Chapter 9 Outline
... Emulsifier – a substance composed of large molecules that are polar at one end and nonpolar at the other. Polar end is attracted to water while the nonpolar molecule such as oil. ...
... Emulsifier – a substance composed of large molecules that are polar at one end and nonpolar at the other. Polar end is attracted to water while the nonpolar molecule such as oil. ...
THERMODYNAMICS Ideal Gases. Also for gases we concentrate on
... Using the entropy concept, another form of the second principle is: iii) 'In real transformations the entropy is always increasing'. An increase means that the Q increases more than T or that T decreases: in both cases energy is degraded at a lower efficiency. We know that the Universe as a whole is ...
... Using the entropy concept, another form of the second principle is: iii) 'In real transformations the entropy is always increasing'. An increase means that the Q increases more than T or that T decreases: in both cases energy is degraded at a lower efficiency. We know that the Universe as a whole is ...
Earthquakes
... i. Is when object of two different temperatures come in contact, and after transferring energy, have become the same temperature. 2. Methods of Heating a. Conduction i. Is the transfer of thermal energy through direct contact. (Remember the person walking on the beach with no shoes on)? ii. As fast ...
... i. Is when object of two different temperatures come in contact, and after transferring energy, have become the same temperature. 2. Methods of Heating a. Conduction i. Is the transfer of thermal energy through direct contact. (Remember the person walking on the beach with no shoes on)? ii. As fast ...
Heat Standard 4a/4d p. 400-409 1. The earth receives energy from
... i. Is when object of two different temperatures come in contact, and after transferring energy, have become the same temperature. 2. Methods of Heating a. Conduction i. Is the transfer of thermal energy through direct contact. (Remember the person walking on the beach with no shoes on)? ii. As fast ...
... i. Is when object of two different temperatures come in contact, and after transferring energy, have become the same temperature. 2. Methods of Heating a. Conduction i. Is the transfer of thermal energy through direct contact. (Remember the person walking on the beach with no shoes on)? ii. As fast ...
Discovery Education Science Connection
... feel as though it is 100° F outside. It is important to understand that the heat index assumes that an individual is standing in a shady place and there is a light breeze. These conditions may not always be the case. Higher winds can cool down the body, particularly when the skin is wet. Evaporative ...
... feel as though it is 100° F outside. It is important to understand that the heat index assumes that an individual is standing in a shady place and there is a light breeze. These conditions may not always be the case. Higher winds can cool down the body, particularly when the skin is wet. Evaporative ...
Specific Heat of Metals Make Up Directions
... 1. Go to the website listed above. Read the information and then scroll down to the applet. Uses JAVA so may need to update or allow JAVA to run. Part 1 is Iron and part 2 is Copper. 2. Use the mass of the water and the metal from your data table below. 3. Using the thermometer on the screen, record ...
... 1. Go to the website listed above. Read the information and then scroll down to the applet. Uses JAVA so may need to update or allow JAVA to run. Part 1 is Iron and part 2 is Copper. 2. Use the mass of the water and the metal from your data table below. 3. Using the thermometer on the screen, record ...
Chemistry 2015-2016 Name: Calorimetry Practice Date: Per
... We don’t always have to use water. Let’s use some aluminum shot. 175 grams of hot aluminum (100.°C) is dropped into an insulated cup that contains 40.0 mL of ice cold water (0.0°C). Follow the example above to determine the final temperature, ...
... We don’t always have to use water. Let’s use some aluminum shot. 175 grams of hot aluminum (100.°C) is dropped into an insulated cup that contains 40.0 mL of ice cold water (0.0°C). Follow the example above to determine the final temperature, ...
Using Specific Heat to Determine the Identity of an
... Fill a 250 ml beaker about half full of water and begin to heat it Obtain a metal sample and determine its mass Place the metal sample in the water Heat the water to boiling. Leave the metal I the water for at least two minutes after the water boils, to assure that the metal is the same temperature ...
... Fill a 250 ml beaker about half full of water and begin to heat it Obtain a metal sample and determine its mass Place the metal sample in the water Heat the water to boiling. Leave the metal I the water for at least two minutes after the water boils, to assure that the metal is the same temperature ...
Slide 1
... 1) YOU ARE SITTING AT BREAKFAST WITH A CUP OF HOT COFFEE. YOU GET A TEXT MESSAGE FROM A FRIEND. BY THE TIME YOU ANSWER IT (10 ...
... 1) YOU ARE SITTING AT BREAKFAST WITH A CUP OF HOT COFFEE. YOU GET A TEXT MESSAGE FROM A FRIEND. BY THE TIME YOU ANSWER IT (10 ...
Specific Heat Equation Practice Worksheet
... c. Determine the heat capacity of a substance using mass, specific heat, and temperature. You have probably noticed that a metal spoon heats up quickly when placed in a cup of soap while a plastic spoon heats more slowly. The difference between the final temperatures of the two spoons depends on whe ...
... c. Determine the heat capacity of a substance using mass, specific heat, and temperature. You have probably noticed that a metal spoon heats up quickly when placed in a cup of soap while a plastic spoon heats more slowly. The difference between the final temperatures of the two spoons depends on whe ...
2016 Q7 - Loreto Balbriggan
... A lot of the water will vaporise on falling In a heat pump, a fluid is used to transfer energy from a cold body to a warmer body. Describe the operation of a heat pump and explain how a heat pump can be used to reduce the temperature of a cold region, for example the interior of a refrigerator. Text ...
... A lot of the water will vaporise on falling In a heat pump, a fluid is used to transfer energy from a cold body to a warmer body. Describe the operation of a heat pump and explain how a heat pump can be used to reduce the temperature of a cold region, for example the interior of a refrigerator. Text ...
