Usha`s presentation - The University of Texas at Dallas
... Holm L., Sander C(1993 a) Protein Structure Comparison by Alignment of Distance Matrices. Journal of Molecular Biol. 233(1): 123-138 Holm L., Park J(2000) DaliLite workbench for protein structure comparison. Bioinformatics 16, 566-567 Holm L., Sander C(1996) Mapping the protein ...
... Holm L., Sander C(1993 a) Protein Structure Comparison by Alignment of Distance Matrices. Journal of Molecular Biol. 233(1): 123-138 Holm L., Park J(2000) DaliLite workbench for protein structure comparison. Bioinformatics 16, 566-567 Holm L., Sander C(1996) Mapping the protein ...
Force generation in dividing E
... This thesis is about cell division in bacteria. What (to me) is fascinating about a bacterium such as Escherichia coli is that it can multiply at an incredibly fast pace by growing in length and then simply splitting itself in two. It has been known for decades that our own cells divide by making us ...
... This thesis is about cell division in bacteria. What (to me) is fascinating about a bacterium such as Escherichia coli is that it can multiply at an incredibly fast pace by growing in length and then simply splitting itself in two. It has been known for decades that our own cells divide by making us ...
FPIA - IMGT
... 2. A protein receptor has a meaning for a given cell (it transduces the signal from the cell membrane to the nucleus). At each step of a pathway, there is a signal reception and transmission. The protein which receives the signal is the receptor. Each protein in a pathway can be successively a recep ...
... 2. A protein receptor has a meaning for a given cell (it transduces the signal from the cell membrane to the nucleus). At each step of a pathway, there is a signal reception and transmission. The protein which receives the signal is the receptor. Each protein in a pathway can be successively a recep ...
Lecture 5: Applications in Biomolecular Simulation and Drug
... Biological and Drug Design Motivation The complex between the two molecules highly stimulates the response of the T-cells of the immune system. The grp94 protein alone does not have this property. The activity that stimulates the immune response is due to the ability of grp94 to bind different pept ...
... Biological and Drug Design Motivation The complex between the two molecules highly stimulates the response of the T-cells of the immune system. The grp94 protein alone does not have this property. The activity that stimulates the immune response is due to the ability of grp94 to bind different pept ...
Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-PCR)
... all genes. • This is done by creating the complementary strands of the known gene sequences and assembling them on a chip. • The sequences are tagged with flourescent tags that glow a certain color when in contact with the complementary ...
... all genes. • This is done by creating the complementary strands of the known gene sequences and assembling them on a chip. • The sequences are tagged with flourescent tags that glow a certain color when in contact with the complementary ...
Solutions to Molecular Biology Unit Exam
... This mutant protein is nearly identical to the normal protein. It is different in that it has two additional amino acids at the very N terminus, but these two terminal amino acids are unlikely to change the overall tertiary structure of the protein, so it is unlikely that this insertion will change ...
... This mutant protein is nearly identical to the normal protein. It is different in that it has two additional amino acids at the very N terminus, but these two terminal amino acids are unlikely to change the overall tertiary structure of the protein, so it is unlikely that this insertion will change ...
PDF File
... emerging understanding of the relationships between enzyme superfamilies, and Khersonsky, Roodveldt and Tawfik focus on a particularly fascinating aspect of evolutionary relationships, properties of ‘catalytic promiscuity’ — the low level of activity of an enzyme for a reaction other than its curren ...
... emerging understanding of the relationships between enzyme superfamilies, and Khersonsky, Roodveldt and Tawfik focus on a particularly fascinating aspect of evolutionary relationships, properties of ‘catalytic promiscuity’ — the low level of activity of an enzyme for a reaction other than its curren ...
Leukaemia Section t(11;20)(q23;q11) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Published in Atlas Database: March 2006 Online updated version: http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org/Anomalies/t1120q23q11ID1415.html DOI: 10.4267/2042/38334 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2006 Atlas of Genetics and Cyt ...
