Wizard Test Maker
... 1. Two planets have the same size but different masses and no atmospheres. Which of the following would be the same for objects of equal mass on the surfaces of the two planets? I. The rate at which each would fall freely. II. The amount of force needed to cause a given horizontal acceleration. III. ...
... 1. Two planets have the same size but different masses and no atmospheres. Which of the following would be the same for objects of equal mass on the surfaces of the two planets? I. The rate at which each would fall freely. II. The amount of force needed to cause a given horizontal acceleration. III. ...
Gravitation and Grav fields
... 3. Two spheres lie along a straight line. The sphere on the left has m = 1000-kg, and the right on the right has m = 100-kg. The distance between their centers is 5-m. Point A lies between the spheres at 2.5-m from the center of ...
... 3. Two spheres lie along a straight line. The sphere on the left has m = 1000-kg, and the right on the right has m = 100-kg. The distance between their centers is 5-m. Point A lies between the spheres at 2.5-m from the center of ...
Universal Gravitation
... in orbit if it is free falling? Given a fast enough initial velocity and misses the Earth because it is curved ...
... in orbit if it is free falling? Given a fast enough initial velocity and misses the Earth because it is curved ...
Chapter 13: universal gravitation
... Newton’s law of universal gravitation Newton’s law of universal gravitation: every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between ...
... Newton’s law of universal gravitation Newton’s law of universal gravitation: every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between ...
Equivalence Principle Acceleration = Gravity Inertial Mass
... – An extension of “special theory of relativity”, which did not include gravity but dealt only with “inertial motion” (i.e., motion with constant velocity) – How do we deal with gravitational force? ...
... – An extension of “special theory of relativity”, which did not include gravity but dealt only with “inertial motion” (i.e., motion with constant velocity) – How do we deal with gravitational force? ...
Unit Review D – General Relativity
... d. An occupant of a rotating room places a ball on the floor and releases it from her hand. By rotating... there is an inward acceleration (centripetal acceleration) which creates the equivalent of a gravitational field in an “outward” direction. The released ball will “fall” outward… this will be m ...
... d. An occupant of a rotating room places a ball on the floor and releases it from her hand. By rotating... there is an inward acceleration (centripetal acceleration) which creates the equivalent of a gravitational field in an “outward” direction. The released ball will “fall” outward… this will be m ...
Announcements
... l But, time also passes more slowly for objects in gravitational fields l Suppose I do an experiment where I take two atomic clocks (incredibly precise), synchronize them and keep one of the ground while the other flies in a commerical jet around the world l Do the clocks agree when they’re br ...
... l But, time also passes more slowly for objects in gravitational fields l Suppose I do an experiment where I take two atomic clocks (incredibly precise), synchronize them and keep one of the ground while the other flies in a commerical jet around the world l Do the clocks agree when they’re br ...
Solids
... characteristic of the vibrational rate of electrons within the atom. • Every atom is therefore a “clock,” and a slowing down of atomic vibration indicates the slowing down of such clocks. • An atom on the sun should emit light of a lower frequency (slower vibration) than light emitted by the same el ...
... characteristic of the vibrational rate of electrons within the atom. • Every atom is therefore a “clock,” and a slowing down of atomic vibration indicates the slowing down of such clocks. • An atom on the sun should emit light of a lower frequency (slower vibration) than light emitted by the same el ...
PowerPoint - UCSD Department of Physics
... The essence of General Relativity: There is no gravitation: in locally inertial coordinate systems, which the Equivalence Principle guarantees are always there, the effects of gravitation are absent! The Einstein Field equations have as there solutions global coordinate systems which cover big patc ...
... The essence of General Relativity: There is no gravitation: in locally inertial coordinate systems, which the Equivalence Principle guarantees are always there, the effects of gravitation are absent! The Einstein Field equations have as there solutions global coordinate systems which cover big patc ...
Solids
... characteristic of the vibrational rate of electrons within the atom. • Every atom is therefore a “clock,” and a slowing down of atomic vibration indicates the slowing down of such clocks. • An atom on the sun should emit light of a lower frequency (slower vibration) than light emitted by the same el ...
... characteristic of the vibrational rate of electrons within the atom. • Every atom is therefore a “clock,” and a slowing down of atomic vibration indicates the slowing down of such clocks. • An atom on the sun should emit light of a lower frequency (slower vibration) than light emitted by the same el ...
9.2.3 Gravity in Space
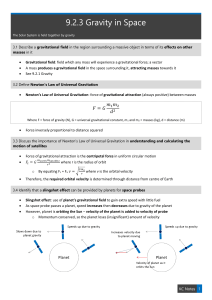
... Various variations in gravitational acceleration is due to: o Altitude: Further away, less gravity (mountains, valleys, satellites) o Local crust density: more dense, more gravity o Oblation/shape: greater radius at equator than poles The spin of the Earth generates a centrifuge effect, less gravity ...
... Various variations in gravitational acceleration is due to: o Altitude: Further away, less gravity (mountains, valleys, satellites) o Local crust density: more dense, more gravity o Oblation/shape: greater radius at equator than poles The spin of the Earth generates a centrifuge effect, less gravity ...
Chapter-08
... Newton’s Law of Gravitation Every body in the Universe attracts every other body in the Universe. ...
... Newton’s Law of Gravitation Every body in the Universe attracts every other body in the Universe. ...