30 Physics
... 1. An object maintains constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced (or non-zero net) force. This is sometimes called Galileo's law of inertia. One property of matter is its inertia....it's tendancy to remain at constant velocity. Matter is inert to chage as far as motion (velocity) is conce ...
... 1. An object maintains constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced (or non-zero net) force. This is sometimes called Galileo's law of inertia. One property of matter is its inertia....it's tendancy to remain at constant velocity. Matter is inert to chage as far as motion (velocity) is conce ...
Motion
... acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied. Greater force = More acceleration Greater mass = Less acceleration All objects fall to the ground with the same acceleration (9.8 m/s²) ...
... acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied. Greater force = More acceleration Greater mass = Less acceleration All objects fall to the ground with the same acceleration (9.8 m/s²) ...
Lecture_6_Chapter_06
... • As long as the tires do not slip, the friction is static. If the tires do start to slip, the friction is kinetic, which is bad in two ways: 1. The kinetic frictional force is smaller than the static. 2. The static frictional force can point towards the center of the circle, but the kinetic frictio ...
... • As long as the tires do not slip, the friction is static. If the tires do start to slip, the friction is kinetic, which is bad in two ways: 1. The kinetic frictional force is smaller than the static. 2. The static frictional force can point towards the center of the circle, but the kinetic frictio ...
Document
... - Forces are often measured by determining the elongation of a calibrated spring. - Forces are vectors!! Remember vector addition. - To calculate net force on an object you must use vector addition. ...
... - Forces are often measured by determining the elongation of a calibrated spring. - Forces are vectors!! Remember vector addition. - To calculate net force on an object you must use vector addition. ...
How Rockets Work
... • In the absence of net external force, objects tend to maintain their state of motion • Acceleration is directly proportional to force applied and inversely proportional to mass • For every action force, there is an equal but opposite reaction force ...
... • In the absence of net external force, objects tend to maintain their state of motion • Acceleration is directly proportional to force applied and inversely proportional to mass • For every action force, there is an equal but opposite reaction force ...
student notes - science
... His 2nd law said that the force applied to an object is directly proportional to its acceleration and that as an object grew in mass it would be harder to make accelerate. So mass becomes the property of a body that resists change in motion. This is summed up by the equation: Force (N) = mass (kg) x ...
... His 2nd law said that the force applied to an object is directly proportional to its acceleration and that as an object grew in mass it would be harder to make accelerate. So mass becomes the property of a body that resists change in motion. This is summed up by the equation: Force (N) = mass (kg) x ...
Chapter 11 Lesson 2- Forces and Motion Vocabulary force friction
... Thrust- push or pull of an airplane forward. Lift- causes the airplane to rise into the air. Lift must be stronger than the weight pulling on the plane in order for it to fly. Drag is a pull that slows the plane down. Forces can crush, stretch, or twist objects and deform them. The harder a substanc ...
... Thrust- push or pull of an airplane forward. Lift- causes the airplane to rise into the air. Lift must be stronger than the weight pulling on the plane in order for it to fly. Drag is a pull that slows the plane down. Forces can crush, stretch, or twist objects and deform them. The harder a substanc ...
Force and Newton`s Laws
... circular motion, the centripetal force is always perpendicular to the motion. The terminal velocity is reached when the force of gravity is balanced by air resistance; the size of the air resistance force depends on the shape of an object and its speed. An object can speed up, slow down, or turn ...
... circular motion, the centripetal force is always perpendicular to the motion. The terminal velocity is reached when the force of gravity is balanced by air resistance; the size of the air resistance force depends on the shape of an object and its speed. An object can speed up, slow down, or turn ...
Newton`s Three Laws: Answer the questions below using pages 389
... the law as an equation in two ways. 4. What is the net force acing on a 0.15 kg object accelerating at 12 m/s2? What is the acceleration of an 800 kg car with a net force of 4000 N? Show your work. 5. What is Newton’s third law? What is another way to state the third law? Give three examples from th ...
... the law as an equation in two ways. 4. What is the net force acing on a 0.15 kg object accelerating at 12 m/s2? What is the acceleration of an 800 kg car with a net force of 4000 N? Show your work. 5. What is Newton’s third law? What is another way to state the third law? Give three examples from th ...
Matter and Forces in Motion (2a-2c)
... 11. A horizontal line on a velocity/time graph shows _______________________________ acceleration. 12. Inertia varies depending on __________________________________. 13. Newton's first law of motion is also called the law of ____________________________________. 14. The upward force on an object fa ...
... 11. A horizontal line on a velocity/time graph shows _______________________________ acceleration. 12. Inertia varies depending on __________________________________. 13. Newton's first law of motion is also called the law of ____________________________________. 14. The upward force on an object fa ...
Name_________________Date___________Period_____ Num
... 11. What happens to an object when there is a balanced force applied? ...
... 11. What happens to an object when there is a balanced force applied? ...
Force/Newton`s First Law Notes
... Force/Newton’s First Law Notes Force is any interaction between any two objects or an object and its environment. Two types of forces: Contact forces are usually pushes or pulls that result from direct contact between objects. Field forces do not result from direct contact but can act over a great ...
... Force/Newton’s First Law Notes Force is any interaction between any two objects or an object and its environment. Two types of forces: Contact forces are usually pushes or pulls that result from direct contact between objects. Field forces do not result from direct contact but can act over a great ...
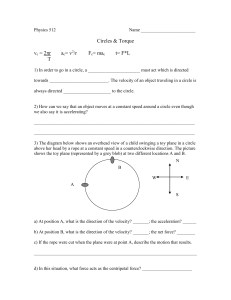
Physics 512 - Scarsdale Schools
... a) At position A, what is the direction of the velocity? _______; the acceleration? ______ b) At position B, what is the direction of the velocity? _______; the net force? ________ c) If the rope were cut when the plane were at point A, describe the motion that results. _____________________________ ...
... a) At position A, what is the direction of the velocity? _______; the acceleration? ______ b) At position B, what is the direction of the velocity? _______; the net force? ________ c) If the rope were cut when the plane were at point A, describe the motion that results. _____________________________ ...
Chapter 5 Notes
... Where F is the gravitational force, G is a constant 6.67 X 10-11 N · m2/ kg2 , m are the masses of the objects, and r is the distance between the objects. Example: Calculate the gravitational force acting on you as a result of the person sitting next to you. Assume that one person has a mass of 50 k ...
... Where F is the gravitational force, G is a constant 6.67 X 10-11 N · m2/ kg2 , m are the masses of the objects, and r is the distance between the objects. Example: Calculate the gravitational force acting on you as a result of the person sitting next to you. Assume that one person has a mass of 50 k ...
Forces
... • The strength of the force of friction depends on two factors. How hard they push together and they type of surfaces involved. A smooth surface is much easier to slide on. ...
... • The strength of the force of friction depends on two factors. How hard they push together and they type of surfaces involved. A smooth surface is much easier to slide on. ...