a version - SEA
... Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs expressed in all living organisms. They are essential components of the translation machinery and are responsible for the synthesis of proteins from messenger RNAs. Viruses are obligate parasites that evolved to minimize the size of their genome. As a ...
... Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs expressed in all living organisms. They are essential components of the translation machinery and are responsible for the synthesis of proteins from messenger RNAs. Viruses are obligate parasites that evolved to minimize the size of their genome. As a ...
Topic 6A Human Physiology
... Essential idea: Immunity is based on recognition of self and destruction of foreign material. Nature of science: 1. Consider ethical implications of research—Jenner tested his vaccine for smallpox on a child. (4.5) Understandings: Applications and skills: 2. Every organism has unique molecules on th ...
... Essential idea: Immunity is based on recognition of self and destruction of foreign material. Nature of science: 1. Consider ethical implications of research—Jenner tested his vaccine for smallpox on a child. (4.5) Understandings: Applications and skills: 2. Every organism has unique molecules on th ...
Invariant NKT cells
... Recognition of antigen iNKT cells express a restricted TCR repertoire that, in humans, is composed of a V24-J18 TCR chain preferentially coupled with a Vβ11 TCRβ chain. Unlike conventional T cells, which mostly recognise peptide antigens presented by MHC molecules, iNKT cells recognise glycolipid ...
... Recognition of antigen iNKT cells express a restricted TCR repertoire that, in humans, is composed of a V24-J18 TCR chain preferentially coupled with a Vβ11 TCRβ chain. Unlike conventional T cells, which mostly recognise peptide antigens presented by MHC molecules, iNKT cells recognise glycolipid ...
Document
... Recognition of antigen iNKT cells express a restricted TCR repertoire that, in humans, is composed of a V24-J18 TCR chain preferentially coupled with a Vβ11 TCRβ chain. Unlike conventional T cells, which mostly recognise peptide antigens presented by MHC molecules, iNKT cells recognise glycolipid ...
... Recognition of antigen iNKT cells express a restricted TCR repertoire that, in humans, is composed of a V24-J18 TCR chain preferentially coupled with a Vβ11 TCRβ chain. Unlike conventional T cells, which mostly recognise peptide antigens presented by MHC molecules, iNKT cells recognise glycolipid ...
Transport circulation
... causing an increase of blood in area Swelling, Redness, Warmth, Pain in area of infection ...
... causing an increase of blood in area Swelling, Redness, Warmth, Pain in area of infection ...
Chapter 21
... Once a T cell has bound to the combination of its specific antigen and the appropriate MHC protein, co-stimulation must occur. a. Think of co-stimulation as a double check that the bound cell is really one that is infected or alien. b. One way this works is that the T cell looks for a second virus p ...
... Once a T cell has bound to the combination of its specific antigen and the appropriate MHC protein, co-stimulation must occur. a. Think of co-stimulation as a double check that the bound cell is really one that is infected or alien. b. One way this works is that the T cell looks for a second virus p ...
Level 2 ZOOL 21014 Immunity
... – Indirectly by attracting more macrophages & increasing phagocytic activity of macrophages ...
... – Indirectly by attracting more macrophages & increasing phagocytic activity of macrophages ...
Document
... – Small molecules act as haptens and complex with skin proteins to be taken up by APCs and presented to Th1 cells to get sensitization. – During secondary exposure Th1 memory cells become activated to cause DTH. ...
... – Small molecules act as haptens and complex with skin proteins to be taken up by APCs and presented to Th1 cells to get sensitization. – During secondary exposure Th1 memory cells become activated to cause DTH. ...
Case Studies for Studying the Immune System
... the immune system and the relevant antigen(s). Students use as many words from the list as possible. 2. Students could use a “storyboard” format instead of a diagram. The teacher looks over the diagrams and/or storyboards and approves of them. 3. Then, the students write a script that dramatizes imm ...
... the immune system and the relevant antigen(s). Students use as many words from the list as possible. 2. Students could use a “storyboard” format instead of a diagram. The teacher looks over the diagrams and/or storyboards and approves of them. 3. Then, the students write a script that dramatizes imm ...
Defenses Against Disease
... • Consist of 2 polypeptide chains – Specific binding sites protrude from the T cell ...
... • Consist of 2 polypeptide chains – Specific binding sites protrude from the T cell ...
1029immunesystem
... In diploid sexual species, full siblings share 1/2 of their genes by common descent. All the cells within a body (vehicle) that descend from a fertilized egg are a clone and share all genes (except for mutations, ex cancers) & kinship = 1; this makes for a very cooperative coalition - a body. Most c ...
... In diploid sexual species, full siblings share 1/2 of their genes by common descent. All the cells within a body (vehicle) that descend from a fertilized egg are a clone and share all genes (except for mutations, ex cancers) & kinship = 1; this makes for a very cooperative coalition - a body. Most c ...
