Time Line of the French Revolution 1789-1815
... most in favour of slavery esp. political leaders (not leaders of the Enlightenment) and property owners ...
... most in favour of slavery esp. political leaders (not leaders of the Enlightenment) and property owners ...
French Revolution WebQuest Worksheet
... What was the name of the Nobles that left France and why did they leave? ...
... What was the name of the Nobles that left France and why did they leave? ...
Chapter 19
... New calendar Equality and Slavery Revolt in Saint Dominigue Decline of the CoPS Execution of Robespierre, July 28, 1794 ...
... New calendar Equality and Slavery Revolt in Saint Dominigue Decline of the CoPS Execution of Robespierre, July 28, 1794 ...
Liberté [Part II] WHAP/Napp Do Now: “Over the next two years, the
... B. By 1791, Austria and Prussia threatened to intervene in support of the monarchy C. The French government responded by declaring war II. The Reign of Terror A. In this period of national crisis and foreign threat, the French Revolution entered its most radical phase (1793-1794) B. A failed effort ...
... B. By 1791, Austria and Prussia threatened to intervene in support of the monarchy C. The French government responded by declaring war II. The Reign of Terror A. In this period of national crisis and foreign threat, the French Revolution entered its most radical phase (1793-1794) B. A failed effort ...
The French Revolution
... Napoleon’s Empire 1. From 17891812, Napoleon took over many countries with military force. 2. Napoleon build up an empire for France, peaking in ...
... Napoleon’s Empire 1. From 17891812, Napoleon took over many countries with military force. 2. Napoleon build up an empire for France, peaking in ...
Chapter 6 notes Sections 1 - 2
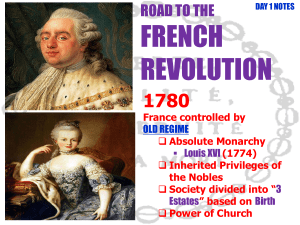
... Estate; the nobility, or Second Estate; and the rest of the population, or Third Estate. • In 1789, France faced social discontent, a severe financial crisis, and serious food shortages. • Louis XVI called on the Estates General to carry out reforms, but members of the Third Estate defied the king a ...
... Estate; the nobility, or Second Estate; and the rest of the population, or Third Estate. • In 1789, France faced social discontent, a severe financial crisis, and serious food shortages. • Louis XVI called on the Estates General to carry out reforms, but members of the Third Estate defied the king a ...
World History Exam Review Lessons 7.1, 7.2, and 7.3 By Rosie
... In 1789, a meeting of the Estates General was called by Louis XVI to try and get rid of French debt. On June 17, 1789, the Estates General system became the National Assembly, ending absolute monarchy in France. This change came about following the unfair voting system in the Estates General, which ...
... In 1789, a meeting of the Estates General was called by Louis XVI to try and get rid of French debt. On June 17, 1789, the Estates General system became the National Assembly, ending absolute monarchy in France. This change came about following the unfair voting system in the Estates General, which ...
wh Unit 4 and Semester Review 15
... European nation which would create the largest colonial empire in the Americas. ...
... European nation which would create the largest colonial empire in the Americas. ...
Unit 4 and Semester Review 16 - USD 475 Geary County Schools
... World History Review: Age of Revolution & Semester ...
... World History Review: Age of Revolution & Semester ...
Chapter 6 Section 4: The Age of Napoleon Begins
... army. December 1793, drove British forces out of French port of Toulon. Later went on to win several victories against Austrians, captured most of Northern Italy, and forced Hapsburg emperor to make peace. Led expedition to Egypt in 1798 which was disastrous. But most in France had no idea of ...
... army. December 1793, drove British forces out of French port of Toulon. Later went on to win several victories against Austrians, captured most of Northern Italy, and forced Hapsburg emperor to make peace. Led expedition to Egypt in 1798 which was disastrous. But most in France had no idea of ...
Liberté [Part II] WHAP/Napp “With the king`s ability to resist
... A. At first, European monarchs welcomed weakening of the French king B. By 1791, Austria and Prussia threatened to intervene C. The French government responded by declaring war II. The Reign of Terror A. In this period of national crisis and foreign threat, the French Revolution entered its most rad ...
