Problems
... Q14.1 An object is moving with SHM of amplitude A on the end of a spring. If the amplitude is doubled, what happens to the total distance the object travels in one period? What happens to the period? What happens to the maximum speed of the object? Discuss how these answers are related. Q14.2 Think ...
... Q14.1 An object is moving with SHM of amplitude A on the end of a spring. If the amplitude is doubled, what happens to the total distance the object travels in one period? What happens to the period? What happens to the maximum speed of the object? Discuss how these answers are related. Q14.2 Think ...
Chapter 4: Forces and Newton`s Laws of Motion
... its surroundings; i.e. the body is “free” of its environment. We will consider only the forces acting on our object of interest. The object is depicted as not connected to any other object – it is “free”. Label the forces appropriately. Do not include the forces that this body exerts on any other bo ...
... its surroundings; i.e. the body is “free” of its environment. We will consider only the forces acting on our object of interest. The object is depicted as not connected to any other object – it is “free”. Label the forces appropriately. Do not include the forces that this body exerts on any other bo ...
Document
... • Acceleration is in the same direction as the net force. Note: #1 holds true only if the mass is constant. #2 holds true only if the net force is constant. In SI mks, all three elements can be combined to form Newton’s second law vector equation ...
... • Acceleration is in the same direction as the net force. Note: #1 holds true only if the mass is constant. #2 holds true only if the net force is constant. In SI mks, all three elements can be combined to form Newton’s second law vector equation ...
AP Physics Review - stoweschools.com
... acceleration due to gravity Universal Gravitational Force is directly proportional to the universal gravitational constant, the mass of one object, the mass of another object and inversely proportional to the distance between the center of the objects squared work – product of parallel component of ...
... acceleration due to gravity Universal Gravitational Force is directly proportional to the universal gravitational constant, the mass of one object, the mass of another object and inversely proportional to the distance between the center of the objects squared work – product of parallel component of ...
New Phenomena: Recent Results and Prospects from the Fermilab
... account that there is friction in the system. This gives a torque (due to the axel) we’ll call this tfric. What is this better estimate of the moment of Inertia? Physics 218, Lecture XVII ...
... account that there is friction in the system. This gives a torque (due to the axel) we’ll call this tfric. What is this better estimate of the moment of Inertia? Physics 218, Lecture XVII ...
Momentum and Its Conservation
... accord with Newton’s 3rd Law. While the forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, the accelerations of the objects are not necessarily equal in magnitude. According to Newton's second law of motion, Bigger mass has smaller acceleration, smaller mass has bigger acceleration ...
... accord with Newton’s 3rd Law. While the forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, the accelerations of the objects are not necessarily equal in magnitude. According to Newton's second law of motion, Bigger mass has smaller acceleration, smaller mass has bigger acceleration ...
Chapter 6: Newton`s Laws of Motion
... which is abbreviated N and named for Isaac Newton. One newton is about the amount of force needed to lift half a cup of water. ...
... which is abbreviated N and named for Isaac Newton. One newton is about the amount of force needed to lift half a cup of water. ...
here.
... In effect we have solved Newton’s second order equation of motion in two steps. Energy is the constant of integration in the first step and x0 is the second constant of integration. Our answer expresses t as a function of x. We must invert it to find trajectories x(t) with energy E and initial locat ...
... In effect we have solved Newton’s second order equation of motion in two steps. Energy is the constant of integration in the first step and x0 is the second constant of integration. Our answer expresses t as a function of x. We must invert it to find trajectories x(t) with energy E and initial locat ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation
... – He used an apparatus similar to that shown above. – He measured the masses of the spheres (m1 and m2), the distance between the spheres (r), and the force of attraction (Fg). ...
... – He used an apparatus similar to that shown above. – He measured the masses of the spheres (m1 and m2), the distance between the spheres (r), and the force of attraction (Fg). ...
Preview Sample 1
... According to Newton’s second law, the acceleration of the refrigerator is due to the sum of the forces on the object. Your push is countered by a frictional force of equal magnitude and opposite direction. Here the forces on the refrigerator sum to zero, so the net force on the refrigerator is zero, ...
... According to Newton’s second law, the acceleration of the refrigerator is due to the sum of the forces on the object. Your push is countered by a frictional force of equal magnitude and opposite direction. Here the forces on the refrigerator sum to zero, so the net force on the refrigerator is zero, ...
Chapter 4 Homework Packet Inertia is the tendency
... between the object and the earth. Answer D (1 point/18) 19) A child's toy is suspended from the ceiling by means of a string. The Earth pulls downward on the toy with its weight force of 8.0 N. If this is the "action force," what is the "reaction force"? A) The string pulling upward on the toy with ...
... between the object and the earth. Answer D (1 point/18) 19) A child's toy is suspended from the ceiling by means of a string. The Earth pulls downward on the toy with its weight force of 8.0 N. If this is the "action force," what is the "reaction force"? A) The string pulling upward on the toy with ...
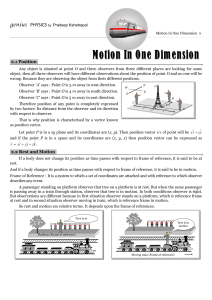
Introduction - PRADEEP KSHETRAPAL PHYSICS
... So distance |Displacement|. (ii) For a moving particle distance can never be negative or zero while displacement can be. (zero displacement means that body after motion has came back to initial position) i.e., Distance > 0 but Displacement > = or < 0 (iii) For motion between two points displacemen ...
... So distance |Displacement|. (ii) For a moving particle distance can never be negative or zero while displacement can be. (zero displacement means that body after motion has came back to initial position) i.e., Distance > 0 but Displacement > = or < 0 (iii) For motion between two points displacemen ...
Honors Review for Midterm
... ____ 12. You are pushing a rock along level ground and making the rock speed up. How does the size of the force you exert on the rock compare with the size of the force the rock exerts on you? The force you exert a. is larger than the force the rock exerts on you. b. is the same size as the force th ...
... ____ 12. You are pushing a rock along level ground and making the rock speed up. How does the size of the force you exert on the rock compare with the size of the force the rock exerts on you? The force you exert a. is larger than the force the rock exerts on you. b. is the same size as the force th ...