some objects need more energy than others to raise their temperature by the same amount- it takes more energy to heat water than the same mass of copper • Why? Water molecules require more energy in order to move around fast enough to increase temperature by 1 K • The heat capacity ...
... • What do we see? Some objects need more energy than others to raise their temperature by the same amount- it takes more energy to heat water than the same mass of copper • Why? Water molecules require more energy in order to move around fast enough to increase temperature by 1 K • The heat capacity ...
specific heat
... Heat capacity of a body is the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of the body by 1oC. The specific heat of a substance is the heat capacity per unit mass. Thus, heat capacity = mass x specific heat. The specific heat is essentially a measure of how thermally insensitive a substance i ...
... Heat capacity of a body is the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of the body by 1oC. The specific heat of a substance is the heat capacity per unit mass. Thus, heat capacity = mass x specific heat. The specific heat is essentially a measure of how thermally insensitive a substance i ...
Lecture Note Topic 2
... heat engine which is 100% efficient. For example, gasoline engines must have a radiator or cooling fins where heat is expelled to the environment. Current gasoline engines are only about 25% efficient as a result (75 cents on the dollar goes to heating the air outside the car). The second law says w ...
... heat engine which is 100% efficient. For example, gasoline engines must have a radiator or cooling fins where heat is expelled to the environment. Current gasoline engines are only about 25% efficient as a result (75 cents on the dollar goes to heating the air outside the car). The second law says w ...
U3 S1 L2 q=mct
... 1. Calculate the heat change involved when 2.00 L of water is heated from 20.0°C to 99.7°C in an electric kettle. 2. Calculate the heat change associated with cooling a 350.0 g aluminum bar from 70.0°C to 25.0°C. Is the change endothermic or exothermic? Why? (Hint: what is the sign of your answer?) ...
... 1. Calculate the heat change involved when 2.00 L of water is heated from 20.0°C to 99.7°C in an electric kettle. 2. Calculate the heat change associated with cooling a 350.0 g aluminum bar from 70.0°C to 25.0°C. Is the change endothermic or exothermic? Why? (Hint: what is the sign of your answer?) ...
Chapter 3 PowerPoint Notes
... directly proportional to its temperature in kelvins if the pressure and the number of particles remains constant. • V = Volume • T = Temperature • 1 = before the change • 2 = after the change ...
... directly proportional to its temperature in kelvins if the pressure and the number of particles remains constant. • V = Volume • T = Temperature • 1 = before the change • 2 = after the change ...
Lab-Temp., Heat, and Thermal Energy
... Temperature is the _______________________________________________ of the particles. Thermal energy is the ___________________________________________ of the particles. Heat is ____________________________________________________________________________. ...
... Temperature is the _______________________________________________ of the particles. Thermal energy is the ___________________________________________ of the particles. Heat is ____________________________________________________________________________. ...
Unit 09 - Midland ISD
... Energy and Change of State You do not have to write this When energy is added to a solid substance, its temperature increases until its melting point is reached. Upon the addition of more energy, the substance begins to melt. ...
... Energy and Change of State You do not have to write this When energy is added to a solid substance, its temperature increases until its melting point is reached. Upon the addition of more energy, the substance begins to melt. ...
Unit 4: Themodynamics
... the specific heat of mercury is .0330 cal/g*C, how much heat must have been given to the mercury? Your answer should be in joules How many calories are in a joule? ...
... the specific heat of mercury is .0330 cal/g*C, how much heat must have been given to the mercury? Your answer should be in joules How many calories are in a joule? ...
New Title - cloudfront.net
... 13. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true of thermal energy. a. Thermal energy partly depends on the temperature of a substance. b. Thermal energy partly depends on the scale used to measure the tem perature of a substance. c. Thermal energy partly depends on how the particles of a substan ...
... 13. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true of thermal energy. a. Thermal energy partly depends on the temperature of a substance. b. Thermal energy partly depends on the scale used to measure the tem perature of a substance. c. Thermal energy partly depends on how the particles of a substan ...
P3_U8doc - Port Fest Baltimore
... Brake Horsepower (BHP)= engine output delivered to drive train (line shaft losses: 2-5%) some of the torque delivered to the reduction gears by the engine is used to overcome friction in the drive train; thus the difference in BHP, SHP and DHP BHP-SHP = Line Losses numerically, HP = Torque ( ...
... Brake Horsepower (BHP)= engine output delivered to drive train (line shaft losses: 2-5%) some of the torque delivered to the reduction gears by the engine is used to overcome friction in the drive train; thus the difference in BHP, SHP and DHP BHP-SHP = Line Losses numerically, HP = Torque ( ...
q - webhosting.au.edu
... of the HCl and NaOH solutions was the same, 22.50°C, and the final temperature of the mixed solution was 25.86°C. Calculate the heat change for the neutralization reaction on a molar basis: ...
... of the HCl and NaOH solutions was the same, 22.50°C, and the final temperature of the mixed solution was 25.86°C. Calculate the heat change for the neutralization reaction on a molar basis: ...
WS- Specific heat
... 1. How many calories of heat are required to raise the temperature of 550 g of water from 12.0 oC to 18.0 oC? (remember the specific heat of water is 1.00 cal/g x oC) 2. How much heat is lost when a 640 g piece of copper cools from 375 oC, to 26 oC? (The specific heat of copper is 0.38452 J/g x oC) ...
... 1. How many calories of heat are required to raise the temperature of 550 g of water from 12.0 oC to 18.0 oC? (remember the specific heat of water is 1.00 cal/g x oC) 2. How much heat is lost when a 640 g piece of copper cools from 375 oC, to 26 oC? (The specific heat of copper is 0.38452 J/g x oC) ...
AP Physics Ch 12-15 – Thermal Physics
... the firing chamber and 600 K in the exhaust chamber is most nearly (A) 33% (B) 40% (C) 60% (D) 67% (E) 100% ...
... the firing chamber and 600 K in the exhaust chamber is most nearly (A) 33% (B) 40% (C) 60% (D) 67% (E) 100% ...
Enthalpy of combustion
... The enthalpy of combustion of a substance is the amount of energy given out when one mole of a substance burns in excess oxygen. ...
... The enthalpy of combustion of a substance is the amount of energy given out when one mole of a substance burns in excess oxygen. ...
Chapter 18
... The ingredients for stew cook in enough liquid for them to float freely during the cooking process ...
... The ingredients for stew cook in enough liquid for them to float freely during the cooking process ...
Chapters 10-12: Thermal Physics Thermal Energy – energy due to
... pressure 1.02 × 105 Pa, and the cylinder is in contact with a water bath at a temperature of 0°C. The gas is then taken through the following four-step process. • A 2.50 kg metal block is placed on top of the piston, compressing the gas to state 2, with the gas still at 0°C. • The cylinder is then ...
... pressure 1.02 × 105 Pa, and the cylinder is in contact with a water bath at a temperature of 0°C. The gas is then taken through the following four-step process. • A 2.50 kg metal block is placed on top of the piston, compressing the gas to state 2, with the gas still at 0°C. • The cylinder is then ...