Document
... separated by areas of normal lining. In the active condition, mucosal inflammation can lead to ulceration of the intestinal wall, although periods of remission are quite common. Symptoms of Crohn's disease vary among afflicted individuals, but include abdominal pain and cramping, diarrhea, need for ...
... separated by areas of normal lining. In the active condition, mucosal inflammation can lead to ulceration of the intestinal wall, although periods of remission are quite common. Symptoms of Crohn's disease vary among afflicted individuals, but include abdominal pain and cramping, diarrhea, need for ...
Commensalism • Benefits both the host and the commensal
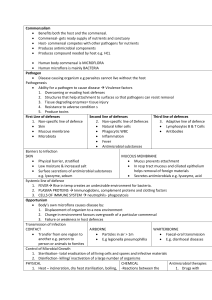
... Produces compound needed by host e.g. HCL Human body commensal is MICROFLORA Human microflora is mainly BACTERIA Pathogen Disease causing organism e.g parasites cannot live without the host Pathogenesis Ability for a pathogen to cause disease Virulence factors 1. Overcoming or evading ho ...
... Produces compound needed by host e.g. HCL Human body commensal is MICROFLORA Human microflora is mainly BACTERIA Pathogen Disease causing organism e.g parasites cannot live without the host Pathogenesis Ability for a pathogen to cause disease Virulence factors 1. Overcoming or evading ho ...
what is onematch stem cell and marrow network?
... Each year, hundreds of Canadians are diagnosed with a life threatening disease such as leukemia, lymphoma, aplastic anemia, sickle cell anemia as well as immune dysfunctions and genetic disorders. Today, nearly 1,000 Canadians are in need of a stem cell transplant. ...
... Each year, hundreds of Canadians are diagnosed with a life threatening disease such as leukemia, lymphoma, aplastic anemia, sickle cell anemia as well as immune dysfunctions and genetic disorders. Today, nearly 1,000 Canadians are in need of a stem cell transplant. ...
B-cells
... Immunity is a state in which the body is protected from infectious diseases and potentially harmful substances. The immune system is a complex network of many different cells and chemicals that act in concert to fight, eliminate, contain and prevent infections and disease. There are two types of imm ...
... Immunity is a state in which the body is protected from infectious diseases and potentially harmful substances. The immune system is a complex network of many different cells and chemicals that act in concert to fight, eliminate, contain and prevent infections and disease. There are two types of imm ...
Gene Therapy for Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases: Should we do it?
... • They are more common than childhood leukemia and lymphoma combined and have four times the incidence of cystic fibrosis. • An estimated 70–90% of PID remain undiagnosed. ...
... • They are more common than childhood leukemia and lymphoma combined and have four times the incidence of cystic fibrosis. • An estimated 70–90% of PID remain undiagnosed. ...
IMMUNE DEFENCE - ASAB-NUST
... proteins and cytokines, especially the interferons. The complement system can be activated by antibodies, and cytokines are involved in activation of antigen presenting cells critical to triggering T lymphocyte response. Cytokines released by macrophages also play a role n acute inflammation ...
... proteins and cytokines, especially the interferons. The complement system can be activated by antibodies, and cytokines are involved in activation of antigen presenting cells critical to triggering T lymphocyte response. Cytokines released by macrophages also play a role n acute inflammation ...
E_Released TAKS Questions
... A fish’s ability to taste food is affected by the clarity of aquarium water Tadpoles’ fear of carnivorous insect larvae increases as the tadpoles age The number of times a dog wags its tail indicates how content the dog is ...
... A fish’s ability to taste food is affected by the clarity of aquarium water Tadpoles’ fear of carnivorous insect larvae increases as the tadpoles age The number of times a dog wags its tail indicates how content the dog is ...
Introduction to Immunity worksheet (LE)
... (1) From the word bank, assign each term to the immunity heading with which it is associated. Some terms may fit more than one category and should be placed in all categories that apply. antibodies in breast milk lymphocytes stomach acid, saliva, tears complement first line of defense ...
... (1) From the word bank, assign each term to the immunity heading with which it is associated. Some terms may fit more than one category and should be placed in all categories that apply. antibodies in breast milk lymphocytes stomach acid, saliva, tears complement first line of defense ...
Viruses and Immunity - Claremont Secondary School
... antibodies. These proteins are on the invader / foreign body & identify it as foreign. Found on surface of pathogen Antibody = Proteins in the blood that react with antigens – flag the pathogen for destruction by a white blood cell ...
... antibodies. These proteins are on the invader / foreign body & identify it as foreign. Found on surface of pathogen Antibody = Proteins in the blood that react with antigens – flag the pathogen for destruction by a white blood cell ...