
chem_1 ILO 2013-9-19 - Faculty Members Websites
... 3. Know the basic concepts and kinetics of enzymes, protein structure and function, regulatory strategies in enzymes and hemoglobin, lipids’ classes and cell membranes channels and pumps, signal transduction pathways, transducing and storing energy. 4. Understand the main concepts of bioenergetics ...
... 3. Know the basic concepts and kinetics of enzymes, protein structure and function, regulatory strategies in enzymes and hemoglobin, lipids’ classes and cell membranes channels and pumps, signal transduction pathways, transducing and storing energy. 4. Understand the main concepts of bioenergetics ...
Publications de l`équipe
... Polarized transport in neurons is fundamental for the formation of neuronal circuitry. A motor domain-containing truncated KIF5 (a kinesin-1) recognizes axonal microtubules, which are enriched in EB1 binding sites, and selectively accumulates at the tips of axons. However, it remains unknown what cu ...
... Polarized transport in neurons is fundamental for the formation of neuronal circuitry. A motor domain-containing truncated KIF5 (a kinesin-1) recognizes axonal microtubules, which are enriched in EB1 binding sites, and selectively accumulates at the tips of axons. However, it remains unknown what cu ...
2_4 Slides
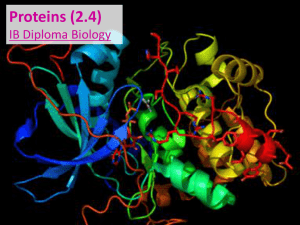
... But before they are functional, they must fold into specific structures based on the order / structure of their amino acid sequence. Remember, different amino acids have different chemical properties (i.e. polar / hydrophilic, non-polar / hydrophobic, +/charged, sulfur-containing, carbon rings, etc. ...
... But before they are functional, they must fold into specific structures based on the order / structure of their amino acid sequence. Remember, different amino acids have different chemical properties (i.e. polar / hydrophilic, non-polar / hydrophobic, +/charged, sulfur-containing, carbon rings, etc. ...
His-tag pull-down assay Possible interaction between PprI protein
... Possible interaction between PprI protein and N-terminal part of DdrO(N-DdrO, a.a. 1-108)were tested using His-tag pull-down assay. 20 µg of purified N-DdrO protein with N-terminal His-tag was incubated with Ni-NTA agarose beads in 1 ml of pull-down buffer (167mM NaCl, 20 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 5% glyc ...
... Possible interaction between PprI protein and N-terminal part of DdrO(N-DdrO, a.a. 1-108)were tested using His-tag pull-down assay. 20 µg of purified N-DdrO protein with N-terminal His-tag was incubated with Ni-NTA agarose beads in 1 ml of pull-down buffer (167mM NaCl, 20 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 5% glyc ...
chem_1 ILO 2013-9-19 - Faculty Members Websites
... 3. Know the basic concepts and kinetics of enzymes, protein structure and function, regulatory strategies in enzymes and hemoglobin, lipids’ classes and cell membranes channels and pumps, signal transduction pathways, transducing and storing energy. 4. Understand the main concepts of bioenergetics ...
... 3. Know the basic concepts and kinetics of enzymes, protein structure and function, regulatory strategies in enzymes and hemoglobin, lipids’ classes and cell membranes channels and pumps, signal transduction pathways, transducing and storing energy. 4. Understand the main concepts of bioenergetics ...
protein
... compact structure. Denaturation often affects the original properties of the protein. Heat is the most common means of denaturing proteins. The extent and speed of protein denaturation depends on the structure of the protein and the temperature applied. Proteins F&N-Protein-Year 9 ...
... compact structure. Denaturation often affects the original properties of the protein. Heat is the most common means of denaturing proteins. The extent and speed of protein denaturation depends on the structure of the protein and the temperature applied. Proteins F&N-Protein-Year 9 ...
Applications of Game Theory in the Computational Biology Domain
... how they affect cells • Usually dependent on how much of, or for how long, a drug molecule is in contact (binds) with a cell structure • Computational approaches can be used to conduct drug simulations in silico – Paper: Perez-Breva et. al, Game theoretic algorithms for protein-DNA binding, NIPS 200 ...
... how they affect cells • Usually dependent on how much of, or for how long, a drug molecule is in contact (binds) with a cell structure • Computational approaches can be used to conduct drug simulations in silico – Paper: Perez-Breva et. al, Game theoretic algorithms for protein-DNA binding, NIPS 200 ...
AP Biology - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... activity. The part of the receptor protein extending into the cytoplasm ...
... activity. The part of the receptor protein extending into the cytoplasm ...
chapter3_Sections 4
... linear sequence of amino acids (a polypeptide chain). Each type of protein has a unique primary structure. ...
... linear sequence of amino acids (a polypeptide chain). Each type of protein has a unique primary structure. ...
