The fluid mosaic model describes the plasma membrane structure
... The main fabric of the membrane is composed of amphiphilic or dual-loving, phospholipid molecules. The hydrophilic or water-loving areas of these molecules are in contact with the aqueous fluid both inside and outside the cell. Hydrophobic, or water-hating molecules, tend to be non-polar. A phosphol ...
... The main fabric of the membrane is composed of amphiphilic or dual-loving, phospholipid molecules. The hydrophilic or water-loving areas of these molecules are in contact with the aqueous fluid both inside and outside the cell. Hydrophobic, or water-hating molecules, tend to be non-polar. A phosphol ...
The plasma membrane
... PLASMA MEMBRANE The plasma membrane has the property of selective permeability. (also called semipermeable) This is how homeostasis is maintained. ...
... PLASMA MEMBRANE The plasma membrane has the property of selective permeability. (also called semipermeable) This is how homeostasis is maintained. ...
What is a cell Cell is the basic living, structural and
... Involved in the movement of the cell and of organelles within the cell, the movement of cilia & possibly the organization of proteins in the plasma membrane. Transport of substances across cell membranes Passive processes Mechanisms that move substances across a membrane without using cellular energ ...
... Involved in the movement of the cell and of organelles within the cell, the movement of cilia & possibly the organization of proteins in the plasma membrane. Transport of substances across cell membranes Passive processes Mechanisms that move substances across a membrane without using cellular energ ...
Key concepts_principles of signaling
... transducers, converting the extracellular signal into intracellular ones that alter the behavior of the target cell. Activated receptors relay the signal into the cell interior by activating intracellular signaling proteins. Some of these signaling proteins transduce, amplify, or spread the signal a ...
... transducers, converting the extracellular signal into intracellular ones that alter the behavior of the target cell. Activated receptors relay the signal into the cell interior by activating intracellular signaling proteins. Some of these signaling proteins transduce, amplify, or spread the signal a ...
Membrane Structure and Function POGIL
... • When you get to a stop sign, make sure your team has all of the answers for each question and that they are consistent (NOT IDENTICAL). The spokesperson should raise their hand for me to check answers. I WILL CHOOSE the paper to check. • I will give you some guidance with how much time you should ...
... • When you get to a stop sign, make sure your team has all of the answers for each question and that they are consistent (NOT IDENTICAL). The spokesperson should raise their hand for me to check answers. I WILL CHOOSE the paper to check. • I will give you some guidance with how much time you should ...
Biopharmaceutics
... Here fluid mean structure is not rigid (not one unit) so it’s a flexible membrane .In this theory we could explain the way that drug transport 3. Lipid membrane structure in the relation to drug research : They said when they try to transfer a drug to cross the membrane they notice they view the mem ...
... Here fluid mean structure is not rigid (not one unit) so it’s a flexible membrane .In this theory we could explain the way that drug transport 3. Lipid membrane structure in the relation to drug research : They said when they try to transfer a drug to cross the membrane they notice they view the mem ...
Biopharma Dr Rana L2
... Here fluid mean structure is not rigid (not one unit) so it’s a flexible membrane .In this theory we could explain the way that drug transport 3. Lipid membrane structure in the relation to drug research : They said when they try to transfer a drug to cross the membrane they notice they view the mem ...
... Here fluid mean structure is not rigid (not one unit) so it’s a flexible membrane .In this theory we could explain the way that drug transport 3. Lipid membrane structure in the relation to drug research : They said when they try to transfer a drug to cross the membrane they notice they view the mem ...
Lecture 9 MEMBRANES
... The cylindrical shape of phospholipids causes them to form extended, disk-like micelles that are best described as lipid bilayers. Lysolipids and detergents containing only a single acyl chain form micelles. Modified from Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th edition ...
... The cylindrical shape of phospholipids causes them to form extended, disk-like micelles that are best described as lipid bilayers. Lysolipids and detergents containing only a single acyl chain form micelles. Modified from Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th edition ...
membrane notes - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Power point notes- Cell membrane Slide2: Artificial membranes. Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules- they have a hydrophobic and hydrophilic section. When they come in contact with water (since water is polar) the hydrophilic section sticks into water and the hydrophobic section is held away. Ple ...
