DF33642645
... The total circuit apart from SRAM cell array there are sense amplifier and write driver which are work together as read-write circuitry, row decoder and column decoder both for address location, write enable and bit line voltage level switch are work together as multi Vdd [3] (Vdd_High and Vdd_Low). ...
... The total circuit apart from SRAM cell array there are sense amplifier and write driver which are work together as read-write circuitry, row decoder and column decoder both for address location, write enable and bit line voltage level switch are work together as multi Vdd [3] (Vdd_High and Vdd_Low). ...
Evaluates: MAX13487E/MAX13488E MAX13487E Evaluation Kit General Description Features
... load for the RS-485 bus and can communicate up to 500kbps. The MAX13487E AutoDirection and reduceddriver slew-rate features are demonstrated on the EV kit circuit. The EV kit can also be used to evaluate the MAX13488E IC, which can communicate up to 16Mbps. Power for the transceiver circuit is provi ...
... load for the RS-485 bus and can communicate up to 500kbps. The MAX13487E AutoDirection and reduceddriver slew-rate features are demonstrated on the EV kit circuit. The EV kit can also be used to evaluate the MAX13488E IC, which can communicate up to 16Mbps. Power for the transceiver circuit is provi ...
M1601_Intersection_Traffic_Light_PDA_Manual
... This Power Distribution Assembly (PDA) was designed as a “UPS ready” power supply for traffic cabinets. This power supply allows for easy connection of a UPS to the power supply and allows the UPS to be a detachable unit that may be added or removed from the panel at any time, without interruption o ...
... This Power Distribution Assembly (PDA) was designed as a “UPS ready” power supply for traffic cabinets. This power supply allows for easy connection of a UPS to the power supply and allows the UPS to be a detachable unit that may be added or removed from the panel at any time, without interruption o ...
MAX1807/MAX1808 Micropower Adjustable Overvoltage Protection Controllers General Description
... Signal Overvoltage Condition Output. This open-drain N-channel output is latched low when an overvoltage condition is detected. (MAX1807 only) ...
... Signal Overvoltage Condition Output. This open-drain N-channel output is latched low when an overvoltage condition is detected. (MAX1807 only) ...
Good Layout
... – Keep loop area small for high frequency, di/dt, signals and away from high impedance circuits (Magnetic coupling) – Keep high dV/dt signal’s area small and away from high impedance circuits (Electric Coupling) ...
... – Keep loop area small for high frequency, di/dt, signals and away from high impedance circuits (Magnetic coupling) – Keep high dV/dt signal’s area small and away from high impedance circuits (Electric Coupling) ...
PSCAD/EMTDC Simulation of Powe
... Now a day , in power system the term “Power Quality” is commonly used. Users as well as producers of Electricity are more concerned about the Power Quality. Any power problem manifested in voltage, current, or frequency deviation that results in failure or disoperation of customer equipment is Power ...
... Now a day , in power system the term “Power Quality” is commonly used. Users as well as producers of Electricity are more concerned about the Power Quality. Any power problem manifested in voltage, current, or frequency deviation that results in failure or disoperation of customer equipment is Power ...
Sepic inductor ..Degree of coupling
... switching period, the dv on the sepic capacitor should be no more than 10% of V(in). {preferably no more than 5% of V(in)}. In the above sepic of ‘schematic A’, this means a sepic capacitor of 10uF, as shown. With a typical tight coupling coefficient of 0.98 (as found in eg coilcraft’s MSD1583 coupl ...
... switching period, the dv on the sepic capacitor should be no more than 10% of V(in). {preferably no more than 5% of V(in)}. In the above sepic of ‘schematic A’, this means a sepic capacitor of 10uF, as shown. With a typical tight coupling coefficient of 0.98 (as found in eg coilcraft’s MSD1583 coupl ...
Enclosures for being installed in Outdoors
... This enclosure will have based on four different ventilation architectures for helping and adapting the best cooling system according to the application. The maximum dissipated extraction per enclosure using ventilation system is 1,5kW with a medium delta T of 5ºCelsius. In any case is strongly reco ...
... This enclosure will have based on four different ventilation architectures for helping and adapting the best cooling system according to the application. The maximum dissipated extraction per enclosure using ventilation system is 1,5kW with a medium delta T of 5ºCelsius. In any case is strongly reco ...
Fire Extinguisher Training and Education
... Copper wires sheathed in plastic and enclosed in an aluminum cable ...
... Copper wires sheathed in plastic and enclosed in an aluminum cable ...
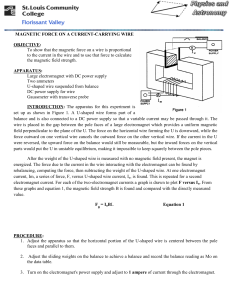
MAGNETIC FORCE ON A CURRENT
... U-shaped wire suspended from balance DC power supply for wire Gaussmeter with transverse probe INTRODUCTION: The apparatus for this experiment is set up as shown in Figure 1. A U-shaped wire forms part of a balance and is also connected to a DC power supply so that a variable current may be passed t ...
... U-shaped wire suspended from balance DC power supply for wire Gaussmeter with transverse probe INTRODUCTION: The apparatus for this experiment is set up as shown in Figure 1. A U-shaped wire forms part of a balance and is also connected to a DC power supply so that a variable current may be passed t ...
MAX31913 - Maxim Part Number Search
... allows a significant reduction in power consumed from the field voltage supply as compared to traditional discrete resistor-divider implementations. Selectable onchip lowpass filters allow flexible debouncing and filtering of sensor outputs based on the application. On-chip serialization allows a dr ...
... allows a significant reduction in power consumed from the field voltage supply as compared to traditional discrete resistor-divider implementations. Selectable onchip lowpass filters allow flexible debouncing and filtering of sensor outputs based on the application. On-chip serialization allows a dr ...
Chapter 2 FAULT IMPEDANCE LOOPS AND OVERHEAD LINE
... a combination of positive, negative and zero-sequence networks. The simplified diagram of Figure 2.2 depicts the theoretical network for a radial transmission network. The source voltage E and network sequence components of voltage (V1, V2, V0), current (I1, I2, I0) and impedances (Z1, Z2, Z0) are s ...
... a combination of positive, negative and zero-sequence networks. The simplified diagram of Figure 2.2 depicts the theoretical network for a radial transmission network. The source voltage E and network sequence components of voltage (V1, V2, V0), current (I1, I2, I0) and impedances (Z1, Z2, Z0) are s ...
Section 5
... A simple transformer consists of two coils of wire, separated from one another (electrically insulated). They are arranged so that a current in one coil (called the primary coil) will induce a current in the other coil (called the secondary coil). The diagram shows a step-down transformer. Notice th ...
... A simple transformer consists of two coils of wire, separated from one another (electrically insulated). They are arranged so that a current in one coil (called the primary coil) will induce a current in the other coil (called the secondary coil). The diagram shows a step-down transformer. Notice th ...
Resistor Terminology
... Bracket Terminal Resistor: A resistor equipped with slotted metal end j brackets that serve as a means of mounting and connecting to the resistor. Capacitance: That property of a system of conductors and dielectrics which permits the storage of electricity when potential differences exist between th ...
... Bracket Terminal Resistor: A resistor equipped with slotted metal end j brackets that serve as a means of mounting and connecting to the resistor. Capacitance: That property of a system of conductors and dielectrics which permits the storage of electricity when potential differences exist between th ...