Chapter 14 Topics - Defense Mechanisms - Non
... • Contain granules with hydrolytic enzymes • Attach and destroy large eucaryotic pathogens (worms) • Associated with inflammation and allergies ...
... • Contain granules with hydrolytic enzymes • Attach and destroy large eucaryotic pathogens (worms) • Associated with inflammation and allergies ...
File
... Non-Specific Defenses 1st line of Defense – •SKIN (Layers of dead cells for protection) •Mucous lining, sweat, tears, and hair 2nd Line of Defense – Inflammatory Response •Blood vessels expand near site, causing swelling and local temperature increase •White blood cells move from vessels to infecte ...
... Non-Specific Defenses 1st line of Defense – •SKIN (Layers of dead cells for protection) •Mucous lining, sweat, tears, and hair 2nd Line of Defense – Inflammatory Response •Blood vessels expand near site, causing swelling and local temperature increase •White blood cells move from vessels to infecte ...
PowerPoint bemutató - Department of Immunology
... Diversity Fast development In the active phase of the HIV 10billion viruses develop/day parasites Bacteria may divide in every 20 minutes ...
... Diversity Fast development In the active phase of the HIV 10billion viruses develop/day parasites Bacteria may divide in every 20 minutes ...
such as bacteria and viruses. Platelets
... ii. White (leukocytes) – remove old cells and attack infectious agents (pathogens) such as bacteria and viruses. iii. Platelets – forms clots which stop up blood vessels when they break, stopping bleeding. A scab. 4. Bacterial Infections a. Infection – an organism invades another organism to get its ...
... ii. White (leukocytes) – remove old cells and attack infectious agents (pathogens) such as bacteria and viruses. iii. Platelets – forms clots which stop up blood vessels when they break, stopping bleeding. A scab. 4. Bacterial Infections a. Infection – an organism invades another organism to get its ...
2006 – San Diego, CA
... J. Laskin – Overview: Cytokines and Growth Factors Rich Irons – Regulation of Hematopoiesis by Cytokines Kevin Driscoll – Cytokines and Lung Inflammation and Fibrosis Debbie Laskin – The Involvement of Cytokines and Growth Factors in Hepatic Toxicity D. Heck – Chemical-Induced Injury to Skin ...
... J. Laskin – Overview: Cytokines and Growth Factors Rich Irons – Regulation of Hematopoiesis by Cytokines Kevin Driscoll – Cytokines and Lung Inflammation and Fibrosis Debbie Laskin – The Involvement of Cytokines and Growth Factors in Hepatic Toxicity D. Heck – Chemical-Induced Injury to Skin ...
Specific Immunity POGIL
... Figure 1: Lymphocytes are the type of white blood cells essential for specific immunity. All lymphocytes originate in the bone marrow. T cells mature in the thymus. Cytotoxic T cells directly attack foreign cells. Helper T cells stimulate B cells. B cells convert into plasma cells which release anti ...
... Figure 1: Lymphocytes are the type of white blood cells essential for specific immunity. All lymphocytes originate in the bone marrow. T cells mature in the thymus. Cytotoxic T cells directly attack foreign cells. Helper T cells stimulate B cells. B cells convert into plasma cells which release anti ...
Infectious Diseases
... of infectious waste – toxic dumping – can be deadly • Air – toxic chemicals released from factories ...
... of infectious waste – toxic dumping – can be deadly • Air – toxic chemicals released from factories ...
SELF DEFENSE SYSTEMS
... of serum proteins that function in the control of inflammation “Alternative pathway” (innate): Complement molecules coat microorganism – Acute phase proteins – Spontaneously activated “Classical pathway” (adaptive): Complement molecules activated by antibodies bound to pathogen (cascade) ...
... of serum proteins that function in the control of inflammation “Alternative pathway” (innate): Complement molecules coat microorganism – Acute phase proteins – Spontaneously activated “Classical pathway” (adaptive): Complement molecules activated by antibodies bound to pathogen (cascade) ...
Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer Therapy: New Insights and
... The existence of multiple non-redundant inhibitory pathways that limit T cell responses offers novel strategies for mobilizing the immune system to attack cancer cells. The best characterized of these immune checkpoints is CTLA-4, which inhibits T cell proliferation by interfering with the interacti ...
... The existence of multiple non-redundant inhibitory pathways that limit T cell responses offers novel strategies for mobilizing the immune system to attack cancer cells. The best characterized of these immune checkpoints is CTLA-4, which inhibits T cell proliferation by interfering with the interacti ...
GENERAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THE
... Recognition by highly specific antigen receptors B cell receptor BCR (sIg) T cell receptor TCR Several millions antigen receptors ...
... Recognition by highly specific antigen receptors B cell receptor BCR (sIg) T cell receptor TCR Several millions antigen receptors ...
