HistorySage
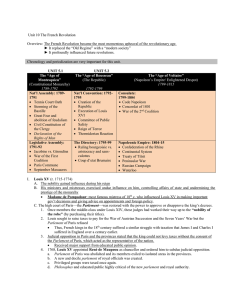
... b. Tennis Court Oath: The Third Estate swore to remain together until it had given France a constitution. c. Third Estate thus assumed sovereign power on behalf of the nation. In response, Louis XVI brought an army of 18,000 troops to Versailles d. Defections from the 1st and 2nd Estates caused Lo ...
... b. Tennis Court Oath: The Third Estate swore to remain together until it had given France a constitution. c. Third Estate thus assumed sovereign power on behalf of the nation. In response, Louis XVI brought an army of 18,000 troops to Versailles d. Defections from the 1st and 2nd Estates caused Lo ...
Napoleonic Code 1804 - Arlington Public Schools
... Louis Bonaparte (1778-1846), who at the beginning of the empire received the title of grand constable, King of Holland, in 1806. He married Hortense de Beauharnais, the daughter of Josephine. Joseph Bonaparte (1768-1844), who was not invited and did not attend because of an argument with Napoleon. T ...
... Louis Bonaparte (1778-1846), who at the beginning of the empire received the title of grand constable, King of Holland, in 1806. He married Hortense de Beauharnais, the daughter of Josephine. Joseph Bonaparte (1768-1844), who was not invited and did not attend because of an argument with Napoleon. T ...
Dew - Eighteenth-Century France - H
... This course covers the history of France from the late seventeenth century to the Revolution, or the period which begins with the accession of Louis XIV (1643) and ends with the outbreak of the French Revolution (1789). This period of French history is often known by the name the Revolution gave i ...
... This course covers the history of France from the late seventeenth century to the Revolution, or the period which begins with the accession of Louis XIV (1643) and ends with the outbreak of the French Revolution (1789). This period of French history is often known by the name the Revolution gave i ...
French Revolution packet - Binghamton City School District
... property, security and resistance to oppression” as well as guaranteeing citizens equal justice and freedom of speech and religion. With a new constitution by 1791, France had become a limited monarchy. The National Assembly gave way to a Legislative Assembly who made laws. Factions in the assembly ...
... property, security and resistance to oppression” as well as guaranteeing citizens equal justice and freedom of speech and religion. With a new constitution by 1791, France had become a limited monarchy. The National Assembly gave way to a Legislative Assembly who made laws. Factions in the assembly ...
McKay Ch19 Study Guide 11e - District 196 e
... had the power to berate us, to fleece us and to oppress us with impunity, will now agree, with good grace, to be our equals.” Jean-Paul Marat ...
... had the power to berate us, to fleece us and to oppress us with impunity, will now agree, with good grace, to be our equals.” Jean-Paul Marat ...
French Revolution
... departments, each administered by an elected assembly. On June 20, 1790, the assembly officially abolished the nobility. On August 16, it reorganized the judiciary and abolished the old, nobility-controlled parlements, or law courts. In the summer of 1791, Louis and his family escaped Paris but were ...
... departments, each administered by an elected assembly. On June 20, 1790, the assembly officially abolished the nobility. On August 16, it reorganized the judiciary and abolished the old, nobility-controlled parlements, or law courts. In the summer of 1791, Louis and his family escaped Paris but were ...
French Revolution
... departments, each administered by an elected assembly. On June 20, 1790, the assembly officially abolished the nobility. On August 16, it reorganized the judiciary and abolished the old, nobility-controlled parlements, or law courts. In the summer of 1791, Louis and his family escaped Paris but were ...
... departments, each administered by an elected assembly. On June 20, 1790, the assembly officially abolished the nobility. On August 16, it reorganized the judiciary and abolished the old, nobility-controlled parlements, or law courts. In the summer of 1791, Louis and his family escaped Paris but were ...
C1: Revolution and Reaction in Europe, 1789-1848
... The new constitution granted the vote to about 60% of Frenchmen, who were considered to be ‘active citizens’, i.e. they were over 25, had lived in one place for 12 months and paid taxes worth three days’ work. ...
