CentralForces - University of Colorado Boulder
... frame) then Newton's Laws don't hold. However, we can pretend that Newton's Laws hold in an accelerating frame if we pretend that "pseudo-forces" exist. That is, we can get the right answer if we makes two mistakes. In my opinion, this is a Devil's bargain. Computational convenience has come at the ...
... frame) then Newton's Laws don't hold. However, we can pretend that Newton's Laws hold in an accelerating frame if we pretend that "pseudo-forces" exist. That is, we can get the right answer if we makes two mistakes. In my opinion, this is a Devil's bargain. Computational convenience has come at the ...
test1
... Show detailed calculations to receive full points. Use proper units. If your work is not legible it will NOT be graded. 1. (A) (1 point) Define a vector quantity? ...
... Show detailed calculations to receive full points. Use proper units. If your work is not legible it will NOT be graded. 1. (A) (1 point) Define a vector quantity? ...
IPC Force Momentum Freefall Newtons Law Test Review
... 7. Compare and contrast contact forces and field forces using the Venn diagram. Be sure to include examples of each. ...
... 7. Compare and contrast contact forces and field forces using the Venn diagram. Be sure to include examples of each. ...
Objective:
... 1. Student will be able to describe the effects of balanced forces acting on an object. 2. Student will be able to describe the effects of unbalanced forces acting on an object. 3. Student will be able to determine the relationship between forces, mass and acceleration, i.e. F ma . 4. Student will ...
... 1. Student will be able to describe the effects of balanced forces acting on an object. 2. Student will be able to describe the effects of unbalanced forces acting on an object. 3. Student will be able to determine the relationship between forces, mass and acceleration, i.e. F ma . 4. Student will ...
Examination Paper (Mechanics)
... (6) A rigid body is made of three identical thin rods, each with length L, fastened together in the form of a letter H, as shown in the diagram. The body is free to rotate about a horizontal axis that runs along the length of one of the legs of the H. The body is allowed to fall from rest from a pos ...
... (6) A rigid body is made of three identical thin rods, each with length L, fastened together in the form of a letter H, as shown in the diagram. The body is free to rotate about a horizontal axis that runs along the length of one of the legs of the H. The body is allowed to fall from rest from a pos ...
Name: Date:______ Period:_____ Chapter 19 Honors Study Guide
... What are the proper units for: -acceleration? ___m/s2_______ -velocity? ___m/s + direction - speed? _________m/s________ Essays 1. A pitcher releases a fastball that moves toward home plate. Other than the force exerted by the pitcher, what are two forces that act on the ball as it travels between t ...
... What are the proper units for: -acceleration? ___m/s2_______ -velocity? ___m/s + direction - speed? _________m/s________ Essays 1. A pitcher releases a fastball that moves toward home plate. Other than the force exerted by the pitcher, what are two forces that act on the ball as it travels between t ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion and Vectors
... The motions we observe in our everyday life follow some simple rules. These rules are called Newton’s Laws and can be expressed as follows: First Law: ...
... The motions we observe in our everyday life follow some simple rules. These rules are called Newton’s Laws and can be expressed as follows: First Law: ...
newton`s laws of motion
... one force acts on the particle, the equation of motion can be written F = FR = ma where FR is the resultant force, which is a vector summation of all the forces. To illustrate the equation, consider a particle acted on by two forces. First, draw the particle’s free-body diagram, showing all forces ...
... one force acts on the particle, the equation of motion can be written F = FR = ma where FR is the resultant force, which is a vector summation of all the forces. To illustrate the equation, consider a particle acted on by two forces. First, draw the particle’s free-body diagram, showing all forces ...
Net Force
... Newton’s Second Law requires a net force. • One or more forces act on an object • Forces are vectors that can be added ...
... Newton’s Second Law requires a net force. • One or more forces act on an object • Forces are vectors that can be added ...