The Immune System Second Edition
... Listeria monocytogenes - escapes from the phagosome to live in the cytoplasm (makes a virulence factor called lysteriolysin). Toxoplasma gondii – generates its own vesicle inside the cells that won’t fuse with the lysosome to protect it and its peptides from being available for presentation via MHCI ...
... Listeria monocytogenes - escapes from the phagosome to live in the cytoplasm (makes a virulence factor called lysteriolysin). Toxoplasma gondii – generates its own vesicle inside the cells that won’t fuse with the lysosome to protect it and its peptides from being available for presentation via MHCI ...
Chapter One Concept Checks
... Assess your knowledge of the immune system by matching components of the immune system with their function in the body: (a) macrophages, (b) B cells, (c) immunoglobins, (d) killer T cells, (e) suppressor T cells, (f) memory cells. 1. This subgroup targets viral infections within the cells by directl ...
... Assess your knowledge of the immune system by matching components of the immune system with their function in the body: (a) macrophages, (b) B cells, (c) immunoglobins, (d) killer T cells, (e) suppressor T cells, (f) memory cells. 1. This subgroup targets viral infections within the cells by directl ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Defense against Disease
... So what’s a body to do? • First line defenses: Nonspecific anatomical barriers and secretions that prevent entry, such as skin, saliva, tears (lysozyme), mucus, stomach acid, fever • Second line defenses: Inflammation A nonspecific response triggered by histamine secreted by basophils when tissue i ...
... So what’s a body to do? • First line defenses: Nonspecific anatomical barriers and secretions that prevent entry, such as skin, saliva, tears (lysozyme), mucus, stomach acid, fever • Second line defenses: Inflammation A nonspecific response triggered by histamine secreted by basophils when tissue i ...
IMMUNOLOGY AND THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
... the immune system) - general introduction in immunology ( innate and adaptive immunity - Antigen characteristic - Antibody characteristic - B and T cells - Complement - Hypersensitivity types - Oncogenic immunity - Autoimmune disease - Immune deficiency diseases ...
... the immune system) - general introduction in immunology ( innate and adaptive immunity - Antigen characteristic - Antibody characteristic - B and T cells - Complement - Hypersensitivity types - Oncogenic immunity - Autoimmune disease - Immune deficiency diseases ...
Innate immune responses to cationic antimicrobial peptides in the lung
... The airway inflammation observed in CF patients is believed to be a result of prior or concurrent infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa or other pathogens. However, it has been shown that infants, prior to chronic colonization of P. aeruginosa have elevated levels of neutrophils, elastase, α1-antipr ...
... The airway inflammation observed in CF patients is believed to be a result of prior or concurrent infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa or other pathogens. However, it has been shown that infants, prior to chronic colonization of P. aeruginosa have elevated levels of neutrophils, elastase, α1-antipr ...
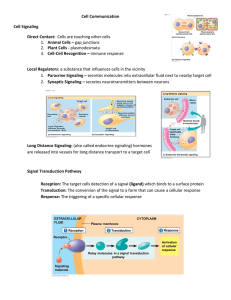
Cell Communication Cell Signaling Direct Contact: Cells are
... 4. Intracellular Responses: these involve proteins that are dissolved in the cytoplasm of the cell. The signal molecules must be able to dissolve through the plasma membrane Ex. Steroid hormones Transduction: Relay signals from receptors to cellular responses. This is usually done by protein kinase ...
... 4. Intracellular Responses: these involve proteins that are dissolved in the cytoplasm of the cell. The signal molecules must be able to dissolve through the plasma membrane Ex. Steroid hormones Transduction: Relay signals from receptors to cellular responses. This is usually done by protein kinase ...
Innate immune system

The innate immune system, also known as the nonspecific immune system, is an important subsystem of the overall immune system that comprises the cells and mechanisms that defend the host from infection by other organisms. The cells of the innate system recognize and respond to pathogens in a generic way, but, unlike the adaptive immune system (which is found only in vertebrates), it does not confer long-lasting or protective immunity to the host. Innate immune systems provide immediate defense against infection, and are found in all classes of plant and animal life. They include both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.The innate immune system is an evolutionarily older defense strategy, and is the dominant immune system found in plants, fungi, insects, and primitive multicellular organisms.The major functions of the vertebrate innate immune system include: Recruiting immune cells to sites of infection, through the production of chemical factors, including specialized chemical mediators, called cytokines Activation of the complement cascade to identify bacteria, activate cells, and promote clearance of antibody complexes or dead cells The identification and removal of foreign substances present in organs, tissues, the blood and lymph, by specialised white blood cells Activation of the adaptive immune system through a process known as antigen presentation Acting as a physical and chemical barrier to infectious agents.↑ ↑ ↑