... The new constitution granted the vote to about 60% of Frenchmen, who were considered to be ‘active citizens’, i.e. they were over 25, had lived in one place for 12 months and paid taxes worth three days’ work. ...
Middle Class - Fortress Web Design
... “Kings are justly called Gods, for they exercise a power similar to God’s power upon earth... God has the power to create or destroy, to make and unmake, at his Pleasure; to give life or send to death, to judge all and not be judged or accountable to anyone... Kings have the same power. They make an ...
... “Kings are justly called Gods, for they exercise a power similar to God’s power upon earth... God has the power to create or destroy, to make and unmake, at his Pleasure; to give life or send to death, to judge all and not be judged or accountable to anyone... Kings have the same power. They make an ...
Convention and Terror
... The new constitution granted the vote to about 60% of Frenchmen, who were considered to be ‘active citizens’, i.e. they were over 25, had lived in one place for 12 months and paid taxes worth three days’ work. ...
... The new constitution granted the vote to about 60% of Frenchmen, who were considered to be ‘active citizens’, i.e. they were over 25, had lived in one place for 12 months and paid taxes worth three days’ work. ...
English-Notes
... was her navy. The strength of France laid in her commerce. Hence Napoleon decided to attack England by destroying her trade and commerce. He issued two decrees from Berlin in 1806 and Milan in 1807.Accardingly British goods were fully excluded from the whole of Europe. This was called the Continenta ...
... was her navy. The strength of France laid in her commerce. Hence Napoleon decided to attack England by destroying her trade and commerce. He issued two decrees from Berlin in 1806 and Milan in 1807.Accardingly British goods were fully excluded from the whole of Europe. This was called the Continenta ...
ap test review part three
... boundaries, weak monarchs, poor economic conditions, & a weak military that couldn’t fight off foreign invaders. • Huge gap between the nobility & peasants. No middle class. • Cruel treatment of the serfs. • Poland was threatened on the west by Prussia, the North by Sweden, and on the east by Russia ...
... boundaries, weak monarchs, poor economic conditions, & a weak military that couldn’t fight off foreign invaders. • Huge gap between the nobility & peasants. No middle class. • Cruel treatment of the serfs. • Poland was threatened on the west by Prussia, the North by Sweden, and on the east by Russia ...
The French Revolution of 1789 PowerPoint Presentation
... • Voters began electing representatives for a new convention which would write a republican constitution for France – Meanwhile, thousands of nobles were executed under the suspicion that they were conspirators in the invasion ...
... • Voters began electing representatives for a new convention which would write a republican constitution for France – Meanwhile, thousands of nobles were executed under the suspicion that they were conspirators in the invasion ...
The French Revolution and Napoleon Chapter 6 World History A
... revolutionary ideas would spread to other parts of Europe and to their possible demise as a monarch or noble Women marched on Versailles demanding to speak with the King about more rights and food—they also required the King and Queen to return to Paris A document from the emperor of ...
... revolutionary ideas would spread to other parts of Europe and to their possible demise as a monarch or noble Women marched on Versailles demanding to speak with the King about more rights and food—they also required the King and Queen to return to Paris A document from the emperor of ...
Closure Question #2
... To make clear the limits of royal power, Parliament drafted a Bill of Rights in 1689. This document listed many things that a ruler could not do: no suspending of Parliament’s laws, no levying of taxes without a specific grant from Parliament, no interfering with freedom of speech in Parliament, and ...
... To make clear the limits of royal power, Parliament drafted a Bill of Rights in 1689. This document listed many things that a ruler could not do: no suspending of Parliament’s laws, no levying of taxes without a specific grant from Parliament, no interfering with freedom of speech in Parliament, and ...
19 The French Revolution and Napoleon 1789–1815
... severe economic crisis but thought that financial reforms would ease the problem. Then, rioters would be hanged, as they deserved. The nobles were wrong. The crisis went deeper than government finances. Reform would not be enough. By July, the hungry, unemployed, and poorly paid people of Paris had ...
