A Practical Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithm
... avoid duplication, and thus minimize bugs. From a pedagogical standpoint, however, inheritance often makes code examples harder to understand since it tends to spread the description for one logical unit among several classes. Thus, my class definitions only use inheritance where inheritance is expl ...
... avoid duplication, and thus minimize bugs. From a pedagogical standpoint, however, inheritance often makes code examples harder to understand since it tends to spread the description for one logical unit among several classes. Thus, my class definitions only use inheritance where inheritance is expl ...
a comparative evaluation of matlab, octave, freemat - here
... and Scilab have state-of-the-art variable-order, variable-timestep methods for both non-stiff and stiff ODEs available, with Matlab’s implementation being the richest and its stiff solvers being possibly more efficient. FreeMat is clearly significantly weaker than the other packages in that it does ...
... and Scilab have state-of-the-art variable-order, variable-timestep methods for both non-stiff and stiff ODEs available, with Matlab’s implementation being the richest and its stiff solvers being possibly more efficient. FreeMat is clearly significantly weaker than the other packages in that it does ...
Overview of Computer Science - CSE User Home Pages
... at the University of Minnesota-Twin Cities. More information about that class and these notes are in the opening chapter. The original version of these notes was used in the Spring 2014 offering of that class. This current version, Version 1.2, is a small update, containing some minor clarifications ...
... at the University of Minnesota-Twin Cities. More information about that class and these notes are in the opening chapter. The original version of these notes was used in the Spring 2014 offering of that class. This current version, Version 1.2, is a small update, containing some minor clarifications ...
Multiplying Monomials Multiply a Polynomial by a Monomial Multiply
... Multiply Any Two Polynomials Multiplying Polynomials To multiply two polynomials, multiply each term of one polynomial by each term of the other polynomial, and then combine like terms. Example 6: (Multiplying polynomials) Multiply the following polynomials. a) ...
... Multiply Any Two Polynomials Multiplying Polynomials To multiply two polynomials, multiply each term of one polynomial by each term of the other polynomial, and then combine like terms. Example 6: (Multiplying polynomials) Multiply the following polynomials. a) ...
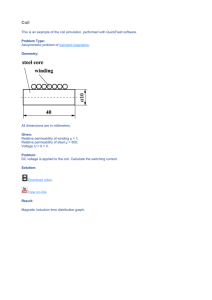
HMagn4: Coil with ferromagnetic core
... Electrical conductivity of steel σ= 10000000 Sm/m. Electrical conductivity of aluminum σ=37000000 Sm/m. Coils are wound by insulated wire, so cross-section conductivity in coils σ= 0 Sm/m. Boundary conditions Along the horizontal symmetry axis (line ab) Bn =0. Equation B=rot A in cylindrical coordin ...
... Electrical conductivity of steel σ= 10000000 Sm/m. Electrical conductivity of aluminum σ=37000000 Sm/m. Coils are wound by insulated wire, so cross-section conductivity in coils σ= 0 Sm/m. Boundary conditions Along the horizontal symmetry axis (line ab) Bn =0. Equation B=rot A in cylindrical coordin ...
A KRYLOV METHOD FOR THE DELAY EIGENVALUE PROBLEM 1
... Chapter 2] for more methods. The DEP belongs to a class of problems called nonlinear eigenvalue problems. There are several general purpose methods for nonlinear eigenvalue problems; see [Ruh73, MV04]. There are, for instance, the Newton-type methods [Sch08, Neu85] and a nonlinear version of Jacobi- ...
... Chapter 2] for more methods. The DEP belongs to a class of problems called nonlinear eigenvalue problems. There are several general purpose methods for nonlinear eigenvalue problems; see [Ruh73, MV04]. There are, for instance, the Newton-type methods [Sch08, Neu85] and a nonlinear version of Jacobi- ...
A GENERAL THEOREM ON ERROR ESTIMATES WITH
... 1. Introduction. This paper has two main aims. First, we develop a general theory of error analysis for smooth nonlinear programming problems in Banach spaces, which is applicable in particular to optimal control problems. Second, as main application, we prove new error estimates for optimal control ...
... 1. Introduction. This paper has two main aims. First, we develop a general theory of error analysis for smooth nonlinear programming problems in Banach spaces, which is applicable in particular to optimal control problems. Second, as main application, we prove new error estimates for optimal control ...
TROUBLESHOOTING
... technicians and clinical engineers. Historically, troubleshooting instruments has been a self-taught art form slowly mastered by relatively few individuals. This document is intended to be a brief guide to a basic, uniform troubleshooting technique which has been successfully used with medical instr ...
... technicians and clinical engineers. Historically, troubleshooting instruments has been a self-taught art form slowly mastered by relatively few individuals. This document is intended to be a brief guide to a basic, uniform troubleshooting technique which has been successfully used with medical instr ...
Robust Ray Intersection with Interval Arithmetic
... root-isolation algorithms conform to this paradigm, whether they use Descarte’s Rule, Lipschitz conditions, or interval arithmetic to test for root inclusion. The algorithm above is slightly different than the one described by Moore which assumes that root refinement will also be performed by an int ...
... root-isolation algorithms conform to this paradigm, whether they use Descarte’s Rule, Lipschitz conditions, or interval arithmetic to test for root inclusion. The algorithm above is slightly different than the one described by Moore which assumes that root refinement will also be performed by an int ...
MATH 176 Page 1 of 3 Curriculum Committee Approval: 4-29
... Utilize sequences and series equations to solve theoretical and applied problems from various disciplines such as science, business and engineering. Select and apply appropriate technology including but not limited to computer programs and graphing utilities to model, analyze and interpret a collect ...
... Utilize sequences and series equations to solve theoretical and applied problems from various disciplines such as science, business and engineering. Select and apply appropriate technology including but not limited to computer programs and graphing utilities to model, analyze and interpret a collect ...
Math 176 - Cuyamaca College
... 12) Utilize sequences and series equations to solve theoretical and applied problems from various disciplines such as science, business and engineering. 13) Select and apply appropriate technology including but not limited to computer programs and graphing utilities to model, analyze and interpret a ...
... 12) Utilize sequences and series equations to solve theoretical and applied problems from various disciplines such as science, business and engineering. 13) Select and apply appropriate technology including but not limited to computer programs and graphing utilities to model, analyze and interpret a ...
MATH 176 Page 1 of 3 Curriculum Committee Approval: 12-2
... Utilize sequences and series equations to solve theoretical and applied problems from various disciplines such as science, business and engineering. Select and apply appropriate technology including but not limited to computer programs and graphing utilities to model, analyze and interpret a collect ...
... Utilize sequences and series equations to solve theoretical and applied problems from various disciplines such as science, business and engineering. Select and apply appropriate technology including but not limited to computer programs and graphing utilities to model, analyze and interpret a collect ...
Accelerating Correctly Rounded Floating
... In Section 5.1, we show that, under some conditions on y, that could be checked at compile-time, we can return a correctly rounded quotient using one multiplication and one fused-mac. In Section 5.2, we show that, if a larger internal precision than the target precision is available (one more bit su ...
... In Section 5.1, we show that, under some conditions on y, that could be checked at compile-time, we can return a correctly rounded quotient using one multiplication and one fused-mac. In Section 5.2, we show that, if a larger internal precision than the target precision is available (one more bit su ...
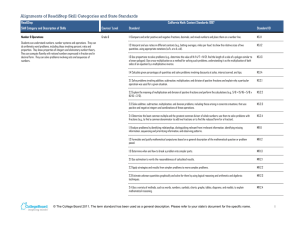
Alignments of ReadiStep Skill Categories and State Standards
... Students can understand numbers, number systems and operations. They can do arithmetic word problems, including those involving percent, ratio and proportion. They know properties of integers and elementary number theory. They can compute fluently with rational numbers expressed in fraction and in d ...
... Students can understand numbers, number systems and operations. They can do arithmetic word problems, including those involving percent, ratio and proportion. They know properties of integers and elementary number theory. They can compute fluently with rational numbers expressed in fraction and in d ...
1.10 Euler`s Method
... the points x1 , x2 , . . . , where xn+1 = xn + h, n = 0, 1, . . . , and h is a real number. We emphasize that numerical methods do not generate a formula for the solution to the differential equation. Rather they generate a sequence of approximations to the value of the solution at specified points. ...
... the points x1 , x2 , . . . , where xn+1 = xn + h, n = 0, 1, . . . , and h is a real number. We emphasize that numerical methods do not generate a formula for the solution to the differential equation. Rather they generate a sequence of approximations to the value of the solution at specified points. ...
Lecture 3 - United International College
... • Definition: We say that a numerical algorithm to solve some problem is convergent if the numerical solution generated by the algorithm approaches the actual solution as the number of steps in the algorithm increases. • Definition: Stability of an algorithm refers to the ability of a numerical algo ...
... • Definition: We say that a numerical algorithm to solve some problem is convergent if the numerical solution generated by the algorithm approaches the actual solution as the number of steps in the algorithm increases. • Definition: Stability of an algorithm refers to the ability of a numerical algo ...
Unconstrained Nonlinear Optimization, Constrained Nonlinear
... Number of states grows exponentially in n (assuming some fixed number of discretization levels per coordinate) In practice n ...
... Number of states grows exponentially in n (assuming some fixed number of discretization levels per coordinate) In practice n ...
16. Algorithm stability
... • we subtract two numbers that are almost equal • one or both numbers are subject to error Algorithm stability ...
... • we subtract two numbers that are almost equal • one or both numbers are subject to error Algorithm stability ...
Multiobjective Optimal VAR Dispatch Using Strength Pareto
... the optimal one. Moreover, calculation of the sensitivity factors is a time consuming process and inefficient for largescale system applications. The third approach utilizes the heuristic methods to search for the optimal solution in the problem space [3-6]. It has been theoretically proved that the ...
... the optimal one. Moreover, calculation of the sensitivity factors is a time consuming process and inefficient for largescale system applications. The third approach utilizes the heuristic methods to search for the optimal solution in the problem space [3-6]. It has been theoretically proved that the ...
Case-Based Reasoning as a Tool to Improve the Usability of
... in reasonable detail, we might need, say, 10 points in each dimension, giving 710 records altogether. ł The solution set could be very large and hence unhelpful in decision making. ł Equality constraints might mean there are no solutions at all to the SQL query. Some of these problems can be approac ...
... in reasonable detail, we might need, say, 10 points in each dimension, giving 710 records altogether. ł The solution set could be very large and hence unhelpful in decision making. ł Equality constraints might mean there are no solutions at all to the SQL query. Some of these problems can be approac ...
Rice Workshop LV-Maraton 20081218 - CMS
... connections and needed repairs made before power was restored to system – Subsequently the connections were systematically rechecked manually and with temperature sensors, plus the individual current outputs were analyzed for the system looking for resistive channels. ...
... connections and needed repairs made before power was restored to system – Subsequently the connections were systematically rechecked manually and with temperature sensors, plus the individual current outputs were analyzed for the system looking for resistive channels. ...
Chapter 1 Problems
... The repetitive exchange of energy from the magnetic field of an inductor to an electric charge on a capacitor in a resonant circuit is known as: a. the flywheel effect b. Barkhausen criteria c. the piezoelectric effect d. frequency synthesis ...
... The repetitive exchange of energy from the magnetic field of an inductor to an electric charge on a capacitor in a resonant circuit is known as: a. the flywheel effect b. Barkhausen criteria c. the piezoelectric effect d. frequency synthesis ...
ON THE NUMERICAL SOLUTION
... The number of chemical species involved in a modern air pollution model sometimes reaches 200, or even more, which results in a huge system of partial differential equations. The analytical solution of such a problem is obviously impossible to find. Hence we have to treat it numerically. We note tha ...
... The number of chemical species involved in a modern air pollution model sometimes reaches 200, or even more, which results in a huge system of partial differential equations. The analytical solution of such a problem is obviously impossible to find. Hence we have to treat it numerically. We note tha ...
A new approach to analysis of free beam vibrations
... The initial-boundary problem for the linear theory of elasticity is considered. Based on the method of integrodifferential relations a new dynamical variational principle in which displacement, stress, and momentum functions are varied is proposed and discussed [1–5]. To minimize the nonnegative fun ...
... The initial-boundary problem for the linear theory of elasticity is considered. Based on the method of integrodifferential relations a new dynamical variational principle in which displacement, stress, and momentum functions are varied is proposed and discussed [1–5]. To minimize the nonnegative fun ...
P versus NP problem
The P versus NP problem is a major unsolved problem in computer science. Informally, it asks whether every problem whose solution can be quickly verified by a computer can also be quickly solved by a computer. It was essentially first mentioned in a 1956 letter written by Kurt Gödel to John von Neumann. Gödel asked whether a certain NP-complete problem could be solved in quadratic or linear time. The precise statement of the P versus NP problem was introduced in 1971 by Stephen Cook in his seminal paper ""The complexity of theorem proving procedures"" and is considered by many to be the most important open problem in the field. It is one of the seven Millennium Prize Problems selected by the Clay Mathematics Institute to carry a US$1,000,000 prize for the first correct solution.The informal term quickly, used above, means the existence of an algorithm for the task that runs in polynomial time. The general class of questions for which some algorithm can provide an answer in polynomial time is called ""class P"" or just ""P"". For some questions, there is no known way to find an answer quickly, but if one is provided with information showing what the answer is, it is possible to verify the answer quickly. The class of questions for which an answer can be verified in polynomial time is called NP.Consider the subset sum problem, an example of a problem that is easy to verify, but whose answer may be difficult to compute. Given a set of integers, does some nonempty subset of them sum to 0? For instance, does a subset of the set {−2, −3, 15, 14, 7, −10} add up to 0? The answer ""yes, because the subset {−2, −3, −10, 15} adds up to zero"" can be quickly verified with three additions. However, there is no known algorithm to find such a subset in polynomial time (there is one, however, in exponential time, which consists of 2n-n-1 tries), but such an algorithm exists if P = NP; hence this problem is in NP (quickly checkable) but not necessarily in P (quickly solvable).An answer to the P = NP question would determine whether problems that can be verified in polynomial time, like the subset-sum problem, can also be solved in polynomial time. If it turned out that P ≠ NP, it would mean that there are problems in NP (such as NP-complete problems) that are harder to compute than to verify: they could not be solved in polynomial time, but the answer could be verified in polynomial time.Aside from being an important problem in computational theory, a proof either way would have profound implications for mathematics, cryptography, algorithm research, artificial intelligence, game theory, multimedia processing, philosophy, economics and many other fields.