Contagious Ecthyma
... disease may contract it. The disease often occurs as an outbreak in the late summer, fall and winter when animals are on pasture or around lambing/kidding in early spring. It also occurs in feedlots during the winter. It causes weight loss in young animals because the lesions on the mouths of lambs ...
... disease may contract it. The disease often occurs as an outbreak in the late summer, fall and winter when animals are on pasture or around lambing/kidding in early spring. It also occurs in feedlots during the winter. It causes weight loss in young animals because the lesions on the mouths of lambs ...
Lesson Overview - Southgate Schools
... A vaccine stimulates the immune system with an antigen. The immune system produces memory B cells and memory T cells that quicken and strengthen the body’s response to repeated infection. Antibodies produced against a pathogen by other individuals or animals can be used to produce temporary immunity ...
... A vaccine stimulates the immune system with an antigen. The immune system produces memory B cells and memory T cells that quicken and strengthen the body’s response to repeated infection. Antibodies produced against a pathogen by other individuals or animals can be used to produce temporary immunity ...
Continuous Health Monitoring and Early Disease Detection
... this profile, named immunosignature, can serve as a highly sensitive and specific indicator of health status. The B-cells that produce the antibodies are constantly patrolling the body. When they encounter an aberrant protein, cell or foreign pathogen they are activated and amplify their response 10 ...
... this profile, named immunosignature, can serve as a highly sensitive and specific indicator of health status. The B-cells that produce the antibodies are constantly patrolling the body. When they encounter an aberrant protein, cell or foreign pathogen they are activated and amplify their response 10 ...
Answers to Chapter Review Questions
... Syndrome: a collection of signs and symptoms associated with a disease process 2. What is an epidemic? An epidemic is a widespread outbreak of a contagious disease 3. Name five classes of infectious agents The many thousands of pathogens that can threaten human health have been categorized into five ...
... Syndrome: a collection of signs and symptoms associated with a disease process 2. What is an epidemic? An epidemic is a widespread outbreak of a contagious disease 3. Name five classes of infectious agents The many thousands of pathogens that can threaten human health have been categorized into five ...
Feline Leukemia Virus Infection
... extreme weight loss with muscle wasting (known as ―cachexia‖) until condition is stable • Blood transfusions—emergency support; multiple transfusions may be necessary • Management of secondary and opportunistic infections—primary consideration; ―opportunistic infections‖ are infections caused by org ...
... extreme weight loss with muscle wasting (known as ―cachexia‖) until condition is stable • Blood transfusions—emergency support; multiple transfusions may be necessary • Management of secondary and opportunistic infections—primary consideration; ―opportunistic infections‖ are infections caused by org ...
The Silent Epidemic - Xavier High School
... • The Most Common STIs – STIs are caused by pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and protozoans. – spread from person to person through blood and body fluids such as semen, vaginal secretions, and breast milk. – Three of the most common STIs in the United States are trichomoniasis, human papillom ...
... • The Most Common STIs – STIs are caused by pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and protozoans. – spread from person to person through blood and body fluids such as semen, vaginal secretions, and breast milk. – Three of the most common STIs in the United States are trichomoniasis, human papillom ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... CATALOG DESCRIPTION: This course provides an introduction to the microbial world. Students will receive an overview of the infectious diseases the dental team is potentially exposed to while providing treatment in the dental office, with a strong emphasis on hepatitis, tuberculosis, HIV, and the her ...
... CATALOG DESCRIPTION: This course provides an introduction to the microbial world. Students will receive an overview of the infectious diseases the dental team is potentially exposed to while providing treatment in the dental office, with a strong emphasis on hepatitis, tuberculosis, HIV, and the her ...
feline_leukemia_virus_infection
... extreme weight loss with muscle wasting (known as “cachexia”) until condition is stable • Blood transfusions—emergency support; multiple transfusions may be necessary • Management of secondary and opportunistic infections—primary consideration; “opportunistic infections” are infections caused by org ...
... extreme weight loss with muscle wasting (known as “cachexia”) until condition is stable • Blood transfusions—emergency support; multiple transfusions may be necessary • Management of secondary and opportunistic infections—primary consideration; “opportunistic infections” are infections caused by org ...