Verdana 30 pt - Liceo Statale Aprosio
... which we can describe the behavior with relatively simple and accurate laws, based on measures of volume, pressure and temperature, said state quantities; these, we add the internal energy U of an ideal gas, which is all kinetic and depends only on the temperature. ...
... which we can describe the behavior with relatively simple and accurate laws, based on measures of volume, pressure and temperature, said state quantities; these, we add the internal energy U of an ideal gas, which is all kinetic and depends only on the temperature. ...
Ch. 9 Heat and States of Matter!
... Matter can change from one state to another by melting, freezing, boiling, vaporizing, condensing, etc. ...
... Matter can change from one state to another by melting, freezing, boiling, vaporizing, condensing, etc. ...
Lab 1
... container and measure the temperature of the warm water. If you start with water about 5 oC to 10oC above room temperature and end with the water about 5 oC to 10oC below room temperature, the heat that sneaks into the cooler room from the warm water will nearly cancel the heat that sneaks into the ...
... container and measure the temperature of the warm water. If you start with water about 5 oC to 10oC above room temperature and end with the water about 5 oC to 10oC below room temperature, the heat that sneaks into the cooler room from the warm water will nearly cancel the heat that sneaks into the ...
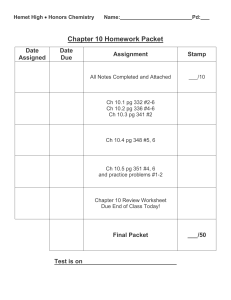
Chapter 10 – States of Matter
... Based on the idea that particles of matter are always in _______________. ...
... Based on the idea that particles of matter are always in _______________. ...
Name: Date: ______ Bill Nye - Phases of Matter http://www
... 1. Everything you can touch is made of __________________________ . 2. Solid, liquid, and gas are the 3 phases of energy / matter. 3. The atoms in a solid move more ____________________________ than in a liquid. 4. Matter can change phases by changing the amount of __________________________ . 5. Ai ...
... 1. Everything you can touch is made of __________________________ . 2. Solid, liquid, and gas are the 3 phases of energy / matter. 3. The atoms in a solid move more ____________________________ than in a liquid. 4. Matter can change phases by changing the amount of __________________________ . 5. Ai ...
Climate influences File
... 1. Elevation or altitude - The higher the elevation, the colder the climate. Less dense air cannot hold heat, while more dense air can hold heat. 2. Distance from an ocean or large body of water - Moderates the temperature, less extreme heat and cold. Water is “thermal mass” and holds heat 3. Latitu ...
... 1. Elevation or altitude - The higher the elevation, the colder the climate. Less dense air cannot hold heat, while more dense air can hold heat. 2. Distance from an ocean or large body of water - Moderates the temperature, less extreme heat and cold. Water is “thermal mass” and holds heat 3. Latitu ...
Physics 1301, Exam 4 Review
... 3. Two identical cans are filled with gas, one with helium and the other with argon. Each can contains the same number of atoms of its respective gas, and the average speed of the gas atoms in each can is the same. Based on this, what can you conclude about the temperatures in the cans? (a) The temp ...
... 3. Two identical cans are filled with gas, one with helium and the other with argon. Each can contains the same number of atoms of its respective gas, and the average speed of the gas atoms in each can is the same. Based on this, what can you conclude about the temperatures in the cans? (a) The temp ...
Cold Weather Heat Pump Operation Air to Air heat Pump Systems
... During the heating mode the unit extracts heat from the outside air and rejects it into the living space. During the cooling mode the unit extracts heat from the inside space and rejects it outside. As you can see from this operation the colder it gets the harder the machine has to work to extract h ...
... During the heating mode the unit extracts heat from the outside air and rejects it into the living space. During the cooling mode the unit extracts heat from the inside space and rejects it outside. As you can see from this operation the colder it gets the harder the machine has to work to extract h ...
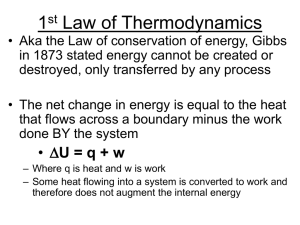
Lecture 5 - Thermodynamics II
... • Besides knowing volume changes, need to figure out how S changes with T For internal energy of a thing: dU = dqtot – PdV; determining this at constant volume dU = CVdT where CV is the heat required to raise T by 1°C ...
... • Besides knowing volume changes, need to figure out how S changes with T For internal energy of a thing: dU = dqtot – PdV; determining this at constant volume dU = CVdT where CV is the heat required to raise T by 1°C ...
Topic 5 Temperature, Pressure, and Moisture
... • The fact that supercells (thunderstorms) occur where warm, moist air meets cold, dry air suggests the source of energy for both t-storm and tornado: • latent heat is in the warm, moist air. Latent heat is heat you can't detect with ...
... • The fact that supercells (thunderstorms) occur where warm, moist air meets cold, dry air suggests the source of energy for both t-storm and tornado: • latent heat is in the warm, moist air. Latent heat is heat you can't detect with ...
Thermal Expansion and Temperature Scales
... 1. Why do your hands feel warmer when you hold a cup of hot chocolate? 2. While grilling hamburgers, the meat is placed directly over the coals instead of to the side of the coals to increase the heat transfer by _______ 3. The transfer of energy that does not require any matter is _____________. 4. ...
... 1. Why do your hands feel warmer when you hold a cup of hot chocolate? 2. While grilling hamburgers, the meat is placed directly over the coals instead of to the side of the coals to increase the heat transfer by _______ 3. The transfer of energy that does not require any matter is _____________. 4. ...