... Power point notes- Cell membrane Slide2: Artificial membranes. Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules- they have a hydrophobic and hydrophilic section. When they come in contact with water (since water is polar) the hydrophilic section sticks into water and the hydrophobic section is held away. Ple ...
Chapter 5
... Membrane Composition and Structure • Cell membranes are bilayered, dynamic structures that: Perform vital physiological roles Form boundaries between cells and their environments Regulate movement of molecules into and out of cells ...
... Membrane Composition and Structure • Cell membranes are bilayered, dynamic structures that: Perform vital physiological roles Form boundaries between cells and their environments Regulate movement of molecules into and out of cells ...
File
... other side according to concentration this process is known as diffusion b- Carrier proteins: Carrier proteins change their shape to transport certain molecules from one side of the membrane to the other side against concentration this process is known as active transport. ...
... other side according to concentration this process is known as diffusion b- Carrier proteins: Carrier proteins change their shape to transport certain molecules from one side of the membrane to the other side against concentration this process is known as active transport. ...
Cellular lipidomics
... occurring inside the Golgi, the compositional differences between the apical and basolateral plasma membrane had to be caused by specificity in transport. Indeed, newly synthesized fluorescent GlcCer and SM were sorted from each other before reaching the cell surface. Their apical/ basolateral ratios ...
... occurring inside the Golgi, the compositional differences between the apical and basolateral plasma membrane had to be caused by specificity in transport. Indeed, newly synthesized fluorescent GlcCer and SM were sorted from each other before reaching the cell surface. Their apical/ basolateral ratios ...
Structure and Function of Cells
... Strong, stiff, nonliving layer outside the cell membrane; can be made of cellulose Outermost living layer of the cell; elastic and flexible; contains pores Region between the nucleus and the cell membrane; consists of a jellylike substance that contains many organelles Large, oval structure in the c ...
... Strong, stiff, nonliving layer outside the cell membrane; can be made of cellulose Outermost living layer of the cell; elastic and flexible; contains pores Region between the nucleus and the cell membrane; consists of a jellylike substance that contains many organelles Large, oval structure in the c ...
Nanodevices
... (often small molecule) that can enter into a crevice in the molecule or (ii) to change configuration in the presence of light, and electricity or mechanical pull. Most important take home message: Protein nanodevices respond to stimuli with a small and reversible stepwise changes in conformation ove ...
... (often small molecule) that can enter into a crevice in the molecule or (ii) to change configuration in the presence of light, and electricity or mechanical pull. Most important take home message: Protein nanodevices respond to stimuli with a small and reversible stepwise changes in conformation ove ...
Look at chapter 3 chemistry worksheet
... • In phospholipids, two of the OH groups are linked to fatty acids and one of the OH groups is linked to a phosphorylated alcohol • Fatty acids have a carboxyl group with long ...
... • In phospholipids, two of the OH groups are linked to fatty acids and one of the OH groups is linked to a phosphorylated alcohol • Fatty acids have a carboxyl group with long ...
Q4 Describe the factors that affect the flux of
... Plasma K levels à as per Fick’s Law of Diffusion, the diffusion of a substance across a semipermeable membrane is directly proportional to the concentration gradient across the membrane. Temperature à ...
... Plasma K levels à as per Fick’s Law of Diffusion, the diffusion of a substance across a semipermeable membrane is directly proportional to the concentration gradient across the membrane. Temperature à ...
Unit 4 Study Guide: Cell Membrane and Homeostasis Answer Key
... - hydrophobic tails (inside membrane) repel water (water-hating) - transport proteins move particles in or out of the cell ...
... - hydrophobic tails (inside membrane) repel water (water-hating) - transport proteins move particles in or out of the cell ...
Human Scent
... Sebaceous Glands – located at the base of hair follicles on your scalp, face and upper torso. They open directly to the skin and emit fatty oils, called sebum, that spread over the skin. Bacterial Buddies –such as mites, fungus, yeasts and viruses can never be completely removed by washing. We are c ...