... severe economic crisis but thought that financial reforms would ease the problem. Then, rioters would be hanged, as they deserved. The nobles were wrong. The crisis went deeper than government finances. Reform would not be enough. By July, the hungry, unemployed, and poorly paid people of Paris had ...
1. The French Revolution was partly influenced - AP EURO
... vote together. A 6-week deadlock followed until the Third Estate asserted its power in June, aided by some parish priests who defected from the First Estate. IV. The French Revolution and the “Age of Montesquieu” A. National Assembly, 1789-1791 1. June 17, the Third Estate declared itself the true ...
... vote together. A 6-week deadlock followed until the Third Estate asserted its power in June, aided by some parish priests who defected from the First Estate. IV. The French Revolution and the “Age of Montesquieu” A. National Assembly, 1789-1791 1. June 17, the Third Estate declared itself the true ...
French Revolution
... From Estates-General to National Assembly (cont.) • When the National Assembly was locked out of Versailles and had to meet in an indoor tennis court, they swore that they would continue meeting until they had a constitution. This oath is known as the Tennis Court Oath. • Louis XVI prepared to use ...
... From Estates-General to National Assembly (cont.) • When the National Assembly was locked out of Versailles and had to meet in an indoor tennis court, they swore that they would continue meeting until they had a constitution. This oath is known as the Tennis Court Oath. • Louis XVI prepared to use ...
French revolution
... throughout the capital, King Louis XVI placed troops throughout the capital city, as well as around the palace. Seeing this troop build up, many of the supporters of the National Assembly worried that the King planned to use these troops to put an end to the National Assembly, and to the reforms t ...
... throughout the capital, King Louis XVI placed troops throughout the capital city, as well as around the palace. Seeing this troop build up, many of the supporters of the National Assembly worried that the King planned to use these troops to put an end to the National Assembly, and to the reforms t ...
Chapter 18 Vocabulary Marie Antoinette (1755
... complexities of human nature and society. Although he did not believe in divinely appointed monarchs or and that the people had the right to replace an oppressive government, he did believe in hereditary government, private property, and argued strenuously for gradual, constitutional reform, not rad ...
... complexities of human nature and society. Although he did not believe in divinely appointed monarchs or and that the people had the right to replace an oppressive government, he did believe in hereditary government, private property, and argued strenuously for gradual, constitutional reform, not rad ...
French Revolution - NDHonorsWorldHistory
... - She was seen as being anti-reform and bored with the French court - She retreated to Petit Trianon, a small chateau on the grounds at Versailles - Women refused to leave until the king met their demands – to return to Paris - The king unhappily agreed - The royal family moved into the Tuileries Pa ...
... - She was seen as being anti-reform and bored with the French court - She retreated to Petit Trianon, a small chateau on the grounds at Versailles - Women refused to leave until the king met their demands – to return to Paris - The king unhappily agreed - The royal family moved into the Tuileries Pa ...
Refer to the Powerpoint on the French Revolution The French Revolution Begins
... - She was seen as being anti-reform and bored with the French court - She retreated to Petit Trianon, a small chateau on the grounds at Versailles - Women refused to leave until the king met their demands – to return to Paris - The king unhappily agreed - The royal family moved into the Tuileries Pa ...
... - She was seen as being anti-reform and bored with the French court - She retreated to Petit Trianon, a small chateau on the grounds at Versailles - Women refused to leave until the king met their demands – to return to Paris - The king unhappily agreed - The royal family moved into the Tuileries Pa ...
Germaine de Staël

Anne Louise Germaine de Staël-Holstein (French: [stal]; 22 April 1766 – 14 July 1817), commonly known as Madame de Staël, was a French woman of letters of Swiss origin whose lifetime overlapped with the events of the French Revolution and the Napoleonic era. She was one of Napoleon's principal opponents. Celebrated for her conversational eloquence, she participated actively in the political and intellectual life of her times. Her works, both critical and fictional, made their mark on the history of European Romanticism.