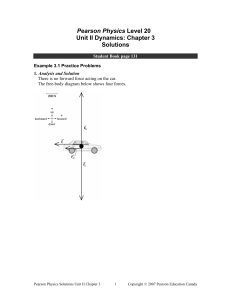
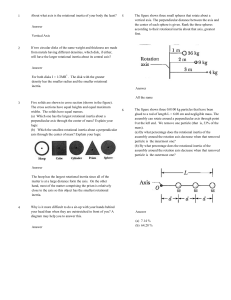
Chapter 2 and 3 - Fayetteville State University
... A) TRUE B) FALSE Answer: B Feedback A: Incorrect. See section 3.4. Feedback B: Correct. Potential energy is energy of location in space. Kinetic energy is energy of motion and depends on speed. Question 3.09 A ball is thrown straight up into the air (with no air resistance). Where is the ball’s pot ...
... A) TRUE B) FALSE Answer: B Feedback A: Incorrect. See section 3.4. Feedback B: Correct. Potential energy is energy of location in space. Kinetic energy is energy of motion and depends on speed. Question 3.09 A ball is thrown straight up into the air (with no air resistance). Where is the ball’s pot ...
momentum
... 1. A high-speed bus and an innocent bug have a head-on collision. The sudden change of momentum for the bug spatters it all over the windshield. Is the change in momentum of the bus greater, less, or the same as the change in momentum experienced by the unfortunate bug? 2. The Starship Enterprise is ...
... 1. A high-speed bus and an innocent bug have a head-on collision. The sudden change of momentum for the bug spatters it all over the windshield. Is the change in momentum of the bus greater, less, or the same as the change in momentum experienced by the unfortunate bug? 2. The Starship Enterprise is ...
Physical Response to Collision between Deformable Objects
... Table 2.1: Comparative analysis of the different methods ............................................... 30 Table 4.1: Simulation Parameters .................................................................................... 57 Table 4.2: Computation time ........................................... ...
... Table 2.1: Comparative analysis of the different methods ............................................... 30 Table 4.1: Simulation Parameters .................................................................................... 57 Table 4.2: Computation time ........................................... ...
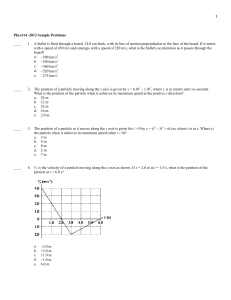
AP Physics C - Mechanics Spring and a Block
... Next attach just one mass to the two spring combination. Let's calculate the effective spring constant of two springs in parallel, each with spring constant = k', by using a free body diagram. y is the distance each spring is stretched. ...
... Next attach just one mass to the two spring combination. Let's calculate the effective spring constant of two springs in parallel, each with spring constant = k', by using a free body diagram. y is the distance each spring is stretched. ...
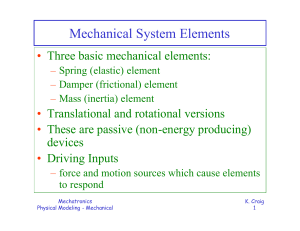
Everyday Forces and Laws of Motion
... also causes seat belts to lock into place. The illustration shows how one type of shoulder harness operates. When the car suddenly slows down, inertia causes the large mass under the seat to continue moving, which activates the lock on the safety belt. ...
... also causes seat belts to lock into place. The illustration shows how one type of shoulder harness operates. When the car suddenly slows down, inertia causes the large mass under the seat to continue moving, which activates the lock on the safety belt. ...
Teaching Aid: Circular Motion PowerPoint
... The magnitude of the velocity of the body is constant but the direction is constantly changing, therefore, the body is accelerating At any instant, the direction of the velocity is a tangent to the circular path ...
... The magnitude of the velocity of the body is constant but the direction is constantly changing, therefore, the body is accelerating At any instant, the direction of the velocity is a tangent to the circular path ...
ClassicalMechanics_1..
... Complications: Circular Motion The length of the velocity vector remains constant, and so the acceleration is changing its direction. For an object traveling with speed v to move in a circle of radius r the centripetal acceleration must be ...
... Complications: Circular Motion The length of the velocity vector remains constant, and so the acceleration is changing its direction. For an object traveling with speed v to move in a circle of radius r the centripetal acceleration must be ...
ClassicalMechanics_1..
... Complications: Circular Motion The length of the velocity vector remains constant, and so the acceleration is changing its direction. For an object traveling with speed v to move in a circle of radius r the centripetal acceleration must be ...
... Complications: Circular Motion The length of the velocity vector remains constant, and so the acceleration is changing its direction. For an object traveling with speed v to move in a circle of radius r the centripetal acceleration must be ...
CHAPTER 8: Rotational Motion Answers to Questions
... 16. In order to do a somersault, the diver needs some initial angular momentum when she leaves the diving board, because angular momentum will be conserved during the free-fall motion of the dive. She cannot exert a torque on herself in isolation, and so if there is no angular momentum initially, th ...
... 16. In order to do a somersault, the diver needs some initial angular momentum when she leaves the diving board, because angular momentum will be conserved during the free-fall motion of the dive. She cannot exert a torque on herself in isolation, and so if there is no angular momentum initially, th ...
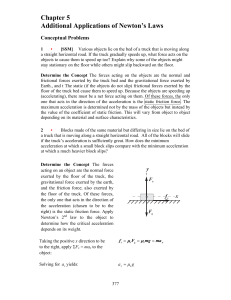
CH. 2 forces sample test
... ____ 33. According to Newton’s second law of motion, weight depends on an object’s mass and the net force acting on the object._________________________ ____ 34. Friction depends on the types of surfaces involved and how hard the surfaces push together. _________________________ ____ 35. Mass and ai ...
... ____ 33. According to Newton’s second law of motion, weight depends on an object’s mass and the net force acting on the object._________________________ ____ 34. Friction depends on the types of surfaces involved and how hard the surfaces push together. _________________________ ____ 35. Mass and ai ...