questions on Newton`s laws File
... 9. A truck loaded with sand accelerates along a highway. If the driving force on the truck remains constant, what happens to the truck's acceleration if its trailer leaks sand at a constant rate through a hole in its bottom? 10. A ball is held in a person's hand. (a) Identify all the external forces ...
... 9. A truck loaded with sand accelerates along a highway. If the driving force on the truck remains constant, what happens to the truck's acceleration if its trailer leaks sand at a constant rate through a hole in its bottom? 10. A ball is held in a person's hand. (a) Identify all the external forces ...
Newton`s second law of motion
... To verify Newton’s second law of motion using a tickertimer, weights and a small trolley. The second law of motion can be written F=m·a W here F : F orce m : mass a : acceleration ...
... To verify Newton’s second law of motion using a tickertimer, weights and a small trolley. The second law of motion can be written F=m·a W here F : F orce m : mass a : acceleration ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Everyone unconsciously knows the Second Law- We already know that heavier objects require more force to move the same distance as lighter objects. Example: How can you increase the acceleration of the wagon? One way is to increase the force. If the mass is constant, acceleration and force change ...
... Everyone unconsciously knows the Second Law- We already know that heavier objects require more force to move the same distance as lighter objects. Example: How can you increase the acceleration of the wagon? One way is to increase the force. If the mass is constant, acceleration and force change ...
Lecture powerpoint
... you may feel as if a force “throws” you forward toward the windshield. • There really is no such force. • Nonetheless, the fact that you seem to be hurled forward relative to the car is a very real experience! • You can describe your experience in terms of what are called fictitious forces. • These ...
... you may feel as if a force “throws” you forward toward the windshield. • There really is no such force. • Nonetheless, the fact that you seem to be hurled forward relative to the car is a very real experience! • You can describe your experience in terms of what are called fictitious forces. • These ...
Lecture 7: Forces and the motion they produce
... underlying much of the behavior we observe in world around us. However though the above laws look simple, solving problems using them can be complex and requires a good physical understanding of what Newton’s laws tell us. In fact there are many applications of even the simple case where there is P ...
... underlying much of the behavior we observe in world around us. However though the above laws look simple, solving problems using them can be complex and requires a good physical understanding of what Newton’s laws tell us. In fact there are many applications of even the simple case where there is P ...
hw 1246914222829 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... What is the net force on a box that is being pulled to the right w/ 40 N and to the left with 30 N? ...
... What is the net force on a box that is being pulled to the right w/ 40 N and to the left with 30 N? ...
Ch 6 Work, Power, Energy
... A dancer lifts a 40 kg ballerina 1.4 m in the air and then walks forward 2.2 m. How much work is done on the ballerina during and after the lift? ...
... A dancer lifts a 40 kg ballerina 1.4 m in the air and then walks forward 2.2 m. How much work is done on the ballerina during and after the lift? ...
1st Law An object will not change its speed or direction unless an
... When two or more motions are required, athletes must execute movements continuously in sequence. For example, if a javelin thrower hesitates or stops at the end of the approach just prior to the throw, the advantage of the the approach is lost. Athletes can increase mass and/or velocity to realize p ...
... When two or more motions are required, athletes must execute movements continuously in sequence. For example, if a javelin thrower hesitates or stops at the end of the approach just prior to the throw, the advantage of the the approach is lost. Athletes can increase mass and/or velocity to realize p ...
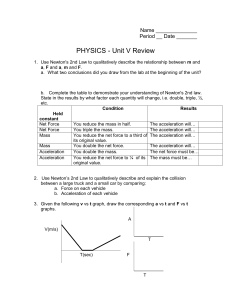
Unit V review
... b. resolving forces into x and y components, then finding the vector sum of the forces. c. analysis of the kinematic behavior of the object. 4. Solve quantitative problems involving forces, mass and acceleration using Newton's 2nd Law. a. Having determined the net force (as in #3), and given the mas ...
... b. resolving forces into x and y components, then finding the vector sum of the forces. c. analysis of the kinematic behavior of the object. 4. Solve quantitative problems involving forces, mass and acceleration using Newton's 2nd Law. a. Having determined the net force (as in #3), and given the mas ...
Lecture 9
... • thus “we are describing motions relative to a rotating reference frame” and “an object moving in a straight line with respect to the stars appears to follow a curved path” (does follow a curved path) relative to the coordinates fixed on the earth’s surface • as a result we may say there is an extr ...
... • thus “we are describing motions relative to a rotating reference frame” and “an object moving in a straight line with respect to the stars appears to follow a curved path” (does follow a curved path) relative to the coordinates fixed on the earth’s surface • as a result we may say there is an extr ...
Dynamics_NewtonLaws - University of Manchester
... Introduce a co-ordinate system for each object. For each object, determine the components of the forces along each of the object’s co-ordinate axes. For each object, write a separate equation for each component of Newton’s 2nd Law ( equation of motion). Solve the equations of motion. ...
... Introduce a co-ordinate system for each object. For each object, determine the components of the forces along each of the object’s co-ordinate axes. For each object, write a separate equation for each component of Newton’s 2nd Law ( equation of motion). Solve the equations of motion. ...
Newton`s second law of motion
... Resolving the weight into its components of force, the force acting down the slope, X = 600 cos 50◦ = 386N (to 3 significant figures) and the force acting perpendicular to the slope Y = 600 sin 50◦ = 460N. From Newton’s second law in the direction of the slope, X = ma ⇒ 386 = 60 × a. Therefore, the ...
... Resolving the weight into its components of force, the force acting down the slope, X = 600 cos 50◦ = 386N (to 3 significant figures) and the force acting perpendicular to the slope Y = 600 sin 50◦ = 460N. From Newton’s second law in the direction of the slope, X = ma ⇒ 386 = 60 × a. Therefore, the ...
Momentum
... A property of a moving body that determines the length of time required to bring it to rest when under the action of a constant force or moment. ...
... A property of a moving body that determines the length of time required to bring it to rest when under the action of a constant force or moment. ...
Study Guide motion key
... 27. Explain the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces. Balanced forces acting on an object equal zero, unbalanced forces are when all the forces acting on an object do not equal zero. ...
... 27. Explain the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces. Balanced forces acting on an object equal zero, unbalanced forces are when all the forces acting on an object do not equal zero. ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation
... object directed along a line tangent to its circular path • What would uniform circular motion mean? ...
... object directed along a line tangent to its circular path • What would uniform circular motion mean? ...
Forces can change the direction of motion.
... Mass is also a variable in Newton’s second law. If the same force acts on two objects, the object with less mass will have the greater acceleration. For instance, if you push a soccer ball and a bowling ball with equal force, the soccer ball will have a greater acceleration. If objects lose mass, th ...
... Mass is also a variable in Newton’s second law. If the same force acts on two objects, the object with less mass will have the greater acceleration. For instance, if you push a soccer ball and a bowling ball with equal force, the soccer ball will have a greater acceleration. If objects lose mass, th ...
Newtons Laws - Cardinal Newman High School
... Examples: A wheelchair racer finishes a 132 meter race in 18 seconds, what is his speed? ...
... Examples: A wheelchair racer finishes a 132 meter race in 18 seconds, what is his speed? ...
angular velocity
... Centrifugal force “center-fleeing”, away from center Apparent outward force experienced by a rotating body Fictitious force – it is not real but do to the effect of inertia ...
... Centrifugal force “center-fleeing”, away from center Apparent outward force experienced by a rotating body Fictitious force – it is not real but do to the effect of inertia ...