Step Response: 1st Order Circuits
... the capacitor voltage (Vo) is determined by replacing the capacitor with an open circuit and then calculating the voltage across the terminals. The inductor current (Io) is determined by replacing the inductor with a short circuit and then calculating the current flowing through the short. ...
... the capacitor voltage (Vo) is determined by replacing the capacitor with an open circuit and then calculating the voltage across the terminals. The inductor current (Io) is determined by replacing the inductor with a short circuit and then calculating the current flowing through the short. ...
File
... What is the maximum current that it can take each time? There is a difference between the two leads for the current they can take when unwound because the leads are of different thicknesses. Leads have to be thicker to carry larger currents. ...
... What is the maximum current that it can take each time? There is a difference between the two leads for the current they can take when unwound because the leads are of different thicknesses. Leads have to be thicker to carry larger currents. ...
SURGE PROTECTIVE DEVICES
... extent, continuity of supply, insulation co-ordination aims at reducing the likelihood of equipment dielectric failure. Several components can be used to limit and/or eliminate the surges. This document provides general specification for the surge protective devices (SPDs) to be installed in LV elec ...
... extent, continuity of supply, insulation co-ordination aims at reducing the likelihood of equipment dielectric failure. Several components can be used to limit and/or eliminate the surges. This document provides general specification for the surge protective devices (SPDs) to be installed in LV elec ...
Download PGR-6800 Datasheet
... Relay is ideally suited for applications where operating without load can induce failure. Motor current is monitored and an undercurrent trip occurs when the current drops below a preset level. No additional level detectors are required. ...
... Relay is ideally suited for applications where operating without load can induce failure. Motor current is monitored and an undercurrent trip occurs when the current drops below a preset level. No additional level detectors are required. ...
fault location on distribution systems - Working Group
... ground fault, Zl=ZS is about one ohm per mile. If the line-to-ground voltage, V=5000 V, and the fault current, I=1500 A, the fault is at about 3.3 miles (5000/1500). Remember to use the phaseto-phase voltage and |Ia – Ib| (and not |Ia| – |Ib|) for faults involving more than one phase. We can calcula ...
... ground fault, Zl=ZS is about one ohm per mile. If the line-to-ground voltage, V=5000 V, and the fault current, I=1500 A, the fault is at about 3.3 miles (5000/1500). Remember to use the phaseto-phase voltage and |Ia – Ib| (and not |Ia| – |Ib|) for faults involving more than one phase. We can calcula ...
Step-up Transformers - Pacific Crest Transformers
... current flows in both windings. Protective fuse designers use the rule of thumb that the inrush current should not exceed 12 X normal for 0.01 second. Transformer designers limit the inrush current so as not to exceed the fault current rating of the device. The higher the normal current, the more im ...
... current flows in both windings. Protective fuse designers use the rule of thumb that the inrush current should not exceed 12 X normal for 0.01 second. Transformer designers limit the inrush current so as not to exceed the fault current rating of the device. The higher the normal current, the more im ...
Vocabulary Terms and Definitions
... Patent: A document granting the right to take credit for an invention. (SS) Pole: Either of two opposing forces or parts, such as the poles of a magnet. (SS) Prediction: An educated guess based on data or previous experience. (TG) Repel: To push away, as similar poles of two magnets push away from o ...
... Patent: A document granting the right to take credit for an invention. (SS) Pole: Either of two opposing forces or parts, such as the poles of a magnet. (SS) Prediction: An educated guess based on data or previous experience. (TG) Repel: To push away, as similar poles of two magnets push away from o ...
... Fig.16: Phase plane diagram for q=5 including MOSA and neutral earth resistance Figs. 16 and 17 show the phase plan diagram and time domain simulation in the case of considering including MOSA and neutral earth resistance. By comparing these figures with Figs. 7 and 8, it can be concluded that these ...
1.2mm High Low-Profile Wire Wound Inductor Achieves Highest
... 1A (at the inductance value of 10É H). The new product achieves the highest rated current for its size in the industry. In mobile equipment such as notebook PCs, LCD panels are essential for display of various kinds of information. In order to drive the modules for these LCD panels, DC-DC converters ...
... 1A (at the inductance value of 10É H). The new product achieves the highest rated current for its size in the industry. In mobile equipment such as notebook PCs, LCD panels are essential for display of various kinds of information. In order to drive the modules for these LCD panels, DC-DC converters ...
8-channel source driver with over-current protection
... The channel output current trip point is specified as -370 mA, minimum; therefore, attempted operation at current levels greater than -370 mA may cause a fault indication and channel shutdown. The device is tested at a maximum of -350 mA and that is the recommended maximum output current per driver. ...
... The channel output current trip point is specified as -370 mA, minimum; therefore, attempted operation at current levels greater than -370 mA may cause a fault indication and channel shutdown. The device is tested at a maximum of -350 mA and that is the recommended maximum output current per driver. ...
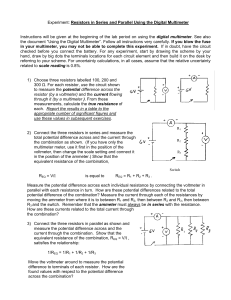
Lab5 NYB -Resistors in Series and Parallel
... Instructions will be given at the beginning of the lab period on using the digital multimeter. See also the document “Using the Digital Multimeter”. Follow all instructions very carefully. If you blow the fuse in your multimeter, you may not be able to complete this experiment. If in doubt, have the ...
... Instructions will be given at the beginning of the lab period on using the digital multimeter. See also the document “Using the Digital Multimeter”. Follow all instructions very carefully. If you blow the fuse in your multimeter, you may not be able to complete this experiment. If in doubt, have the ...
Download FPS Datasheet
... Optional protection (MPS-RTD module) for load-temperature monitoring Limits stress to insulation Detects a damaging brown-out condition Detects unhealthy supply voltage Minimizes Arc-Flash hazards during maintenance Allows local and remote operation; reduces component count Displays the measured and ...
... Optional protection (MPS-RTD module) for load-temperature monitoring Limits stress to insulation Detects a damaging brown-out condition Detects unhealthy supply voltage Minimizes Arc-Flash hazards during maintenance Allows local and remote operation; reduces component count Displays the measured and ...
RPI-5100
... The products listed in this document are designed to be used with ordinary electronic equipment or devices (such as audio visual equipment, office-automation equipment, communications devices, electrical appliances and electronic toys). Should you intend to use these products with equipment or devic ...
... The products listed in this document are designed to be used with ordinary electronic equipment or devices (such as audio visual equipment, office-automation equipment, communications devices, electrical appliances and electronic toys). Should you intend to use these products with equipment or devic ...
FA01 ELEC-CHAR
... impedance measurement accuracy. ==>In a TDR probe, both a signal and a ground contact are normally required duringthe measurement. ...
... impedance measurement accuracy. ==>In a TDR probe, both a signal and a ground contact are normally required duringthe measurement. ...