PHY101 - National Open University of Nigeria
... is said to be at rest when it does not change its position with time. It is said to be in motion when it changes its position with time. But to know if the position of an object changes with time or not, we require a point absolutely fixed in space to be known. Such a fixed or stationary point is no ...
... is said to be at rest when it does not change its position with time. It is said to be in motion when it changes its position with time. But to know if the position of an object changes with time or not, we require a point absolutely fixed in space to be known. Such a fixed or stationary point is no ...
momentum
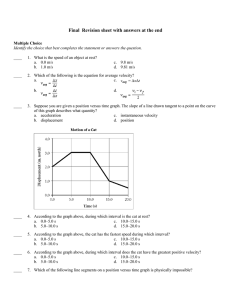
... One object might change momentum, while another object changes momentum in an opposite manner, picking up the momentum that was lost by the first. ...
... One object might change momentum, while another object changes momentum in an opposite manner, picking up the momentum that was lost by the first. ...
Document
... also causes seat belts to lock into place. The illustration shows how one type of shoulder harness operates. When the car suddenly slows down, inertia causes the large mass under the seat to continue moving, which activates the lock on the safety belt. ...
... also causes seat belts to lock into place. The illustration shows how one type of shoulder harness operates. When the car suddenly slows down, inertia causes the large mass under the seat to continue moving, which activates the lock on the safety belt. ...
physics workbook
... experiencing as a multiple of the acceleration due to gravity. This is also referred to as the g-force (even though we are not actually measuring force) or simply how many “g’s.” This acceleration is usually the result of the ride’s seat pushing on you to hold you up or change the direction that you ...
... experiencing as a multiple of the acceleration due to gravity. This is also referred to as the g-force (even though we are not actually measuring force) or simply how many “g’s.” This acceleration is usually the result of the ride’s seat pushing on you to hold you up or change the direction that you ...
Preview Sample 2
... Answer: C Diff: 2 Topic: Newton's First Law 21) If your automobile runs out of fuel while driving, the engine stops. You don't come to an abrupt stop due to A) inertia. B) gravity. C) resistance. D) the principle of continuation. Answer: A Diff: 2 Topic: Newton's First Law 22) When a rocket ship gai ...
... Answer: C Diff: 2 Topic: Newton's First Law 21) If your automobile runs out of fuel while driving, the engine stops. You don't come to an abrupt stop due to A) inertia. B) gravity. C) resistance. D) the principle of continuation. Answer: A Diff: 2 Topic: Newton's First Law 22) When a rocket ship gai ...
- Lake Fenton Community School District
... 1. In which of the following situations does the car undergo acceleration? (There may be more than one correct answer to circle.) A) ...
... 1. In which of the following situations does the car undergo acceleration? (There may be more than one correct answer to circle.) A) ...
GET WORKSHEETS FROM MY ASSIGNMENTS PAGE Mrs
... How did changing the mass affect acceleration? Increasing the mass of an object causes the acceleration to slow down. For example, with one book the speed was the fastest but with four books the speed was the slowest. ...
... How did changing the mass affect acceleration? Increasing the mass of an object causes the acceleration to slow down. For example, with one book the speed was the fastest but with four books the speed was the slowest. ...