... Sebaceous Glands – located at the base of hair follicles on your scalp, face and upper torso. They open directly to the skin and emit fatty oils, called sebum, that spread over the skin. Bacterial Buddies –such as mites, fungus, yeasts and viruses can never be completely removed by washing. We are c ...
BLM 3 7 FluidMosaicModelAnswers File
... 3. The cell membrane is said to be selectively permeable. What does this mean? The cell membrane will allow only certain molecules to pass through it. 4. Describe the fluid-mosaic model. The cell membrane (plasma membrane) consists of a phospholipid bilayer that has a fluid consistency. Various type ...
... 3. The cell membrane is said to be selectively permeable. What does this mean? The cell membrane will allow only certain molecules to pass through it. 4. Describe the fluid-mosaic model. The cell membrane (plasma membrane) consists of a phospholipid bilayer that has a fluid consistency. Various type ...
The Cell Theory and Membrane Transport
... transferring a Phosphate to the pump Step 3: The pump changes shape— moving Na+ outside! Step 4: Na+ break off & 2 K+ bind to site Step 5: Phosphate (P) is hydrolyzed, changing the ATP to ADP ...
... transferring a Phosphate to the pump Step 3: The pump changes shape— moving Na+ outside! Step 4: Na+ break off & 2 K+ bind to site Step 5: Phosphate (P) is hydrolyzed, changing the ATP to ADP ...
5.1-5.9 Study Guide
... take energy, therefore it is spontaneous or “passive” ● 5.4 - Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a membrane ○ Osmosis - diffusion of water across a membrane ○ If the membrane is permeable to water but not to a solute in water, the water will have a net movement until both sides have an equal c ...
... take energy, therefore it is spontaneous or “passive” ● 5.4 - Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a membrane ○ Osmosis - diffusion of water across a membrane ○ If the membrane is permeable to water but not to a solute in water, the water will have a net movement until both sides have an equal c ...
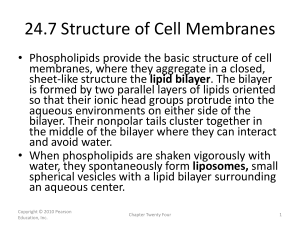
24.7 Structure of Cell Membranes
... membranes, where they aggregate in a closed, sheet-like structure the lipid bilayer. The bilayer is formed by two parallel layers of lipids oriented so that their ionic head groups protrude into the aqueous environments on either side of the bilayer. Their nonpolar tails cluster together in the midd ...
... membranes, where they aggregate in a closed, sheet-like structure the lipid bilayer. The bilayer is formed by two parallel layers of lipids oriented so that their ionic head groups protrude into the aqueous environments on either side of the bilayer. Their nonpolar tails cluster together in the midd ...
Biological membranes are sheet-like structures
... of two Fatty Acid 'tails' and a Phosphate 'head'. The Phosphate 'heads' are Hydrophilic whereas the Fatty Acid 'tails' are Hydrophobic, meaning that Phospholipids are Amphipathic. When placed in water, the 'heads' orientate themselves towards water molecules and the 'tails' away, meaning that phosph ...
... of two Fatty Acid 'tails' and a Phosphate 'head'. The Phosphate 'heads' are Hydrophilic whereas the Fatty Acid 'tails' are Hydrophobic, meaning that Phospholipids are Amphipathic. When placed in water, the 'heads' orientate themselves towards water molecules and the 'tails' away, meaning that phosph ...
Lipid raft
The plasma membranes of cells contain combinations of glycosphingolipids and protein receptors organized in glycolipoprotein microdomains termed lipid rafts. These specialized membrane microdomains compartmentalize cellular processes by serving as organizing centers for the assembly of signaling molecules, influencing membrane fluidity and membrane protein trafficking, and regulating neurotransmission and receptor trafficking. Lipid rafts are more ordered and tightly packed than the surrounding bilayer, but float freely in the membrane bilayer. Although more common in plasma membrane, lipid rafts have also been reported in other parts of the cell, such as Golgi and lysosomes.