Is Genetic Drift a Force? - Philsci-Archive
... some components of evolutionary theory really can be described as forces. The force interpretation’s detractors hold that such language is at best merely suggestive, if not entirely devoid of value.4 If true, the force interpretation makes evolution, in the apt terminology deployed by Maudlin, a “qu ...
... some components of evolutionary theory really can be described as forces. The force interpretation’s detractors hold that such language is at best merely suggestive, if not entirely devoid of value.4 If true, the force interpretation makes evolution, in the apt terminology deployed by Maudlin, a “qu ...
MP sols
... Review the workenergy theorem and apply it to a simple problem. If you push a particle of mass M in the direction in which it is already moving, you expect the particle's speed to increase. If you push with a constant force F , then the particle will accelerate with acceleration a = F /M (from Ne ...
... Review the workenergy theorem and apply it to a simple problem. If you push a particle of mass M in the direction in which it is already moving, you expect the particle's speed to increase. If you push with a constant force F , then the particle will accelerate with acceleration a = F /M (from Ne ...
Teacher: Christopher Reed Year: 2013
... translational motion or simple harmonic What are the motion of objects. Relate torque and force rotational inertia to explain rotational characteristics motion. of an object 3.2.P.B.6-PATTERNS SCALE whose speed MODELS CONSTANCY/CHANGE or direction is Use Newton's laws of motion and changing? gravit ...
... translational motion or simple harmonic What are the motion of objects. Relate torque and force rotational inertia to explain rotational characteristics motion. of an object 3.2.P.B.6-PATTERNS SCALE whose speed MODELS CONSTANCY/CHANGE or direction is Use Newton's laws of motion and changing? gravit ...
P2 02 Forces and Motion
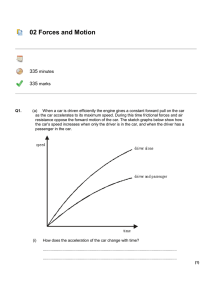
... as the car accelerates to its maximum speed. During this time frictional forces and air resistance oppose the forward motion of the car. The sketch graphs below show how the car’s speed increases when only the driver is in the car, and when the driver has a passenger in the car. ...
... as the car accelerates to its maximum speed. During this time frictional forces and air resistance oppose the forward motion of the car. The sketch graphs below show how the car’s speed increases when only the driver is in the car, and when the driver has a passenger in the car. ...
master notes ch 4 (midterm prep)
... also causes seat belts to lock into place. The illustration shows how one type of shoulder harness operates. When the car suddenly slows down, inertia causes the large mass under the seat to continue moving, which activates the lock on the safety belt. ...
... also causes seat belts to lock into place. The illustration shows how one type of shoulder harness operates. When the car suddenly slows down, inertia causes the large mass under the seat to continue moving, which activates the lock on the safety belt. ...
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh, Conceptual Integrated Science
... Consider a cart pushed along a track with a certain force. If the force remains the same while the mass of the cart decreases to half, the acceleration of the cart ...
... Consider a cart pushed along a track with a certain force. If the force remains the same while the mass of the cart decreases to half, the acceleration of the cart ...
PRE-LAB PREPARATION SHEET FOR LAB 8:
... experienced by an object and its momentum change. It can be shown mathematically from Newton’s laws and experimentally from our own observations that the change in momentum of an object is equal to a quantity called impulse. Impulse takes into account both the applied force at each instant in time a ...
... experienced by an object and its momentum change. It can be shown mathematically from Newton’s laws and experimentally from our own observations that the change in momentum of an object is equal to a quantity called impulse. Impulse takes into account both the applied force at each instant in time a ...