Exponential Maps for Computer Vision
... In 3D computer vision, the problem of tracking an object in video is typically addressed by maintaining a transformation for each of the object’s degrees of freedom. The result is an estimation of the 3D pose with reference to several coordinate frames. Simplification of the problem is possible when ...
... In 3D computer vision, the problem of tracking an object in video is typically addressed by maintaining a transformation for each of the object’s degrees of freedom. The result is an estimation of the 3D pose with reference to several coordinate frames. Simplification of the problem is possible when ...
Chapter 1
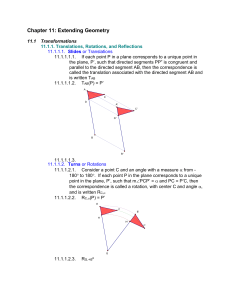
... 11.1.2.1.1. Reflectional symmetry 11.1.2.1.2. line of symmetry 11.1.2.1.3. n rotational symmetry 11.1.2.1.4. center of rotational symmetry 11.1.3. Transformations that Change Size 11.1.3.1. size transformations 11.1.3.1.1. If point O corresponds to itself, and each other point P in the plane corres ...
... 11.1.2.1.1. Reflectional symmetry 11.1.2.1.2. line of symmetry 11.1.2.1.3. n rotational symmetry 11.1.2.1.4. center of rotational symmetry 11.1.3. Transformations that Change Size 11.1.3.1. size transformations 11.1.3.1.1. If point O corresponds to itself, and each other point P in the plane corres ...
_____ Target 3 (Reflections): (1 MORE day) CCSS.MATH
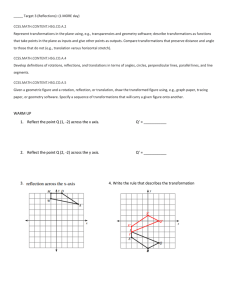
... that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch). CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.A.4 Develop definitions of rotations, reflections, and translations in terms ...
... that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch). CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.CO.A.4 Develop definitions of rotations, reflections, and translations in terms ...
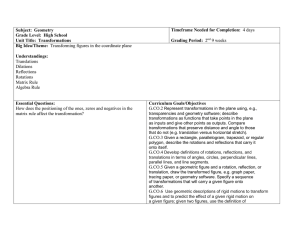
Subject: Geometry - Currituck County Schools
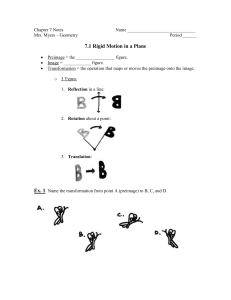
... to show that two triangles are congruent if and only if corresponding pairs of sides and corresponding pairs of angles are congruent G.CO.8 Explain how the criteria for triangle congruence (ASA, SAS, and SSS) follow from the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions. G.SRT.1.a Verify experi ...
... to show that two triangles are congruent if and only if corresponding pairs of sides and corresponding pairs of angles are congruent G.CO.8 Explain how the criteria for triangle congruence (ASA, SAS, and SSS) follow from the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions. G.SRT.1.a Verify experi ...
Section 25
... • H = 0 (when E2 > H2), i.e. pure electric. • In other words, we can always make the smaller field vanish by suitable transform. • Except when E2 = H2, e.g. electromagnetic wave ...
... • H = 0 (when E2 > H2), i.e. pure electric. • In other words, we can always make the smaller field vanish by suitable transform. • Except when E2 = H2, e.g. electromagnetic wave ...
Lecture 8: Examples of linear transformations
... onto the entire space. Projections also have the property that P 2 = P . If we do it twice, it is the same transformation. If we combine a projection with a dilation, we get a rotation dilation. ...
... onto the entire space. Projections also have the property that P 2 = P . If we do it twice, it is the same transformation. If we combine a projection with a dilation, we get a rotation dilation. ...