Worksheet - 2
... 8.Derive graphically the position-velocity equation of motion v2-u2=2as 9. A ball is dropped from a height of 50m. If its velocity increases uniformly at the rate of 10m/sec2 a) With what velocity will it strike the ground? b) After what time will it strike the ground? 10. A car accelerating uniform ...
... 8.Derive graphically the position-velocity equation of motion v2-u2=2as 9. A ball is dropped from a height of 50m. If its velocity increases uniformly at the rate of 10m/sec2 a) With what velocity will it strike the ground? b) After what time will it strike the ground? 10. A car accelerating uniform ...
Mechanical Equilibrium Questions/Answers PPT
... A force is a push or pull. Net force is the combination (sum) of all acting forces. ...
... A force is a push or pull. Net force is the combination (sum) of all acting forces. ...
Name: Sect:______ Date
... 26. What does it mean to say that momentum is conserved after two pool balls hit each other? (hint: compare their momentum before and after the collision) ...
... 26. What does it mean to say that momentum is conserved after two pool balls hit each other? (hint: compare their momentum before and after the collision) ...
1 - Hingham Schools
... A girl stood at first base on a level playing field and tossed a softball at an angle of 35 degrees above the horizontal. It was caught by another player over home base at the same height above the ground as it was originally thrown. 1. At which point along its trajectory was the softball traveling ...
... A girl stood at first base on a level playing field and tossed a softball at an angle of 35 degrees above the horizontal. It was caught by another player over home base at the same height above the ground as it was originally thrown. 1. At which point along its trajectory was the softball traveling ...
Forces - New Haven Science
... 2) What acceleration will you give to a 24.3 kg box if you push it with a force of 85.5 N? 3) A 1850 kg car is moving to the right at a constant velocity of 1.44 m/s. What is the net force on the cart? 4) A man is pushing a 200 Newton box with a force of 50 Newtons along the floor. A dog is pushing ...
... 2) What acceleration will you give to a 24.3 kg box if you push it with a force of 85.5 N? 3) A 1850 kg car is moving to the right at a constant velocity of 1.44 m/s. What is the net force on the cart? 4) A man is pushing a 200 Newton box with a force of 50 Newtons along the floor. A dog is pushing ...
Lever Arm
... • A 7.0 m beam is hanging from the ceiling by two ropes on its ends. The bar has a mass of 300 kg and it is non-uniform, with its center of mass 3.0 m from one end. A 400kg mass is hung from the beam’s light end and a 200 kg mass is hung from its heavy end. What force is acting on each rope? ...
... • A 7.0 m beam is hanging from the ceiling by two ropes on its ends. The bar has a mass of 300 kg and it is non-uniform, with its center of mass 3.0 m from one end. A 400kg mass is hung from the beam’s light end and a 200 kg mass is hung from its heavy end. What force is acting on each rope? ...
Newtons laws
... At the beginning of the 20th century, Albert Einstein (1879– 1955) developed the theory of relativity and, along with many other scientists, developed quantum theory. This theory does not have the constraints present in classical physics. ...
... At the beginning of the 20th century, Albert Einstein (1879– 1955) developed the theory of relativity and, along with many other scientists, developed quantum theory. This theory does not have the constraints present in classical physics. ...
Name Class Date Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section
... 1. In science, a push or a pull exerted on an object is known as ...
... 1. In science, a push or a pull exerted on an object is known as ...
Chapter 11: Circular Motion
... (Essentially a chair on a support.) If the chair were 8.0 meters from the center, how fast would it need to be moving for an astronaut to be undergoing 4.0 g’s of acceleration? (That means 4 times g.) ...
... (Essentially a chair on a support.) If the chair were 8.0 meters from the center, how fast would it need to be moving for an astronaut to be undergoing 4.0 g’s of acceleration? (That means 4 times g.) ...
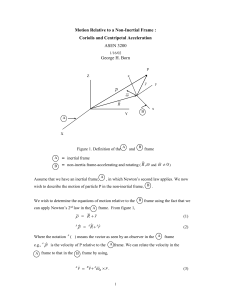
Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...