Protein Folding
... • Collapsed, with native-like 2º structure (far UV CD) • Weak or transient side-chain interactions (near UV CD) • Binds hydrophobic dyes • Many proteins form molten globules at low pH • Model for early stages of protein folding (hydrophobic collapse) ...
... • Collapsed, with native-like 2º structure (far UV CD) • Weak or transient side-chain interactions (near UV CD) • Binds hydrophobic dyes • Many proteins form molten globules at low pH • Model for early stages of protein folding (hydrophobic collapse) ...
The role of haemoglobin
... – Issues arise because glycosylated haemoglobin does not give up oxygen to respiring tissues very easily – Organs can be damaged by this, including blood vessels in the eyes, which can lead to blindness (diabetic retinopathy) ...
... – Issues arise because glycosylated haemoglobin does not give up oxygen to respiring tissues very easily – Organs can be damaged by this, including blood vessels in the eyes, which can lead to blindness (diabetic retinopathy) ...
Keystone Biology Cram Sheet: MODULE 1 1. Because carbon has 4
... Keystone Biology Cram Sheet: MODULE 1 1. Because carbon has 4 electrons it can form 4 covalent bonds with other atoms. This makes it the only atom that can be used to build the variety of molecules needed for complex life. 2. Carbon can be used to build large molecules (polymers, macromolecules) lik ...
... Keystone Biology Cram Sheet: MODULE 1 1. Because carbon has 4 electrons it can form 4 covalent bonds with other atoms. This makes it the only atom that can be used to build the variety of molecules needed for complex life. 2. Carbon can be used to build large molecules (polymers, macromolecules) lik ...
[Fe 4 S 4 Cys 4 ] 1
... • Ferredoxins: [Fe4S4Cys4]3- → [Fe4S4Cys4]2• HiPIPs: [Fe4S4Cys4]2- → [Fe4S4Cys4]1• HiPIPs are more hydrophobic: Favours -1 • NH...S bonds: 8-9 in Fd, only 5 in HiPIPs ...
... • Ferredoxins: [Fe4S4Cys4]3- → [Fe4S4Cys4]2• HiPIPs: [Fe4S4Cys4]2- → [Fe4S4Cys4]1• HiPIPs are more hydrophobic: Favours -1 • NH...S bonds: 8-9 in Fd, only 5 in HiPIPs ...
The Function of Chloroplast Ribosomes Effects of a
... BRIAN W. J. MAHY (Department of Pathology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge CB2 1 QP, U.K.) a.-Amanitin, a bicyclic octapeptide from the toadstool Amanita phalloides (Fiume & Wieland, 1970), inhibits DNA transcription by binding specifically to RNA polymerase form II of eukaryotic organisms withou ...
... BRIAN W. J. MAHY (Department of Pathology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge CB2 1 QP, U.K.) a.-Amanitin, a bicyclic octapeptide from the toadstool Amanita phalloides (Fiume & Wieland, 1970), inhibits DNA transcription by binding specifically to RNA polymerase form II of eukaryotic organisms withou ...
Chapter 3
... tertiary structure units within a protein. The respective globular and fibrous structural domains of the hemagglutinin monomer (which happen to be individual polypeptide chains) are illustrated above in Fig. 3.10a. Domains (such as the EGF domain) also may be encoded within a single polypeptide chai ...
... tertiary structure units within a protein. The respective globular and fibrous structural domains of the hemagglutinin monomer (which happen to be individual polypeptide chains) are illustrated above in Fig. 3.10a. Domains (such as the EGF domain) also may be encoded within a single polypeptide chai ...
Replicate OPM - MultiscaleLab
... to create an empty molecule with Ni*Nj atoms and then set manually the attributes record, beta, resid, resname, name, coords for each dummy atom in the slab. Take a dummy slab from OPM as example. 2) Aromatic residues form anchors on the membrane, use the orientation of their ring plane to orient th ...
... to create an empty molecule with Ni*Nj atoms and then set manually the attributes record, beta, resid, resname, name, coords for each dummy atom in the slab. Take a dummy slab from OPM as example. 2) Aromatic residues form anchors on the membrane, use the orientation of their ring plane to orient th ...
Novel Types of Two-Domain Multi
... newly found proteins are similar to that of laccase, ascorbate oxidase or ceruloplasmin, rather than that of nitrite reductase. All eleven sequences are found in bacteria. Most of those organisms such as rhizobia and halobacteria are known to be capable of nitrogen fixation. Therefore, it is plausib ...
... newly found proteins are similar to that of laccase, ascorbate oxidase or ceruloplasmin, rather than that of nitrite reductase. All eleven sequences are found in bacteria. Most of those organisms such as rhizobia and halobacteria are known to be capable of nitrogen fixation. Therefore, it is plausib ...
Population Genetics
... a polypeptide • A protein has an amino (the first amino acid in the chain) and a carboxyl (the last amino acid in a chain) ends ...