... Published in Atlas Database: March 2006 Online updated version: http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org/Anomalies/t1120q23q11ID1415.html DOI: 10.4267/2042/38334 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2006 Atlas of Genetics and Cyt ...
5.36 Biochemistry Laboratory
... • The tag was introduced by the pET-28a vector (see map). • The Yop phosphatase is NOT His-tagged. You will use affinity tag purification to isolate the H396P Abl kinase domain. Studies have shown that an N-terminal His tag does not significantly affect Abl kinase domain activity, so we will not remove ...
... • The tag was introduced by the pET-28a vector (see map). • The Yop phosphatase is NOT His-tagged. You will use affinity tag purification to isolate the H396P Abl kinase domain. Studies have shown that an N-terminal His tag does not significantly affect Abl kinase domain activity, so we will not remove ...
Schedule
... • As the DNA sequence has 11 base pairs deleted / mutated this will change the order of base pairing (concept of codons shifted because of deletion / mutation) as the RNA is synthesised during transcription. This will affect the final mRNA product, changing the codon sequence (shortening the RNA pos ...
... • As the DNA sequence has 11 base pairs deleted / mutated this will change the order of base pairing (concept of codons shifted because of deletion / mutation) as the RNA is synthesised during transcription. This will affect the final mRNA product, changing the codon sequence (shortening the RNA pos ...
(Submitted) Genetic Synthesis of Periodic Protein Materials M. J.
... proteins is the bacterium Escherichia coli. A superior base of molecular genetic knowledge exists for E. coli and growth and processing technologies are well established for recombinant products expressed by this organism. In addition to the actual protein sequence decisions about the design of a sy ...
... proteins is the bacterium Escherichia coli. A superior base of molecular genetic knowledge exists for E. coli and growth and processing technologies are well established for recombinant products expressed by this organism. In addition to the actual protein sequence decisions about the design of a sy ...
Judgement Statement – 2012
... • As the DNA sequence has 11 base pairs deleted / mutated this will change the order of base pairing (concept of codons shifted because of deletion / mutation) as the RNA is synthesised during transcription. This will affect the final mRNA product, changing the codon sequence (shortening the RNA pos ...
... • As the DNA sequence has 11 base pairs deleted / mutated this will change the order of base pairing (concept of codons shifted because of deletion / mutation) as the RNA is synthesised during transcription. This will affect the final mRNA product, changing the codon sequence (shortening the RNA pos ...
View Full PDF - Biochemical Society Transactions
... from particular biological sources. The chapter on lysosomal enzymes has been almost completely rewritten, and contains extremely useful and comprehensive reviews on all of those enzymes currently considered to be associated with lysosomes. Relevant biochemical information concerning these enzymes, ...
... from particular biological sources. The chapter on lysosomal enzymes has been almost completely rewritten, and contains extremely useful and comprehensive reviews on all of those enzymes currently considered to be associated with lysosomes. Relevant biochemical information concerning these enzymes, ...
No Slide Title
... holds sister chromatids together through metaphase INTERmolecular linking of two DNAs (compare to condensin) established at replication fork-preloaded in G1? degraded at onset of anaphase to allow sister separation cohesin in pericentromeric regions recruited by HP1/K9me, may be regulated differentl ...
... holds sister chromatids together through metaphase INTERmolecular linking of two DNAs (compare to condensin) established at replication fork-preloaded in G1? degraded at onset of anaphase to allow sister separation cohesin in pericentromeric regions recruited by HP1/K9me, may be regulated differentl ...
HW - 1
... d. Bacteria that live in and on our bodies that may have a symbiotic function 6. Which of the following is NOT a Prokaryote? a. Fungi b. Bacteria c. Archaebacteria d. The Bubonic Plague 7. What is the Spontaneous Generation Hypothesis and how was it disproved? ...
... d. Bacteria that live in and on our bodies that may have a symbiotic function 6. Which of the following is NOT a Prokaryote? a. Fungi b. Bacteria c. Archaebacteria d. The Bubonic Plague 7. What is the Spontaneous Generation Hypothesis and how was it disproved? ...
