Lecture Notes on Classical Mechanics for Physics 106ab Sunil
... Thornton, and Goldstein, but cover the material in a different order than any one of these texts and deviate from them widely in some places and less so in others. The reader will no doubt ask the question I asked myself many times while writing these notes: why bother? There are a large number of m ...
... Thornton, and Goldstein, but cover the material in a different order than any one of these texts and deviate from them widely in some places and less so in others. The reader will no doubt ask the question I asked myself many times while writing these notes: why bother? There are a large number of m ...
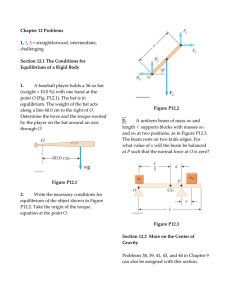
Chapter 12 Problems
... The beam rests on two knife edges. For what value of x will the beam be balanced at P such that the normal force at O is zero? ...
... The beam rests on two knife edges. For what value of x will the beam be balanced at P such that the normal force at O is zero? ...
Use example problem 9-3 to solve practice problems 9-3
... consisting of many particles. The gas particles are constantly colliding with each otter and the walls of the flask. Their momenta are changing with every collision. In these collisions, the momentum gained by one particle is equal to the momentum lost by the other particle. Thus, the total momentum ...
... consisting of many particles. The gas particles are constantly colliding with each otter and the walls of the flask. Their momenta are changing with every collision. In these collisions, the momentum gained by one particle is equal to the momentum lost by the other particle. Thus, the total momentum ...
Ex. 37 PowerPoint
... An ideal system is one which has no friction. Frictionless systems do not exist in nature. However, since they simplify the solving of physics problems, it is often convenient to assume a system is frictionless. Once the problem is solved without friction, the effects caused by friction are added to ...
... An ideal system is one which has no friction. Frictionless systems do not exist in nature. However, since they simplify the solving of physics problems, it is often convenient to assume a system is frictionless. Once the problem is solved without friction, the effects caused by friction are added to ...
Forces
... Suppose you are pushing on a loaded shopping cart. Which of the following is true? A) If action force always equals reaction force, you cannot move the cart because the cart pushes you backward just as hard as you push forward on the cart. B) You push the cart slightly harder than the cart pushes yo ...
... Suppose you are pushing on a loaded shopping cart. Which of the following is true? A) If action force always equals reaction force, you cannot move the cart because the cart pushes you backward just as hard as you push forward on the cart. B) You push the cart slightly harder than the cart pushes yo ...
Section 9.6: Work done on a many
... • What is the box's speed at t = 5.0 s if it starts from rest? Ignore any friction between the box and the floor. • What is the box's speed at t = 5.0 s if at t = 0 it has a velocity of 3.5 m/s in the direction opposite the direction of Fslide? Ignore any friction between the box and the floor. © 20 ...
... • What is the box's speed at t = 5.0 s if it starts from rest? Ignore any friction between the box and the floor. • What is the box's speed at t = 5.0 s if at t = 0 it has a velocity of 3.5 m/s in the direction opposite the direction of Fslide? Ignore any friction between the box and the floor. © 20 ...
No Slide Title
... also causes seat belts to lock into place. The illustration shows how one type of shoulder harness operates. When the car suddenly slows down, inertia causes the large mass under the seat to continue moving, which activates the lock on the safety belt. ...
... also causes seat belts to lock into place. The illustration shows how one type of shoulder harness operates. When the car suddenly slows down, inertia causes the large mass under the seat to continue moving, which activates the lock on the safety belt. ...
Ch 10 Solutions Glencoe 2013
... 36. A satellite orbits Earth in a circular orbit. Does Earth’s gravity do work on the satellite? Explain. SOLUTION: No, the force of gravity is directed toward Earth and is perpendicular to the direction of displacement of the satellite. 37. An object slides at constant speed on a frictionless sur ...
... 36. A satellite orbits Earth in a circular orbit. Does Earth’s gravity do work on the satellite? Explain. SOLUTION: No, the force of gravity is directed toward Earth and is perpendicular to the direction of displacement of the satellite. 37. An object slides at constant speed on a frictionless sur ...
Physics 1st Semester Exam Answer Section
... ____ 30. A girl pulls on a 10-kg wagon with a constant force of 20 N. What is the wagon's acceleration? a. 0.5 m/s2 b. 2 m/s2 c. 10 m/s2 d. 20 m/s2 e. 200 m/s2 ____ 31. A box is dragged without acceleration in a straight-line path across a level surface by a force of 13 N. What is the frictional fo ...
... ____ 30. A girl pulls on a 10-kg wagon with a constant force of 20 N. What is the wagon's acceleration? a. 0.5 m/s2 b. 2 m/s2 c. 10 m/s2 d. 20 m/s2 e. 200 m/s2 ____ 31. A box is dragged without acceleration in a straight-line path across a level surface by a force of 13 N. What is the frictional fo ...
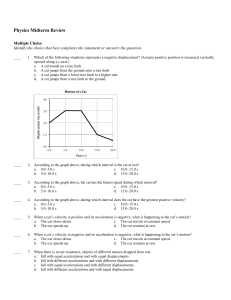
Physics Midterm Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best
... 53. Why does it require much less force to accelerate a low-mass object than it does to accelerate a high-mass object the same amount? 54. How do mass and weight vary with altitude? 55. Distinguish between mass and weight. 56. When a car is moving, what happens to the velocity and acceleration of th ...
... 53. Why does it require much less force to accelerate a low-mass object than it does to accelerate a high-mass object the same amount? 54. How do mass and weight vary with altitude? 55. Distinguish between mass and weight. 56. When a car is moving, what happens to the velocity and acceleration of th ...
Linear Momentum and Collisions
... tum, and electric charge. We will eventually discuss all of these because the conser vation laws are among the most important in all of science. In this chapter, we discuss linear momentum and its conservation. We then make use of the laws of conservation of linear momentum and of energy to analyze ...
... tum, and electric charge. We will eventually discuss all of these because the conser vation laws are among the most important in all of science. In this chapter, we discuss linear momentum and its conservation. We then make use of the laws of conservation of linear momentum and of energy to analyze ...
A x - Description
... dissipation (no force displacement) • Kinetic friction does cause irreversible change, including causing microscopic damage to the surfaces. • The force of kinetic friction is not an elastic force and so causes energy dissipation. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... dissipation (no force displacement) • Kinetic friction does cause irreversible change, including causing microscopic damage to the surfaces. • The force of kinetic friction is not an elastic force and so causes energy dissipation. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
LCP1 INTUITIVE PHYSICS
... a. you feel yourself being pushed back into your seat. b. you feel yourself being pushed forward against your seatbelt. (Is there an unambiguous answer for a. and b.? Discuss briefly.) c. you are sitting freely without feeling a push or pull. d. you feel a force to your right, toward the door. ...
... a. you feel yourself being pushed back into your seat. b. you feel yourself being pushed forward against your seatbelt. (Is there an unambiguous answer for a. and b.? Discuss briefly.) c. you are sitting freely without feeling a push or pull. d. you feel a force to your right, toward the door. ...