HERPESVIRIDAE
... Control: Eradicated in UK in 1971 but a Chineselike virus (as defined by phylogenetics) entered UK in 2000. It almost certainly entered via illegally imported pigs from EU. Previous control programme started in 1963 with crystal violet inactivated vaccine in 1960 followed by slaughter policy in 1963 ...
... Control: Eradicated in UK in 1971 but a Chineselike virus (as defined by phylogenetics) entered UK in 2000. It almost certainly entered via illegally imported pigs from EU. Previous control programme started in 1963 with crystal violet inactivated vaccine in 1960 followed by slaughter policy in 1963 ...
Routes of Bacterial Infection
... in the body the TB bacteria are growing. TB bacteria usually grow in the lungs. TB in the lungs may cause – a bad cough that lasts longer than 2 weeks – pain in the chest – coughing up blood or sputum (phlegm from deep inside the lungs) Other symptoms of TB disease are – weakness or fatigue – weight ...
... in the body the TB bacteria are growing. TB bacteria usually grow in the lungs. TB in the lungs may cause – a bad cough that lasts longer than 2 weeks – pain in the chest – coughing up blood or sputum (phlegm from deep inside the lungs) Other symptoms of TB disease are – weakness or fatigue – weight ...
Human Anatomy #1
... Robert Koch found that he could make healthy animals sick by o Disease causing agent (germ) is called a o From his experiments he concluded that four conditions must be met before it can be said that a certain pathogen causes a disease – Koch’s Postulates: The pathogen thought to be the caus ...
... Robert Koch found that he could make healthy animals sick by o Disease causing agent (germ) is called a o From his experiments he concluded that four conditions must be met before it can be said that a certain pathogen causes a disease – Koch’s Postulates: The pathogen thought to be the caus ...
21.4. Bacterial Infections of the Lower Respiratory System
... • In 1985, incidence began to rise due to expanding AIDS epidemic, increasing prevalence of drug-resistant strains • CDC developed Strategic Plan for the Elimination of Tuberculosis in the US (1989); incidence again began to decrease • Estimated ~1/3 of global population infected; nearly 2 million d ...
... • In 1985, incidence began to rise due to expanding AIDS epidemic, increasing prevalence of drug-resistant strains • CDC developed Strategic Plan for the Elimination of Tuberculosis in the US (1989); incidence again began to decrease • Estimated ~1/3 of global population infected; nearly 2 million d ...
Pathogens and their effect on humans. Viral pathogens. Bacteria:
... Viral pathogens work by taking over cells and getting them to carry out viral cell replication rather than carrying out the processes they were designed to do. An example of this is “the flu”. The flu can enter the cell of the linings of the lungs and throat and take over the lung lining cells and f ...
... Viral pathogens work by taking over cells and getting them to carry out viral cell replication rather than carrying out the processes they were designed to do. An example of this is “the flu”. The flu can enter the cell of the linings of the lungs and throat and take over the lung lining cells and f ...
Microbiology – Alcamo Origins of Aseptic Technique
... • He said sepsis was an infectious disease caused by __________ • It was spread due to contaminated _______, _________, _________ • He made nurses, medical students, and midwives wash hands in a _______ ________ and insisted on ______ _______and ________ for every patient ...
... • He said sepsis was an infectious disease caused by __________ • It was spread due to contaminated _______, _________, _________ • He made nurses, medical students, and midwives wash hands in a _______ ________ and insisted on ______ _______and ________ for every patient ...
Generalised rash of measles Measles is a very contagious (easily
... Incubation period of 7 to 18 days – a person will begin to show symptoms between 7 and 18 days after contact with the measles virus. Period of communicability – a person can spread the virus for at least 7 days after onset of symptoms. The person should be isolated during this time. The infection is ...
... Incubation period of 7 to 18 days – a person will begin to show symptoms between 7 and 18 days after contact with the measles virus. Period of communicability – a person can spread the virus for at least 7 days after onset of symptoms. The person should be isolated during this time. The infection is ...
Aujeszky disease
... Aujeszky’s disease is caused by Aujeszky’s disease virus (ADV), also known as Pseudorabies virus. In most cases, this disease is transmitted through aerosols, contaminated feed and water, directly in closed contact because the virus is mostly present in nasal and oral areas. Pigs and rodents appear ...
