Chapter 9
... Recall kinetic theory of gases (Chapter 5): temperature is associated with the average KE of a large number of molecules. KEav = (3/2) RT Random motion is often called thermal motion. Heat involves the transfer of energy between two objects due to a temperature difference between the two objects. Wh ...
... Recall kinetic theory of gases (Chapter 5): temperature is associated with the average KE of a large number of molecules. KEav = (3/2) RT Random motion is often called thermal motion. Heat involves the transfer of energy between two objects due to a temperature difference between the two objects. Wh ...
Chapter 9: Thermochemistry VanKoppen
... transferred to B, raising B to a higher position thereby increasing the PE of B. Note, however, that the final position of B is lower than the initial position of A. What happened to the remaining energy? Some of the KE of A is transferred to the surface of the hill as heat due to friction. The temp ...
... transferred to B, raising B to a higher position thereby increasing the PE of B. Note, however, that the final position of B is lower than the initial position of A. What happened to the remaining energy? Some of the KE of A is transferred to the surface of the hill as heat due to friction. The temp ...
Foods II Vocabulary 2.01 Chemistry – The study of the makeup
... 22. Electrical Energy – Energy produced by the movement of electrons. 23. Radiant Energy - Energy transmitted in the form of waves through space or some medium. 24. Microwave – A low-frequency electromagnetic wave of radiant energy. 25. Heat – An energy transfer from one body to another caused by a ...
... 22. Electrical Energy – Energy produced by the movement of electrons. 23. Radiant Energy - Energy transmitted in the form of waves through space or some medium. 24. Microwave – A low-frequency electromagnetic wave of radiant energy. 25. Heat – An energy transfer from one body to another caused by a ...
File
... 2nd Law: F=ma – force = mass x acceleration. If you throw a ball harder (more force), it will accelerate faster and go farther. 3rd Law: Action – Reaction. One object exerts a force on a 2nd object (action), and the 2nd exerts an equal and opposite force back on the 1st ...
... 2nd Law: F=ma – force = mass x acceleration. If you throw a ball harder (more force), it will accelerate faster and go farther. 3rd Law: Action – Reaction. One object exerts a force on a 2nd object (action), and the 2nd exerts an equal and opposite force back on the 1st ...
Chapter02a
... • Chemical energy: batteries • Nuclear energy: nuclear powerplants • Heat: steam engines ...
... • Chemical energy: batteries • Nuclear energy: nuclear powerplants • Heat: steam engines ...
Energy Study Guide Key
... to heat; power drill – electrical to mechanical; a lite candle – chemical to light 3. What is potential energy? Energy that is stored or at rest 4. What is kinetic energy? Energy that is in motion 5. List and briefly explain the non-renewable energy sources. a. Coal: formed from the remains of plant ...
... to heat; power drill – electrical to mechanical; a lite candle – chemical to light 3. What is potential energy? Energy that is stored or at rest 4. What is kinetic energy? Energy that is in motion 5. List and briefly explain the non-renewable energy sources. a. Coal: formed from the remains of plant ...
PowerPoint
... • When the temperature of a substance increases, its particles move faster and spread out. This causes the substance to expand and become less dense. ...
... • When the temperature of a substance increases, its particles move faster and spread out. This causes the substance to expand and become less dense. ...
Temperature and Heat
... accommodate thermal expansion. (Reproduced by permission of JLM Visuals) ...
... accommodate thermal expansion. (Reproduced by permission of JLM Visuals) ...
Temperature and Heat Temperature Depends on Particle Movement
... object at a higher temperature to an object at a lower temperature. • Thermal Energy: total random kinetic energy of particles in an object. ...
... object at a higher temperature to an object at a lower temperature. • Thermal Energy: total random kinetic energy of particles in an object. ...
Energy - ability of an object to do work
... Electric energy – form of moving energy that has a flow of electric charges Circuit- a path in which electrons move Conductor – materials that allow electrons, sound, or heat to move Insulator-materials that do not allow electrons to move, sound to travel or heat to flow Heat resistant – materials t ...
... Electric energy – form of moving energy that has a flow of electric charges Circuit- a path in which electrons move Conductor – materials that allow electrons, sound, or heat to move Insulator-materials that do not allow electrons to move, sound to travel or heat to flow Heat resistant – materials t ...
Slide 1
... "You can dance anywhere, even if only in your heart." ~Unknown "If dancing were any easier it would be called football." ~anonymous ...
... "You can dance anywhere, even if only in your heart." ~Unknown "If dancing were any easier it would be called football." ~anonymous ...
Energy Unit Class Notes
... 6. Nuclear energy – energy stored in the nucleus of an atom Fission – nucleus splits releasing energy (uranium in nuclear power plants) Fusion – hydrogen nuclei join together to form helium on the sun Energy Conversion – a change of one form of energy to another Fossil Fuel: a material that stores c ...
... 6. Nuclear energy – energy stored in the nucleus of an atom Fission – nucleus splits releasing energy (uranium in nuclear power plants) Fusion – hydrogen nuclei join together to form helium on the sun Energy Conversion – a change of one form of energy to another Fossil Fuel: a material that stores c ...
Phases of Matter - Bill Nye the Science Guy Wkst
... 10. A soda is liquid that contains__________________________ gas to make it bubble and fizz. ...
... 10. A soda is liquid that contains__________________________ gas to make it bubble and fizz. ...
Brief 2-page Summary
... Heat: energy causing a change in temperature Thermal energy: energy an object or substance possesses as temperature because of the kinetic energy of its molecules Heat flow: heat always moves from warmer objects to cooler objects Energy is can be transferred or transformed into a variety of fo ...
... Heat: energy causing a change in temperature Thermal energy: energy an object or substance possesses as temperature because of the kinetic energy of its molecules Heat flow: heat always moves from warmer objects to cooler objects Energy is can be transferred or transformed into a variety of fo ...
Name_______________________________ Energy, Heat, and
... Energy, Heat, and Temperature Test Study Guide 1. Energy has different forms. The two basic kinds of energy are potential energy and kinetic energy. Energy is the ability to do work. Work is the force that causes an object to move. Power is the rate at which the work is done. Potential energy is the ...
... Energy, Heat, and Temperature Test Study Guide 1. Energy has different forms. The two basic kinds of energy are potential energy and kinetic energy. Energy is the ability to do work. Work is the force that causes an object to move. Power is the rate at which the work is done. Potential energy is the ...
Chapter 10: Heat Energy
... of a material. • You insulate something by wrapping it securely with a material that is not a good conductor of heat. • There are many instances in our everyday lives where it is important to keep heat from entering or leaving something. ...
... of a material. • You insulate something by wrapping it securely with a material that is not a good conductor of heat. • There are many instances in our everyday lives where it is important to keep heat from entering or leaving something. ...
SC.4.P.11.1-11.2 - Energy Transfer and Transformation
... • When any form of matter gets warmer, the kinetic energy of its atoms increases. • The object’s particles move faster, so its thermal energy ...
... • When any form of matter gets warmer, the kinetic energy of its atoms increases. • The object’s particles move faster, so its thermal energy ...
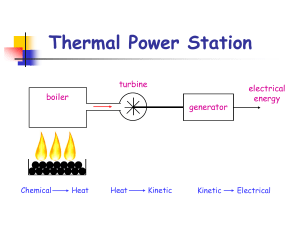
Thermal Power Station
... When the Uranium nucleus splits energy is released (which heats water in boiler). More neutrons are also released which can go on to split more Uranium nuclei. Control rods are used in nuclear reactors to absorb some of these new neutrons preventing too much energy being released in a short time. ...
... When the Uranium nucleus splits energy is released (which heats water in boiler). More neutrons are also released which can go on to split more Uranium nuclei. Control rods are used in nuclear reactors to absorb some of these new neutrons preventing too much energy being released in a short time. ...
924 Lecture, Energy
... 1. Conservation of energy: Energy is neither created nor destroyed; it is transformed. you can't take out of a system more than you put in. you can't win 2. The entropy of the universe is continually increasing. perpetual motion and a heat engine with 100% efficiency are both impossible. you can't b ...
... 1. Conservation of energy: Energy is neither created nor destroyed; it is transformed. you can't take out of a system more than you put in. you can't win 2. The entropy of the universe is continually increasing. perpetual motion and a heat engine with 100% efficiency are both impossible. you can't b ...
TE AWATEA`S ENERGY
... mining the material from deep underground. Coal has been mined for thousands of years but the first oil well was drilled in Pennsylvania in 1859. Significance Fossil fuels are the major source of energy throughout the world. In the United States oil provides 95 percent of all the energy used for tra ...
... mining the material from deep underground. Coal has been mined for thousands of years but the first oil well was drilled in Pennsylvania in 1859. Significance Fossil fuels are the major source of energy throughout the world. In the United States oil provides 95 percent of all the energy used for tra ...
Heat Transfer in the Atmosphere
... Two different materials at the same temperature have different emissivities. Which one glows the brightest? ...
... Two different materials at the same temperature have different emissivities. Which one glows the brightest? ...
Thermal Energy
... – Forced-air system – fuel heats air, which is blown through ducts and vents; cool air is returned to the furnace to be reheated – Radiator system – hot water or steam in a radiator transfers thermal energy to the air – Electric heating system – electrically heated coils in ceilings or floors heat a ...
... – Forced-air system – fuel heats air, which is blown through ducts and vents; cool air is returned to the furnace to be reheated – Radiator system – hot water or steam in a radiator transfers thermal energy to the air – Electric heating system – electrically heated coils in ceilings or floors heat a ...
Energy and its forms
... Energy can be conserved in Non-Mechanical forms The chemical energy in a battery transforms into electrical energy Any reaction where more energy is given off than is used to start it is Exogonic An Endogonic reaction absorbs energy and causes cooling ...
... Energy can be conserved in Non-Mechanical forms The chemical energy in a battery transforms into electrical energy Any reaction where more energy is given off than is used to start it is Exogonic An Endogonic reaction absorbs energy and causes cooling ...
Superconcepts
... a. Kinetic energy is the energy of objects in motion while potential energy is energy stored by position or in chemical bonds. b. In thermochemistry, the system is the chemical reaction itself (only the reactants & products). The surroundings are everything else in the universe. c. First law of ther ...
... a. Kinetic energy is the energy of objects in motion while potential energy is energy stored by position or in chemical bonds. b. In thermochemistry, the system is the chemical reaction itself (only the reactants & products). The surroundings are everything else in the universe. c. First law of ther ...