Post-traumatic stress disorder - Resurrecting Lives Foundation
... reflect a suppression of the immune response.10,11 The redistribution of T cells and their migration away from the skin appears to be a useful model for the study and evaluation of the immune system response. Both acute and chronic stress can be evaluated using the migration of T cells toward and awa ...
... reflect a suppression of the immune response.10,11 The redistribution of T cells and their migration away from the skin appears to be a useful model for the study and evaluation of the immune system response. Both acute and chronic stress can be evaluated using the migration of T cells toward and awa ...
Document
... Cytotoxic t cells - eliminate tumor and virus infected cells by releasing perforin Memory t cells - future response to antigen ...
... Cytotoxic t cells - eliminate tumor and virus infected cells by releasing perforin Memory t cells - future response to antigen ...
Flow Cytometry protocol for Human Immune System Engrafted
... 2. Prepare antibody dilutions according to manufacturer’s recommendations. To ensure proper performance, It is recommended that antibody reagents be titrated and optimized for use in your own facility. For further information on antibody staining, test validations, and cytometer set-up, consult with ...
... 2. Prepare antibody dilutions according to manufacturer’s recommendations. To ensure proper performance, It is recommended that antibody reagents be titrated and optimized for use in your own facility. For further information on antibody staining, test validations, and cytometer set-up, consult with ...
Nature Reviews Immunology
... generally not sufficient to elicit a mucosal immune response - in fact, in the absence of “signal 1 danger” Ag is often toleragenic (e.g. non-replicating protein antigens). Regulation of mucosal immune responses is distinct from systemic “humoral” immunity ...
... generally not sufficient to elicit a mucosal immune response - in fact, in the absence of “signal 1 danger” Ag is often toleragenic (e.g. non-replicating protein antigens). Regulation of mucosal immune responses is distinct from systemic “humoral” immunity ...
File - AP Biology with Mrs. Davis
... 1. Testosterone and estrogen (signals) released by sex organs 2. Travel to target cells and bind to nuclear receptors (reception) 3. Hormone-receptor complex move to DNA (transduction) 4. Bind to DNA and affect transcription (response) ...
... 1. Testosterone and estrogen (signals) released by sex organs 2. Travel to target cells and bind to nuclear receptors (reception) 3. Hormone-receptor complex move to DNA (transduction) 4. Bind to DNA and affect transcription (response) ...
Immune Response – Overview
... bind that specific antigen and immobilize it, preventing it from causing infection. Antibodies are specific for only one antigen. B cells must interact with Helper T cells, other specialized white blood cells, to initiate antibody production. An important concept is that once activated, memory cells ...
... bind that specific antigen and immobilize it, preventing it from causing infection. Antibodies are specific for only one antigen. B cells must interact with Helper T cells, other specialized white blood cells, to initiate antibody production. An important concept is that once activated, memory cells ...
finals_study_guide_2007_hazbun
... 4. How does inflammation occur? Why is inflammation good but sometimes can be bad? 5. Understand the concept of clonal amplification 6. Know the hematopoietic system – how we can stimulate it in some cases such as neulasta 7. Know the basic anatomy of secondary lymphoid tissue (e.g. lymph node – Tce ...
... 4. How does inflammation occur? Why is inflammation good but sometimes can be bad? 5. Understand the concept of clonal amplification 6. Know the hematopoietic system – how we can stimulate it in some cases such as neulasta 7. Know the basic anatomy of secondary lymphoid tissue (e.g. lymph node – Tce ...
Nervous System 4/28/09
... 2. Responding to info – reaction to stimulus (change/signal) 3. Maintaining homeostasis ...
... 2. Responding to info – reaction to stimulus (change/signal) 3. Maintaining homeostasis ...
Health Notes KD16
... Environmental Factors (things outside your body) may also cause or contribute to disease. Ex: Pollution and asthma, Smoking and ...
... Environmental Factors (things outside your body) may also cause or contribute to disease. Ex: Pollution and asthma, Smoking and ...
Topic 6 Checkpoint Answers File
... Q6.7 Write a definition for each of the four types of immunity: passive natural immunity, active natural immunity, active artificial immunity and passive artificial immunity. Passive natural immunity occurs when antibodies pass from a mother to baby either across the placenta before birth, or via b ...
... Q6.7 Write a definition for each of the four types of immunity: passive natural immunity, active natural immunity, active artificial immunity and passive artificial immunity. Passive natural immunity occurs when antibodies pass from a mother to baby either across the placenta before birth, or via b ...
Slide ()
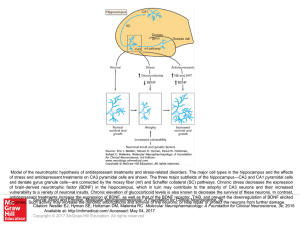
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
Sameer_5
... 2) CD8-positive cytotoxic T-cells- carry the marker CD8 receptor on their surface and are MHC Class I antigen-restricted. They lyse target cells such as virus-infected cells and tumour cells; the main mechanism for elimination of virus-infected cells from the body; also release cytokines. Suppressor ...
