* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Foods II Vocabulary 2.01 Chemistry – The study of the makeup
Cogeneration wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Compressed air energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Micro combined heat and power wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
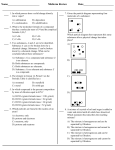
Foods II Vocabulary 2.01 1. Chemistry – The study of the makeup, structure, and properties of substances and the changes that occur to them. 2. Matter – Anything that occupies space and has mass. 3. Atom – The smallest unit of any elemental substance that maintains the characteristics of that substance. 4. Element – A substance that contains only one kind of atom. 5. Atomic Number – The number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of an element. 6. Atomic Mass – Approximately the sum of the masses of all protons and neutrons in an atom. 7. Atomic Mass Unit – A measure approximately equal to the mass of one proton or neutron. 8. Compound – A substance in which two or more elements have been chemically combined. 9. Molecule – The basic unit of any compound. 10. Chemical Formula – A combination of symbols that represents the elements that make up a compound. 11. Physical Change – A transformation of a substance involving a shift in shape, physical state, size, or temperature without a shift in chemical identity. 12. Phase Change – A physical change in the visible structure of matter without changing the molecular structure. 13. Energy – The ability to do work. 14. Potential Energy – Energy that is stored; the energy of position; the measure of work done. 15. Kinetic Energy – The energy of motion. 16. External Energy – Energy applied to an object by another source. 17. Internal Energy – Energy within an object. 18. Mechanical Energy – The total kinetic and potential energy of a system. 19. Chemical Energy – Energy generated by the forming and breaking of chemical bonds during a chemical change. 20. Endothermic Reaction – A reaction whose products have less total heat than the reactants. 21. Exothermic Reaction – A reaction during which energy is released. 22. Electrical Energy – Energy produced by the movement of electrons. 23. Radiant Energy - Energy transmitted in the form of waves through space or some medium. 24. Microwave – A low-frequency electromagnetic wave of radiant energy. 25. Heat – An energy transfer from one body to another caused by a temperature difference between the two bodies. 26. Heat Capacity – The ability of a substance to absorb heat. 27. Specific Heat – The ability of a substance to absorb or transfer heat as compared to water’s ability to absorb or transfer heat. 28. Temperature – The measure of the average kinetic energy of a group of individual molecules; an indirect measure of molecular motion. 29. Conduction – A transfer of heat energy through matter from particle-to-particle collisions. 30. Convection – A transfer of heat energy by the motion of fluids, such as water or air. 31. Latent Heat of Fusion – The energy needed to melt of freeze a substance. 32. Evaporation – The phase change when a substance changes from a liquid to a gas. 33. Vaporization – The phase change when a substance changes from a liquid to a gas. 34. Condensation – The phase change when a substance changes from a gas to a liquid. 35. Liquefaction – The phase change when a substance changes from a gas to a liquid. 36. Latent Heat of Vaporization – The energy needed to evaporate or condense a substance. 37. Latent Heat – The energy needed to complete the rearranging of molecules that occurs at the point of a phase change of a substance. 38. Sublimation – Changing a substance directly from a solid phase to a gas phase. Name: _______________ Period/Block: __________ Date: _________________ Questions and Answers on the Periodic Table 1. How many elements are in the periodic table? 2. Describe each of the four pieces of information presented in the block below. Oxygen 8 O 15.99 3. Identify all of the elements that make up these common food substances? Salt (NaCl) ________________________________________ Water (H20) ________________________________________ Baking soda (NaHCO3) ________________________________________ Cream of tartar (KC4H5O6) ________________________________________ Sugar (C12H22O11) ________________________________________ Ethanol C2H5OH) ________________________________________ Brainstorming Physical Changes to Food BACKGROUND: There are three physical changes that affect food – change in shape and/or size, change in phase, and/or change in the temperature without changing its chemical identity. Identify what change, if any, could be made to the food without altering the chemical identity. FOOD Watermelon Milk Ice cream Bread Solid shortening Peanuts Carrots Sugar Meat Fruit Juice SHAPE/SIZE PHASE TEMPERATURE Graphic Organizer – Matter Power Point Name: Matter Energy & Heat Transfer Power Point Notes Name: Energy (5 Types) Three Ways Heat is Transferred Conduction Convection Radiation Physical Changes Power Point Notes Name: Physical Changes are crucial in: Physical Properties Thermodynamics Heat Transfer Microwave Physical Changes To Matter Changing its shape or size Changing the Temperature Changing Phase