... A. At first, European monarchs welcomed weakening of the French king B. By 1791, Austria and Prussia threatened to intervene C. The French government responded by declaring war II. The Reign of Terror A. In this period of national crisis and foreign threat, the French Revolution entered its most rad ...
The French Revolution, Napoleon, and Congress of Vienna (1770
... You Mean the Revolution Was More than a Bunch of Heads Being Chopped Off? Causes and Events of the French Revolution By the late 1700s, France was on the edge of revolution. The French people were inspired by both the American Revolution and the Enlightenment ideas. The country was struggling due to ...
... You Mean the Revolution Was More than a Bunch of Heads Being Chopped Off? Causes and Events of the French Revolution By the late 1700s, France was on the edge of revolution. The French people were inspired by both the American Revolution and the Enlightenment ideas. The country was struggling due to ...
Chapter 19
... • Radical political clubs Jacobins Continuing financial pressure Composition of Legislative Assembly Opposition from Abroad Declaration of Pillnitz (1791) Declaration of war on Austria, April 20, 1792 Early course of the war ...
... • Radical political clubs Jacobins Continuing financial pressure Composition of Legislative Assembly Opposition from Abroad Declaration of Pillnitz (1791) Declaration of war on Austria, April 20, 1792 Early course of the war ...
The French Revolution
... Conservatives- a group of legislatures that felt the revolution had gone far enough. Thought to have constitutional monarchy. (limited authority of the king) Radicals- a group that wanted more drastic changes than those proposed. They wanted to get rid of the King and establish a ...
... Conservatives- a group of legislatures that felt the revolution had gone far enough. Thought to have constitutional monarchy. (limited authority of the king) Radicals- a group that wanted more drastic changes than those proposed. They wanted to get rid of the King and establish a ...
National Assembly
... France as the French Republic • Split into factions (dissenting groups) over the fate of King Louis • Girondins vs. Mountains (both members of the Jacobin club) ...
... France as the French Republic • Split into factions (dissenting groups) over the fate of King Louis • Girondins vs. Mountains (both members of the Jacobin club) ...
The French Revolution - Marion County Public Schools
... 9. At first, it seemed that King Louis XVI would cooperate with some of the demands of the Third Estate. Why do you think he ultimately reacted so violently against them? ...
... 9. At first, it seemed that King Louis XVI would cooperate with some of the demands of the Third Estate. Why do you think he ultimately reacted so violently against them? ...
Declaration of the Rights of Man
... Louis XIV forced people to convert to Catholicism, but the Church was less powerful and had less support ...
... Louis XIV forced people to convert to Catholicism, but the Church was less powerful and had less support ...
The French Revolution
... 9. At first, it seemed that King Louis XVI would cooperate with some of the demands of the Third Estate. Why do you think he ultimately reacted so violently against them? ...
... 9. At first, it seemed that King Louis XVI would cooperate with some of the demands of the Third Estate. Why do you think he ultimately reacted so violently against them? ...
The French Revolution (1789
... Louis XVI Executed: After putting the king on trial and constant debate within the National Assembly for six weeks, the National Assembly sent King Louis XVI and his wife, Marie Antoinette to the guillotine to be executed. ...
... Louis XVI Executed: After putting the king on trial and constant debate within the National Assembly for six weeks, the National Assembly sent King Louis XVI and his wife, Marie Antoinette to the guillotine to be executed. ...
IBL Exercise – Week 9 – Early Modern Revolutions
... 1 – Find the main library website – http://www.shef.ac.uk/library click ‘Using the Library’ > ‘Find Subject Information’ > ‘Subject Guides’ > ‘History’ > ‘Internet Resources’. Use the INTUTE gateway (a great resource for finding reliable websites that are better than Wikipedia which you should avoid ...
... 1 – Find the main library website – http://www.shef.ac.uk/library click ‘Using the Library’ > ‘Find Subject Information’ > ‘Subject Guides’ > ‘History’ > ‘Internet Resources’. Use the INTUTE gateway (a great resource for finding reliable websites that are better than Wikipedia which you should avoid ...
Chapter 19 Notes - Martin`s Mill ISD
... Threats from Abroad – Marie Antoinette’s brothers issued Declaration of Pilnitz Basically said they would protect French monarchy ...
... Threats from Abroad – Marie Antoinette’s brothers issued Declaration of Pilnitz Basically said they would protect French monarchy ...
French Revolutionary Wars

The French Revolutionary Wars were a series of sweeping military conflicts, lasting from 1792 until 1802, resulting from the French Revolution. Primarily fought between the French First Republic and several European monarchies, they are traditionally divided in two periods: the War of the First Coalition (1792–1797) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). Initially confined to Europe, the wars gradually assumed a global dimension as the political ambitions of the Revolution expanded. After a decade of constant warfare and aggressive diplomacy, France had succeeded in seizing and conquering a wide array of territories, from the Italian Peninsula and the Low Countries in Europe to the Louisiana Territory in North America. French success in these conflicts ensured the spread of revolutionary principles over much of Europe and the Middle East. The wars also led to the rebirth of professional armies and the emergence of total war, which defined all future modern conflicts.The Revolutionary Wars began from increasing political pressure on King Louis XVI of France to prove his loyalty to the new direction France was taking. In the spring of 1792, France declared war on Prussia and Austria, which responded with a coordinated invasion of the country that was eventually turned back at the Battle of Valmy in September 1792. The victory rejuvenated the French nation and emboldened the National Convention to abolish the monarchy. A series of victories by the new French armies abruptly ended with defeat at Neerwinden in the spring of 1793. The remainder of the year witnessed additional defeats for the French, and these difficult times allowed the Jacobins to rise to power and impose the Reign of Terror as a method of attempting to unify the nation. In 1794, the situation improved dramatically for the French, as huge victories at Fleurus against the Austrians and at the Black Mountain against the Spanish signaled the start of a new stage in the wars. By 1795, the French had captured the Austrian Netherlands and knocked Spain and Prussia out of the war with the Peace of Basel. A hitherto unknown general called Napoleon Bonaparte began his first campaign in Italy in April 1796. In less than a year, French armies under Napoleon decimated the Habsburg forces and evicted them from the Italian peninsula, winning almost every battle and capturing 150,000 prisoners. With French forces marching towards Vienna, the Austrians sued for peace and agreed to the Treaty of Campo Formio, ending the First Coalition against the Republic.The War of the Second Coalition began with the French invasion of Egypt, headed by Napoleon, in 1798. The Allies took the opportunity presented by the French strategic effort in the Middle East to regain territories lost from the First Coalition. The war began well for the Allies in Europe, where they gradually pushed the French out of Italy and invaded Switzerland—racking up victories at Magnano, Cassano, and Novi along the way. However, their efforts largely unraveled with the French victory at Zurich in September 1799, which caused Russia to drop out of the war. Meanwhile, Napoleon's forces annihilated a series of Egyptian and Ottoman armies at the battles of the Pyramids, Mount Tabor, and Abukir. These victories and the conquest of Egypt further enhanced Napoleon's popularity back in France; he returned in the fall of 1799 to cheering throngs in the streets. However, the Royal Navy had managed to inflict a humiliating defeat on the French fleet at the Battle of the Nile in 1798, further strengthening British control of the Mediterranean.Napoleon's arrival from the Middle East led to the fall of the Directory in the Coup of 18 Brumaire, with Napoleon installing himself as Consul. Napoleon then reorganized the French army and launched a new assault against the Austrians in Italy during the spring of 1800. This latest effort culminated in a decisive French victory at the Battle of Marengo in June 1800, after which the Austrians withdrew from the peninsula once again. Another crushing French triumph at Hohenlinden in Bavaria forced the Austrians to seek peace for a second time, leading to the Treaty of Lunéville in 1801. With Austria and Russia out of the war, the United Kingdom found itself increasingly isolated and agreed to the Treaty of Amiens with Napoleon's government in 1802, concluding the Revolutionary Wars. The lingering tensions proved too difficult to contain, however, and the Napoleonic Wars began a few years later with the formation of the Third Coalition.



![Liberté [Part II] WHAP/Napp Do Now: “Over the next two years, the](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009489790_1-7bb0610f46f66ad57c1803d62d026d31-300x300.png)








![Liberté [Part II] WHAP/Napp “With the king`s ability to resist](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009029062_1-401a2d399c2f46a2015dc3869ced8dba-300x300.png)