... a polypeptide • A protein has an amino (the first amino acid in the chain) and a carboxyl (the last amino acid in a chain) ends ...
Protein Synthesis part 2
... Translation - This is the part of actually making the protein. A. This process occurs at the Ribosome “the Translator”. B. The process turns the mRNA into a primary (1’) sequence of amino acids for making of the protein. C. This process needs the assistance of tRNA (transfer RNA) to transfer free am ...
... Translation - This is the part of actually making the protein. A. This process occurs at the Ribosome “the Translator”. B. The process turns the mRNA into a primary (1’) sequence of amino acids for making of the protein. C. This process needs the assistance of tRNA (transfer RNA) to transfer free am ...
BIO 208: GENETICS
... Read the pre- laboratory handouts: Glowing Fish, Protein of the Month, and Transformation of E. coli with pGLO Plasmid DNA Use full sentences and answer in your own words. Type. Use a separate piece of paper to answer. 1. What is GFP and from what organism (genus and species) is the GFP gene obtaine ...
... Read the pre- laboratory handouts: Glowing Fish, Protein of the Month, and Transformation of E. coli with pGLO Plasmid DNA Use full sentences and answer in your own words. Type. Use a separate piece of paper to answer. 1. What is GFP and from what organism (genus and species) is the GFP gene obtaine ...
proteins - SharpSchool
... variety of phenotypes because the traits are controlled by many genes. The genes act together as a group to produce a single trait. Example: Height in humans (at least four genes), also skin, eye color, hair ...
... variety of phenotypes because the traits are controlled by many genes. The genes act together as a group to produce a single trait. Example: Height in humans (at least four genes), also skin, eye color, hair ...
PE 690 weight training PPt
... • Body either excrete it, turn it to fat, or use it for energy. • Types of protein (whey, casein, soy, rice) • The major proteins in milk are casein and whey. These two milk proteins are both excellent sources, but they differ in one important aspect—whey is a fast-digesting protein and casein is a ...
... • Body either excrete it, turn it to fat, or use it for energy. • Types of protein (whey, casein, soy, rice) • The major proteins in milk are casein and whey. These two milk proteins are both excellent sources, but they differ in one important aspect—whey is a fast-digesting protein and casein is a ...
Enzymes are catalysts in living things
... • Disruptions in homeostasis can prevent enzymes from functioning. – Enzymes function best in a small range of conditions (remember importance of water’s special properties – water is a buffer). – Changes in temperature and pH can break hydrogen bonds (remember, organisms have a very narrow range of ...
... • Disruptions in homeostasis can prevent enzymes from functioning. – Enzymes function best in a small range of conditions (remember importance of water’s special properties – water is a buffer). – Changes in temperature and pH can break hydrogen bonds (remember, organisms have a very narrow range of ...
Protein moonlighting

Protein moonlighting (or gene sharing) is a phenomenon by which a protein can perform more than one function. Ancestral moonlighting proteins originally possessed a single function but through evolution, acquired additional functions. Many proteins that moonlight are enzymes; others are receptors, ion channels or chaperones. The most common primary function of moonlighting proteins is enzymatic catalysis, but these enzymes have acquired secondary non-enzymatic roles. Some examples of functions of moonlighting proteins secondary to catalysis include signal transduction, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, motility, and structural.Protein moonlighting may occur widely in nature. Protein moonlighting through gene sharing differs from the use of a single gene to generate different proteins by alternative RNA splicing, DNA rearrangement, or post-translational processing. It is also different from multifunctionality of the protein, in which the protein has multiple domains, each serving a different function. Protein moonlighting by gene sharing means that a gene may acquire and maintain a second function without gene duplication and without loss of the primary function. Such genes are under two or more entirely different selective constraints.Various techniques have been used to reveal moonlighting functions in proteins. The detection of a protein in unexpected locations within cells, cell types, or tissues may suggest that a protein has a moonlighting function. Furthermore, sequence or structure homology of a protein may be used to infer both primary function as well as secondary moonlighting functions of a protein.The most well-studied examples of gene sharing are crystallins. These proteins, when expressed at low levels in many tissues function as enzymes, but when expressed at high levels in eye tissue, become densely packed and thus form lenses. While the recognition of gene sharing is relatively recent—the term was coined in 1988, after crystallins in chickens and ducks were found to be identical to separately identified enzymes—recent studies have found many examples throughout the living world. Joram Piatigorsky has suggested that many or all proteins exhibit gene sharing to some extent, and that gene sharing is a key aspect of molecular evolution. The genes encoding crystallins must maintain sequences for catalytic function and transparency maintenance function.Inappropriate moonlighting is a contributing factor in some genetic diseases, and moonlighting provides a possible mechanism by which bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics.











![[Fe 4 S 4 Cys 4 ] 1](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008100934_1-bb8d7235eb07199e709035eea64be997-300x300.png)










