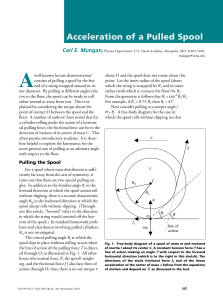
here
... different things you can calculate. Focus on what you know and what you want to know. Draw diagrams of the displacements – so you can see how they are related. The questions are not ordered by ease – look for the easiest questions and do them first. If you have not got the answer after 10 minu ...
... different things you can calculate. Focus on what you know and what you want to know. Draw diagrams of the displacements – so you can see how they are related. The questions are not ordered by ease – look for the easiest questions and do them first. If you have not got the answer after 10 minu ...
class xi physics - Kendriya Vidyalaya No.1
... *One dimensional motion:- The motion of an object is said to be one dimensional motion if only one out of three coordinates specifying the position of the object change with time. In such a motion an object move along a straight line path. *Two dimensional motion:- The motion of an object is said to ...
... *One dimensional motion:- The motion of an object is said to be one dimensional motion if only one out of three coordinates specifying the position of the object change with time. In such a motion an object move along a straight line path. *Two dimensional motion:- The motion of an object is said to ...
4.0 Mechanical systems use forces to transfer energy.
... All the different forces shown in Figure 4.5 can be classified as contact forces or action-at-a-distance forces. Contact forces must touch the object that they push or pull, for example, hitting a tennis ball (Figure 4.7). Another common contact force is friction. Friction is a force that opposes th ...
... All the different forces shown in Figure 4.5 can be classified as contact forces or action-at-a-distance forces. Contact forces must touch the object that they push or pull, for example, hitting a tennis ball (Figure 4.7). Another common contact force is friction. Friction is a force that opposes th ...
PHY 1112 : PHYSICS CHAPTER 3 Newton’s Laws of Motion and
... Displacement is a change from one position x1 to another position x2. Displacement has two features: (1) its magnitude; (2) its direction. Δx = x2 - x1 So it is a vector quantity. The value of the displacement of the object can be +ve /ve. It can move along a horizontal/vertical line. At ref ...
... Displacement is a change from one position x1 to another position x2. Displacement has two features: (1) its magnitude; (2) its direction. Δx = x2 - x1 So it is a vector quantity. The value of the displacement of the object can be +ve /ve. It can move along a horizontal/vertical line. At ref ...
canim-11 - The University of Texas at Dallas
... proportional to the product of the two masses and inversely proportional to their distance squared. The force acts in a direction e along a line from one particle to the other (in an attractive direction) ...
... proportional to the product of the two masses and inversely proportional to their distance squared. The force acts in a direction e along a line from one particle to the other (in an attractive direction) ...
Slide 1
... displacement x = 0 and time t = 0 and is displaced a distance of 20 m. Determine each of the following. a. The accl of the particle when its displacement x is 6 m b. The time taken for the object to be displaced the first 12 m c. The amount of work done displacing the object the first 12 m d. The sp ...
... displacement x = 0 and time t = 0 and is displaced a distance of 20 m. Determine each of the following. a. The accl of the particle when its displacement x is 6 m b. The time taken for the object to be displaced the first 12 m c. The amount of work done displacing the object the first 12 m d. The sp ...
Unit 4 Packet (Labs)
... 1. Measure and record the mass of the ball you plan to use in this experiment. 2. Connect the Motion Detector to the DIG/SONIC 1 channel of the interface. Place the Motion Detector on the floor and protect it by placing a wire basket over it. 3. Open the file “16 Energy of a Tossed Ball” from the Ph ...
... 1. Measure and record the mass of the ball you plan to use in this experiment. 2. Connect the Motion Detector to the DIG/SONIC 1 channel of the interface. Place the Motion Detector on the floor and protect it by placing a wire basket over it. 3. Open the file “16 Energy of a Tossed Ball” from the Ph ...
MOMENTUM! - Bibb County Public School District
... Why does a spinning ice skater speed up when she pulls her arms in? Suppose Mr. Stickman is sitting on a stool that swivels holding a pair of dumbbells. His axis of rotation is vertical. With the weights far from that axis, his moment of inertia is large. When he pulls his arms in as he’s spinning, ...
... Why does a spinning ice skater speed up when she pulls her arms in? Suppose Mr. Stickman is sitting on a stool that swivels holding a pair of dumbbells. His axis of rotation is vertical. With the weights far from that axis, his moment of inertia is large. When he pulls his arms in as he’s spinning, ...
Chapter #11 (Read Please)
... origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector r and its instantaneous linear momentum p ...
... origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector r and its instantaneous linear momentum p ...
Chapter 11
... origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector r and its instantaneous linear momentum p ...
... origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector r and its instantaneous linear momentum p ...
6th Grade - Northern Highlands
... Seat belts (Inertial Restraints) The stopping time of a car in a collision is very short even when crumpling occurs. A passenger without a seat belt will have a momentum that drops from very large value to zero when hitting the windshield, the steering wheel, or dashboard. Seat belts are made of a v ...
... Seat belts (Inertial Restraints) The stopping time of a car in a collision is very short even when crumpling occurs. A passenger without a seat belt will have a momentum that drops from very large value to zero when hitting the windshield, the steering wheel, or dashboard. Seat belts are made of a v ...
Select “A” for True and “B” for False.
... ____________ the combined weight of the arms, trunk, head and neck (W arms+Wthn) for the man to be in equilibrium. a. larger than b. smaller than c. equal to 34. To balance properly when carrying a heavy box in front of you, you must______________. a. lean backwards b. lean forwards c. use your leg ...
... ____________ the combined weight of the arms, trunk, head and neck (W arms+Wthn) for the man to be in equilibrium. a. larger than b. smaller than c. equal to 34. To balance properly when carrying a heavy box in front of you, you must______________. a. lean backwards b. lean forwards c. use your leg ...