... Aujeszky’s disease is caused by Aujeszky’s disease virus (ADV), also known as Pseudorabies virus. In most cases, this disease is transmitted through aerosols, contaminated feed and water, directly in closed contact because the virus is mostly present in nasal and oral areas. Pigs and rodents appear ...
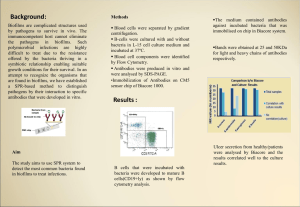
Background: Results
... attempt to recognize the organisms that are found in biofilms, we have established a SPR-based method to distinguish pathogens by their interaction to specific antibodies that were developed in vitro. ...
... attempt to recognize the organisms that are found in biofilms, we have established a SPR-based method to distinguish pathogens by their interaction to specific antibodies that were developed in vitro. ...
Ch.19 Bacteria Viruses
... Bacteria are vital to maintaining the living world. Some are ___________ that capture energy by _________________. Others are ______________ that break down the nutrients in __________________ and the _________________. ...
... Bacteria are vital to maintaining the living world. Some are ___________ that capture energy by _________________. Others are ______________ that break down the nutrients in __________________ and the _________________. ...
Bibliografia di approfondimento Holley JL, Foulks CJ, Moss AH
... Holley JL, Foulks CJ, Moss AH, Willard D. Ultrasound as a tool in the diagnosis and management of exit-site infections in patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Am J Kidney Dis 14 1989; 14: 211–6. Domico j, Warman M, Jaykamur S, Sorkin MI. Is ultrasonography useful in predict ...
... Holley JL, Foulks CJ, Moss AH, Willard D. Ultrasound as a tool in the diagnosis and management of exit-site infections in patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Am J Kidney Dis 14 1989; 14: 211–6. Domico j, Warman M, Jaykamur S, Sorkin MI. Is ultrasonography useful in predict ...
Skills Lab 1
... report) Obtain history from the source patient (HIV, Hepatitis or risk factors) ...
... report) Obtain history from the source patient (HIV, Hepatitis or risk factors) ...
What Causes Illness and How is it Treated
... pioneered the use of carbolic acid as the first antiseptic to clean wounds and surgical instruments. Operations were performed with a fine spray of carbolic acid passed over the patient to kill any microbes in the air. In one Newcastle hospital, use of Lister's antiseptic technique reduced deaths fr ...
... pioneered the use of carbolic acid as the first antiseptic to clean wounds and surgical instruments. Operations were performed with a fine spray of carbolic acid passed over the patient to kill any microbes in the air. In one Newcastle hospital, use of Lister's antiseptic technique reduced deaths fr ...
Appendix A: Definition of Serious Bacterial Infections (SBI) [taken
... culture, respectively. Pneumonia(*) was defined as the presence of a lobar or segmental infiltrate in the chest radiographs. A second pediatrician reviewed the chest radiographs when there was doubt about the interpretation and the final diagnosis was based on the consensus of the two. Mastoiditis w ...
... culture, respectively. Pneumonia(*) was defined as the presence of a lobar or segmental infiltrate in the chest radiographs. A second pediatrician reviewed the chest radiographs when there was doubt about the interpretation and the final diagnosis was based on the consensus of the two. Mastoiditis w ...
FAECAL MULTIPLEX-PCR TEST
... The faecal multiplex RT-PCR profile is capable of rapid, specific and sensitive detection of the bacterial and parasitic pathogens most commonly responsible for causing infectious gastroenteritis that may otherwise go undetected by traditional microbiological techniques. PCR is based on molecular sc ...
... The faecal multiplex RT-PCR profile is capable of rapid, specific and sensitive detection of the bacterial and parasitic pathogens most commonly responsible for causing infectious gastroenteritis that may otherwise go undetected by traditional microbiological techniques. PCR is based on molecular sc ...
Infection

Infection is the invasion of an organism's body tissues by disease-causing agents, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to these organisms and the toxins they produce. Infectious disease, also known as transmissible disease or communicable disease, is illness resulting from an infection.Infections are caused by infectious agents including viruses, viroids, prions, bacteria, nematodes such as parasitic roundworms and pinworms, arthropods such as ticks, mites, fleas, and lice, fungi such as ringworm, and other macroparasites such as tapeworms and other helminths.Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response.Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as Infectious Disease.