Cloning and Expression in Pichia pastoris (Gene to Product)
... available expression vectors. These vectors use methanol-responsive AOX1 promoter and transcription terminator and secretory signal ...
... available expression vectors. These vectors use methanol-responsive AOX1 promoter and transcription terminator and secretory signal ...
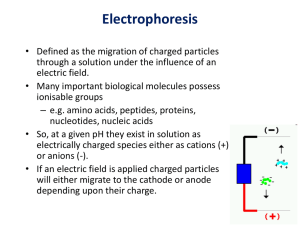
Electrophoresis HCC 2013 BMS2 intro
... needed to properly separate. * Otherwise, the small proteins would just race through the gel matrix with no quantitative results for classifying polypeptides. * The best concentration for particular size ranges has thankfully been determined by previous scientists. ...
... needed to properly separate. * Otherwise, the small proteins would just race through the gel matrix with no quantitative results for classifying polypeptides. * The best concentration for particular size ranges has thankfully been determined by previous scientists. ...
Abstract - UWL faculty websites
... studied by thousands of researchers because yeast contains cell division proteins that are similar to those in human cells. One commonly studied yeast cell growth protein is Cdc7. This protein kinase is required for initiating DNA replication (S phase) during the mitotic cell cycle, although it is n ...
... studied by thousands of researchers because yeast contains cell division proteins that are similar to those in human cells. One commonly studied yeast cell growth protein is Cdc7. This protein kinase is required for initiating DNA replication (S phase) during the mitotic cell cycle, although it is n ...
398 Form Pages _
... we grouped membrane proteins into families and looked at their relative abundance in a number of different genomes. We also looked at the abundance of a number of different motifs -- in particular, GXXXG. In the second paper, we extended our motif work further, looking at the occurrence of protein m ...
... we grouped membrane proteins into families and looked at their relative abundance in a number of different genomes. We also looked at the abundance of a number of different motifs -- in particular, GXXXG. In the second paper, we extended our motif work further, looking at the occurrence of protein m ...
Protein moonlighting

Protein moonlighting (or gene sharing) is a phenomenon by which a protein can perform more than one function. Ancestral moonlighting proteins originally possessed a single function but through evolution, acquired additional functions. Many proteins that moonlight are enzymes; others are receptors, ion channels or chaperones. The most common primary function of moonlighting proteins is enzymatic catalysis, but these enzymes have acquired secondary non-enzymatic roles. Some examples of functions of moonlighting proteins secondary to catalysis include signal transduction, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, motility, and structural.Protein moonlighting may occur widely in nature. Protein moonlighting through gene sharing differs from the use of a single gene to generate different proteins by alternative RNA splicing, DNA rearrangement, or post-translational processing. It is also different from multifunctionality of the protein, in which the protein has multiple domains, each serving a different function. Protein moonlighting by gene sharing means that a gene may acquire and maintain a second function without gene duplication and without loss of the primary function. Such genes are under two or more entirely different selective constraints.Various techniques have been used to reveal moonlighting functions in proteins. The detection of a protein in unexpected locations within cells, cell types, or tissues may suggest that a protein has a moonlighting function. Furthermore, sequence or structure homology of a protein may be used to infer both primary function as well as secondary moonlighting functions of a protein.The most well-studied examples of gene sharing are crystallins. These proteins, when expressed at low levels in many tissues function as enzymes, but when expressed at high levels in eye tissue, become densely packed and thus form lenses. While the recognition of gene sharing is relatively recent—the term was coined in 1988, after crystallins in chickens and ducks were found to be identical to separately identified enzymes—recent studies have found many examples throughout the living world. Joram Piatigorsky has suggested that many or all proteins exhibit gene sharing to some extent, and that gene sharing is a key aspect of molecular evolution. The genes encoding crystallins must maintain sequences for catalytic function and transparency maintenance function.Inappropriate moonlighting is a contributing factor in some genetic diseases, and moonlighting provides a possible mechanism by which bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics.