Sodium dodecyl sulfate (L3771)
... Sigma-Aldrich, Inc. warrants that its products conform to the information contained in this and other Sigma-Aldrich publications. Purchaser must determine the suitability of the product(s) for their particular use. Additional terms and conditions may apply. Please see reverse side of the invoice or ...
... Sigma-Aldrich, Inc. warrants that its products conform to the information contained in this and other Sigma-Aldrich publications. Purchaser must determine the suitability of the product(s) for their particular use. Additional terms and conditions may apply. Please see reverse side of the invoice or ...
Poster 2: Primary Structure - IMSA Digital Commons
... Fig. 1: The general 3D structure of the primary structure of a protein. Note that not everything is in the same plane. Also note the torsion angles; the measurements of these angles will vary between -180 degrees and 180 degrees depending on the R group. (1) However, it will never go to a conformati ...
... Fig. 1: The general 3D structure of the primary structure of a protein. Note that not everything is in the same plane. Also note the torsion angles; the measurements of these angles will vary between -180 degrees and 180 degrees depending on the R group. (1) However, it will never go to a conformati ...
Appendix A: Gene Annotation
... the driver or the UAS line alone, and was found to be the same. The number of eclosed flies from the tub>>SVC crosses was compared to that of crosses where the driver line or the UAS line alone was outcrossed to wild-type flies. No differences in developmental rate or viability were observed. Same-a ...
... the driver or the UAS line alone, and was found to be the same. The number of eclosed flies from the tub>>SVC crosses was compared to that of crosses where the driver line or the UAS line alone was outcrossed to wild-type flies. No differences in developmental rate or viability were observed. Same-a ...
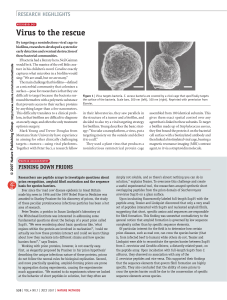
Using PEPscreen to Study Protein Phosphorylation - Sigma
... pathways, regulating diverse processes such as proliferation, metabolism, and apoptosis. In the human proteome, which numbers up to 23,000 proteins, around 650,000 possible phosphorylation sites have been predicted, and about 100,000 of those sites have been confirmed as actual sites of protein phos ...
... pathways, regulating diverse processes such as proliferation, metabolism, and apoptosis. In the human proteome, which numbers up to 23,000 proteins, around 650,000 possible phosphorylation sites have been predicted, and about 100,000 of those sites have been confirmed as actual sites of protein phos ...
Maximilian J. Telford , 764 (2013); DOI: 10.1126/science.1234378
... interacted directly with cGAS. Wu et al. and Sun et al. provide compelling new insights into how DNA is sensed in the cytoplasm of mammalian cells. DNA binds to the enzyme cGAS, which catalyzes the production of the second messenger molecule cGAMP. This molecule in turn binds to STING, which trigger ...
... interacted directly with cGAS. Wu et al. and Sun et al. provide compelling new insights into how DNA is sensed in the cytoplasm of mammalian cells. DNA binds to the enzyme cGAS, which catalyzes the production of the second messenger molecule cGAMP. This molecule in turn binds to STING, which trigger ...
Unique Protein Reporter Assays: Green Fluorescent Proteins (GFP
... Fluorescent reporter proteins are valuable non-invasive molecular tools for in vivo real-time imaging of living cells and tissues as well as in vitro fluorescence labeling. A major drawback of existing GFP-like reporter proteins is their strict requirement for molecular oxygen as a cofactor for the ...
... Fluorescent reporter proteins are valuable non-invasive molecular tools for in vivo real-time imaging of living cells and tissues as well as in vitro fluorescence labeling. A major drawback of existing GFP-like reporter proteins is their strict requirement for molecular oxygen as a cofactor for the ...
Bioseparation Engineering, Vol 16. Progress in Biotechnology Brochure
... Environment". The scope of this book is based on the conference, and deals not only with recent advances in bioseparation engineering in a narrow sence, but also the environmental engineering which includes waste water treatment and bioremediation. The contributors of this book cover many discipline ...
... Environment". The scope of this book is based on the conference, and deals not only with recent advances in bioseparation engineering in a narrow sence, but also the environmental engineering which includes waste water treatment and bioremediation. The contributors of this book cover many discipline ...
primary structure
... 3.14 A protein’s shape depends on four levels of structure Quaternary Structure- occurs in proteins with more than one polypeptide; described as globular or fibrous ...
... 3.14 A protein’s shape depends on four levels of structure Quaternary Structure- occurs in proteins with more than one polypeptide; described as globular or fibrous ...
Cytochrome P450 Proteins
... − Solution: Enzymatically digest the protein or large peptide therapeutic into small peptides and monitor one or more peptides as a surrogate – Trypsin is the enzyme of choice for several reasons: – Tryptic peptides are a good size for MRM assays (not too large) – Tryptic peptides tend to fragment w ...
... − Solution: Enzymatically digest the protein or large peptide therapeutic into small peptides and monitor one or more peptides as a surrogate – Trypsin is the enzyme of choice for several reasons: – Tryptic peptides are a good size for MRM assays (not too large) – Tryptic peptides tend to fragment w ...
Purification and characterization of LasR as a DNA
... are included in our binding regions (regions 1 and 3). The results of DNA-binding analysis of LasR protein to the upstream region of the 1asB promoter suggest that the combination of LasR and OdDHL is necessary for 1asB transcription, and control of its expression. In addition, regions 1 and 3 are s ...
... are included in our binding regions (regions 1 and 3). The results of DNA-binding analysis of LasR protein to the upstream region of the 1asB promoter suggest that the combination of LasR and OdDHL is necessary for 1asB transcription, and control of its expression. In addition, regions 1 and 3 are s ...
Gene Expression
... nucleus, into the cytoplasm. There, it binds to a ribosome, which reads the RNA strand and attaches a "T" nucleotide to the RNA "A" nucleotide, etc, until the entire RNA strand has been paired with nucleotides. This is translation. Then the RNA strand is taken away, taken apart, and its nucleotides ...
... nucleus, into the cytoplasm. There, it binds to a ribosome, which reads the RNA strand and attaches a "T" nucleotide to the RNA "A" nucleotide, etc, until the entire RNA strand has been paired with nucleotides. This is translation. Then the RNA strand is taken away, taken apart, and its nucleotides ...
Biochemical studies on antioxidant
... Background: Many changes can occur in proteins, including amino acid modification, fragmentation, changes in absorption and fluorescence spectra and others. All these modifications can be used as markers of protein damage by free radicals. Aim of the Work: The aim of the present study was to investi ...
... Background: Many changes can occur in proteins, including amino acid modification, fragmentation, changes in absorption and fluorescence spectra and others. All these modifications can be used as markers of protein damage by free radicals. Aim of the Work: The aim of the present study was to investi ...
LS1a Problem Set #4
... c) You further examine the mobility of protein A in cells that have a defect in cholesterol production. The membranes of these cells have very little cholesterol compared to the cells used above. If you repeat your FRAP experiments from part (a) using these cells, how do you predict the mobility of ...
... c) You further examine the mobility of protein A in cells that have a defect in cholesterol production. The membranes of these cells have very little cholesterol compared to the cells used above. If you repeat your FRAP experiments from part (a) using these cells, how do you predict the mobility of ...
introduction - Genomics
... species under study, while taking full advantage of the huge number of experimentally characterised or predicted proteins in other species. In the first instance, the X. tropicalis EST project has focused on early stages of embryonic development, where the Xenopus system has been most effectively ex ...
... species under study, while taking full advantage of the huge number of experimentally characterised or predicted proteins in other species. In the first instance, the X. tropicalis EST project has focused on early stages of embryonic development, where the Xenopus system has been most effectively ex ...
Aim: Why are Enzymes necessary for our survival?
... Is formed when the substrate is bound to the enzyme ...
... Is formed when the substrate is bound to the enzyme ...
Gene Section GPC1 (glypican 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... system (CNS) and skeletal system during development but also in many other tissues in the adult. ...
... system (CNS) and skeletal system during development but also in many other tissues in the adult. ...
Core Topic 2: Molecular biology 21 hours Essential idea: Living
... Amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides. There are 20 different amino acids in polypeptides synthesized on ribosomes. Amino acids can be linked together in any sequence giving a huge range of possible polypeptides. The amino acid sequence of polypeptides is coded ...
... Amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides. There are 20 different amino acids in polypeptides synthesized on ribosomes. Amino acids can be linked together in any sequence giving a huge range of possible polypeptides. The amino acid sequence of polypeptides is coded ...
Use of G-protein fusions to monitor integral membrane protein
... Proteins can be regulated by post-translational modifications, altered localization, or association with regulatory subunits or other components of a supramolecular structure (e.g., ribosome, cytoskeleton). In the past, protein–protein interactions have typically been studied using biochemical techn ...
... Proteins can be regulated by post-translational modifications, altered localization, or association with regulatory subunits or other components of a supramolecular structure (e.g., ribosome, cytoskeleton). In the past, protein–protein interactions have typically been studied using biochemical techn ...
The exocyst, an octameric protein complex conserved among all
... The exocyst, an octameric protein complex conserved among all eukaryotes, mediates tethering of the vesicle prior to its fusion with the target membrane. Apart from the function of exocyst in exocytosis, new studies from both mammalian and plant fields report its involvement in the cellular self-eat ...
... The exocyst, an octameric protein complex conserved among all eukaryotes, mediates tethering of the vesicle prior to its fusion with the target membrane. Apart from the function of exocyst in exocytosis, new studies from both mammalian and plant fields report its involvement in the cellular self-eat ...
Gene Section SOCS2 (suppressor of cytokine signaling 2) in Oncology and Haematology
... SOCS mechanisms of action rely on their ability to bind tyrosine phosphorylated proteins through their SH2 domains, but also to bind Elongin BC through their SOCS box domains. SOCS family proteins form part of a classical negative feedback system that regulates cytokine signal transduction (Rico-Bau ...
... SOCS mechanisms of action rely on their ability to bind tyrosine phosphorylated proteins through their SH2 domains, but also to bind Elongin BC through their SOCS box domains. SOCS family proteins form part of a classical negative feedback system that regulates cytokine signal transduction (Rico-Bau ...
Workshop#7
... Annotated records that represent single contiguous stretches of DNA or RNA-may have more than one coding region. Generated from direct submissions to the DNA sequence databases from the authors. Part of the International Nucleotide ...
... Annotated records that represent single contiguous stretches of DNA or RNA-may have more than one coding region. Generated from direct submissions to the DNA sequence databases from the authors. Part of the International Nucleotide ...
Supporting Information
... reaction, oxidized flavin mononucleotide (FMN) is reduced by two electrons to FMNH2. Molecular oxygen restores the flavin to the fully oxidized state in vitro; in vivo, the oxidant remains unknown. (B) ClustalW alignment of ⬇30 SagB orthologs (includes S. dysgalactiae). Because of divergence at the ...
... reaction, oxidized flavin mononucleotide (FMN) is reduced by two electrons to FMNH2. Molecular oxygen restores the flavin to the fully oxidized state in vitro; in vivo, the oxidant remains unknown. (B) ClustalW alignment of ⬇30 SagB orthologs (includes S. dysgalactiae). Because of divergence at the ...
Protein moonlighting

Protein moonlighting (or gene sharing) is a phenomenon by which a protein can perform more than one function. Ancestral moonlighting proteins originally possessed a single function but through evolution, acquired additional functions. Many proteins that moonlight are enzymes; others are receptors, ion channels or chaperones. The most common primary function of moonlighting proteins is enzymatic catalysis, but these enzymes have acquired secondary non-enzymatic roles. Some examples of functions of moonlighting proteins secondary to catalysis include signal transduction, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, motility, and structural.Protein moonlighting may occur widely in nature. Protein moonlighting through gene sharing differs from the use of a single gene to generate different proteins by alternative RNA splicing, DNA rearrangement, or post-translational processing. It is also different from multifunctionality of the protein, in which the protein has multiple domains, each serving a different function. Protein moonlighting by gene sharing means that a gene may acquire and maintain a second function without gene duplication and without loss of the primary function. Such genes are under two or more entirely different selective constraints.Various techniques have been used to reveal moonlighting functions in proteins. The detection of a protein in unexpected locations within cells, cell types, or tissues may suggest that a protein has a moonlighting function. Furthermore, sequence or structure homology of a protein may be used to infer both primary function as well as secondary moonlighting functions of a protein.The most well-studied examples of gene sharing are crystallins. These proteins, when expressed at low levels in many tissues function as enzymes, but when expressed at high levels in eye tissue, become densely packed and thus form lenses. While the recognition of gene sharing is relatively recent—the term was coined in 1988, after crystallins in chickens and ducks were found to be identical to separately identified enzymes—recent studies have found many examples throughout the living world. Joram Piatigorsky has suggested that many or all proteins exhibit gene sharing to some extent, and that gene sharing is a key aspect of molecular evolution. The genes encoding crystallins must maintain sequences for catalytic function and transparency maintenance function.Inappropriate moonlighting is a contributing factor in some genetic diseases, and moonlighting provides a possible mechanism by which bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics.