CHAPTER 15: General Relativity
... Josef Lense and Hans Thirring proposed in 1918 that a rotating body’s gravitational force can literally drag spacetime around with it as the body rotates. This effect, sometimes called the Lense-Thirring effect, is referred to as frame dragging. All celestial bodies that rotate can modify the spacet ...
... Josef Lense and Hans Thirring proposed in 1918 that a rotating body’s gravitational force can literally drag spacetime around with it as the body rotates. This effect, sometimes called the Lense-Thirring effect, is referred to as frame dragging. All celestial bodies that rotate can modify the spacet ...
Gravity and mass
... speeds past the planet with increased speed, if not, then it will crash into the planet. • The slingshot method was used by Apollo 13 when it used the field strength of the Moon to accelerate back towards the Earth. ...
... speeds past the planet with increased speed, if not, then it will crash into the planet. • The slingshot method was used by Apollo 13 when it used the field strength of the Moon to accelerate back towards the Earth. ...
Gravity - barransclass
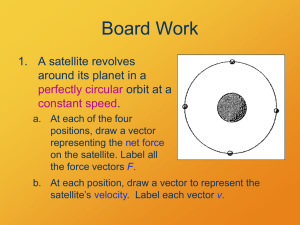
... positions, draw a vector representing the net force on the satellite. Label all the force vectors F. b. At each position, draw a vector to represent the satellite’s velocity. Label each vector v. ...
... positions, draw a vector representing the net force on the satellite. Label all the force vectors F. b. At each position, draw a vector to represent the satellite’s velocity. Label each vector v. ...
Gravity - My CCSD
... Most objects in space move according to strict physical laws. The way in which the Earth moves, for example, causes seasons and even day and night. ...
... Most objects in space move according to strict physical laws. The way in which the Earth moves, for example, causes seasons and even day and night. ...
Newtons Laws of Motion - Instructor Outline
... speed and mass of the cars is remaining constant in accordance with the impulsemomentum formulation of Newton’s Second Law J=FΔt=Δp . The constant-mass formulation (F=ma) is then introduced. The fact that all objects fall with the same acceleration due to gravity is explained using Newton’s Second L ...
... speed and mass of the cars is remaining constant in accordance with the impulsemomentum formulation of Newton’s Second Law J=FΔt=Δp . The constant-mass formulation (F=ma) is then introduced. The fact that all objects fall with the same acceleration due to gravity is explained using Newton’s Second L ...
amanda`sGravity and Free Fall
... in two dimensions under the influence of gravity. The downward acceleration due to gravity does not change a projectile’s horizontal motion, and that does not affect the downward motion. ...
... in two dimensions under the influence of gravity. The downward acceleration due to gravity does not change a projectile’s horizontal motion, and that does not affect the downward motion. ...
Gravity PP
... – Maintained - constant force exerted on object – Force (perpendicular to the velocity as the direction of the velocity changes) – Force - directed towards the center of the circle ...
... – Maintained - constant force exerted on object – Force (perpendicular to the velocity as the direction of the velocity changes) – Force - directed towards the center of the circle ...
The revolution starts with You!!!
... • Near the surface of the Earth, the gravitational field strength is 9.8 N/kg or 9.8 m/s2. • At the surface of Earth, the gravitational force on an object it the object’s weight. ...
... • Near the surface of the Earth, the gravitational field strength is 9.8 N/kg or 9.8 m/s2. • At the surface of Earth, the gravitational force on an object it the object’s weight. ...
File
... In fact, it feels exactly like gravity The essence of General Relativity is the recognition that “gravitational force” is an artifact of doing physics in a particular reference frame! ...
... In fact, it feels exactly like gravity The essence of General Relativity is the recognition that “gravitational force” is an artifact of doing physics in a particular reference frame! ...
Newton`s Law of Universal
... The acceleration due to gravity on Earth is accepted at 9.8 m/s2 toward the center of the Earth. This can be derived using Newton’s Law of Gravitation. Apply Newton’s 2nd Law ...
... The acceleration due to gravity on Earth is accepted at 9.8 m/s2 toward the center of the Earth. This can be derived using Newton’s Law of Gravitation. Apply Newton’s 2nd Law ...
HP Unit GTOR - student handout
... 74 ft. tall tower was but two parts in a thousand trillion. The gravitational redshift detected came within ten percent of the computed value. Also, a team at Princeton University measured the redshift of sunlight. Though small, given the Sun's mass and density, the redshift matched Einstein's predi ...
... 74 ft. tall tower was but two parts in a thousand trillion. The gravitational redshift detected came within ten percent of the computed value. Also, a team at Princeton University measured the redshift of sunlight. Though small, given the Sun's mass and density, the redshift matched Einstein's predi ...
PHYS16 - Lecture 26
... of attraction Proof: apples, moon, celestial bodies fall towards each other between all objects Proof: 130 years later by Cavendish, but at the time seemed nice not to distinguish across empty space, between an apple and a planet proportional to m Proof: None at the time. Galileo said there was no d ...
... of attraction Proof: apples, moon, celestial bodies fall towards each other between all objects Proof: 130 years later by Cavendish, but at the time seemed nice not to distinguish across empty space, between an apple and a planet proportional to m Proof: None at the time. Galileo said there was no d ...