... 2) CD8-positive cytotoxic T-cells- carry the marker CD8 receptor on their surface and are MHC Class I antigen-restricted. They lyse target cells such as virus-infected cells and tumour cells; the main mechanism for elimination of virus-infected cells from the body; also release cytokines. Suppressor ...
Ch 3
... 18. What is the function of the neurotransmitter? Why are neurotransmitters important in psychological functioning? 19. What is plasticity and for what mental function does it play a particularly important role? ...
... 18. What is the function of the neurotransmitter? Why are neurotransmitters important in psychological functioning? 19. What is plasticity and for what mental function does it play a particularly important role? ...
The Immune System - Anderson School District One
... sometimes receptors will be made that are specific for epitopes on own cells/molecules as lymphocytes mature in bone marrow or thymus their agn receptors are tested for self reactivity when discovered are destroyed by apoptosis or rendered nonfunctional ...
... sometimes receptors will be made that are specific for epitopes on own cells/molecules as lymphocytes mature in bone marrow or thymus their agn receptors are tested for self reactivity when discovered are destroyed by apoptosis or rendered nonfunctional ...
Slayt 1
... changes and signals render these cells targets for the immune effector cells. Viruses may infect spme mononüclear phagocytes and/or lymphocytes and replicate within these cells. ...
... changes and signals render these cells targets for the immune effector cells. Viruses may infect spme mononüclear phagocytes and/or lymphocytes and replicate within these cells. ...
Haemophilus influenzae
... Humoral immunity is mediated by B lymphocytes and their secreted products, antibodies, and functions in defense against extracellular microbes. Cell-mediated immunity is mediated by T lymphocytes and their products, such as cytokines, and is important for defense against intracellular microbes. Immu ...
... Humoral immunity is mediated by B lymphocytes and their secreted products, antibodies, and functions in defense against extracellular microbes. Cell-mediated immunity is mediated by T lymphocytes and their products, such as cytokines, and is important for defense against intracellular microbes. Immu ...
Immune System - Leavell Science Home
... If subsequent exposure to antigen that activated B cell occurs, memory cells become plasma cells and secrete antibodies ...
... If subsequent exposure to antigen that activated B cell occurs, memory cells become plasma cells and secrete antibodies ...
lecture-4_theraeutic_vaccine_immune-based
... negative regulators) are involved in dampening immune responses • Expression of these receptors can impair HIV-specific T cell responses • Also appear involved in maintaining latently infected CD4 T cells in quiescent state • Examples include PD-1, CTLA-4, LAG3, TIGIT ...
... negative regulators) are involved in dampening immune responses • Expression of these receptors can impair HIV-specific T cell responses • Also appear involved in maintaining latently infected CD4 T cells in quiescent state • Examples include PD-1, CTLA-4, LAG3, TIGIT ...
Lymphatic System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... blood plasma out of the capillary bed. a. Increased interstitial fluid, ______________ ______________ forces lymph pores open – fluid flows ...
... blood plasma out of the capillary bed. a. Increased interstitial fluid, ______________ ______________ forces lymph pores open – fluid flows ...
robarts research retreat abstract submission form
... Cancer immunotherapy is an emerging research area that uses one’s own immune system to combat cancer. An example involves the ex vivo preparation and loading of antigen presenting cells (APC) with tumor-specific antigen (TSA) to create a cancer vaccine. TSA-loaded APC must track to secondary lymphoi ...
... Cancer immunotherapy is an emerging research area that uses one’s own immune system to combat cancer. An example involves the ex vivo preparation and loading of antigen presenting cells (APC) with tumor-specific antigen (TSA) to create a cancer vaccine. TSA-loaded APC must track to secondary lymphoi ...
How to be a good pathogen
... A. What are antibodies (also called immunoglobulins or Igs)? What do they bind to? What kinds of protection do they provide? Where can you find them? How are they made? How long does it take to make a “substantial amount” of antibody in a primary response? B. How do you avoid antibodies? 1. IgA prot ...
... A. What are antibodies (also called immunoglobulins or Igs)? What do they bind to? What kinds of protection do they provide? Where can you find them? How are they made? How long does it take to make a “substantial amount” of antibody in a primary response? B. How do you avoid antibodies? 1. IgA prot ...
Psychoneuroimmunology

Psychoneuroimmunology (PNI), also referred to as psychoendoneuroimmunology (PENI), is the study of the interaction between psychological processes and the nervous and immune systems of the human body. PNI takes an interdisciplinary approach, incorporating psychology, neuroscience, immunology, physiology, genetics, pharmacology, molecular biology, psychiatry, behavioral medicine, infectious diseases, endocrinology, and rheumatology.The main interests of PNI are the interactions between the nervous and immune systems and the relationships between mental processes and health. PNI studies, among other things, the physiological functioning of the neuroimmune system in health and disease; disorders of the neuroimmune system (autoimmune diseases; hypersensitivities; immune deficiency); and the physical, chemical and physiological characteristics of the components of the neuroimmune system in vitro, in situ, and in vivo.