360° Omnidirectional Vibration Sensor Specification ( Rolling ball
... turning, rotation and change of angle, only one kind of switch needed, short installation time, simplified circuit design, a minimum of electrical parts needed, lower initial cost of investment and lower failure rate. 4. Protected by world patents: Our company have applied for and obtained patents f ...
... turning, rotation and change of angle, only one kind of switch needed, short installation time, simplified circuit design, a minimum of electrical parts needed, lower initial cost of investment and lower failure rate. 4. Protected by world patents: Our company have applied for and obtained patents f ...
Switches & Relays
... A switch is a device that allows you to stop the flow of current entirely. These are usually mechanical devices that separates two bits of metal (contacts). When the metal doesn't touch, current doesn't flow. When the metal touches, is called a closed circuit. When the metal doesn't touch, is called ...
... A switch is a device that allows you to stop the flow of current entirely. These are usually mechanical devices that separates two bits of metal (contacts). When the metal doesn't touch, current doesn't flow. When the metal touches, is called a closed circuit. When the metal doesn't touch, is called ...
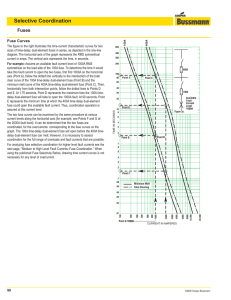
Time-Current Curves (How to Read)
... delay and without instantaneous trip, permits a fault to flow for the length of time of the STD setting, which might be 6, 12, 18, 24 or 30 cycles. This typically is done to achieve fault coordination with downstream circuit breakers. However, there is an adverse consequence associated with using ci ...
... delay and without instantaneous trip, permits a fault to flow for the length of time of the STD setting, which might be 6, 12, 18, 24 or 30 cycles. This typically is done to achieve fault coordination with downstream circuit breakers. However, there is an adverse consequence associated with using ci ...
Aalborg Universitet Elektrisk miljø i svinestalde
... neutral, which is grounded through a ~1.3Ω impedance that is installed between the ground and the point to which the neutral wire is connected. As a result, the return path through the neutral wire has an impedance that is hundreds times lower than the return path through the ground and very little ...
... neutral, which is grounded through a ~1.3Ω impedance that is installed between the ground and the point to which the neutral wire is connected. As a result, the return path through the neutral wire has an impedance that is hundreds times lower than the return path through the ground and very little ...
BD9722FV - uri=media.digikey
... The products listed in this document are designed to be used with ordinary electronic equipment or devices (such as audio visual equipment, office-automation equipment, communications devices, electrical appliances and electronic toys). Should you intend to use these products with equipment or devic ...
... The products listed in this document are designed to be used with ordinary electronic equipment or devices (such as audio visual equipment, office-automation equipment, communications devices, electrical appliances and electronic toys). Should you intend to use these products with equipment or devic ...
HARMONICS - Understanding the Facts - Part 3
... - Isolating harmonic pollution devices on separate circuits with or without the use of harmonic filters. - Loads can be relocated to try to balance the system better. - Phase shifted transformers, such as “zig-zag transformers”, can be used to cancel out specific harmonics by making one voltage circ ...
... - Isolating harmonic pollution devices on separate circuits with or without the use of harmonic filters. - Loads can be relocated to try to balance the system better. - Phase shifted transformers, such as “zig-zag transformers”, can be used to cancel out specific harmonics by making one voltage circ ...
Revisions to ANSI/IEEE C37.100-XXXX and ANSI/IEEE - pes-psrc
... Secondary arc current (single-phase tripping). The current in a phase-to-ground fault after single-phase tripping. It is the sum of two currents derived from the electrostatic and electromagnetic coupling from the remaining energized phases and adjacent lines after the primary arc current contributi ...
... Secondary arc current (single-phase tripping). The current in a phase-to-ground fault after single-phase tripping. It is the sum of two currents derived from the electrostatic and electromagnetic coupling from the remaining energized phases and adjacent lines after the primary arc current contributi ...
Electrical Energy Saving with Improvement of Voltage and Current
... There is no doubt that low voltage and current quality is very common to all electrical installations around the world. This is happening due to: 1) Power electronics (inverter, dc converter, soft starter), for motors control and soft starting, which, however, «pollute» electrical installations with ...
... There is no doubt that low voltage and current quality is very common to all electrical installations around the world. This is happening due to: 1) Power electronics (inverter, dc converter, soft starter), for motors control and soft starting, which, however, «pollute» electrical installations with ...
Elec17 Appendix
... Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) − Resistor or heating element in which the resistance increases with temperature or heat created by current flowing through it. Eventually the resistance will get so high that it will oppose all current flow. Then, the resistor or heating element will cool down ...
... Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) − Resistor or heating element in which the resistance increases with temperature or heat created by current flowing through it. Eventually the resistance will get so high that it will oppose all current flow. Then, the resistor or heating element will cool down ...
SECURITRON POWER SUPPLIES MODELS: BPS-12
... breakers and carry +12 or +24 volts on them (when the emergency release terminals are closed). The “H” terminal carries the full +V output of the supply on a single terminal (when F1 and F2 are closed). Use the “H” terminal for applications where the device being powered requires more than 2 Amps of ...
... breakers and carry +12 or +24 volts on them (when the emergency release terminals are closed). The “H” terminal carries the full +V output of the supply on a single terminal (when F1 and F2 are closed). Use the “H” terminal for applications where the device being powered requires more than 2 Amps of ...
Chapter 8 Section 3
... Direct and Alternating Currents Compare and contrast current in batteries and generators: Compare: Both devices move electrons through the wire Contrast: Batteries have DC. Generators have AC. ...
... Direct and Alternating Currents Compare and contrast current in batteries and generators: Compare: Both devices move electrons through the wire Contrast: Batteries have DC. Generators have AC. ...