Nuclear Forces
... magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. In terms of an equation, the net force is equated to the product of the mass times the acceleration. • Fnet = m a ...
... magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. In terms of an equation, the net force is equated to the product of the mass times the acceleration. • Fnet = m a ...
Lecture 14
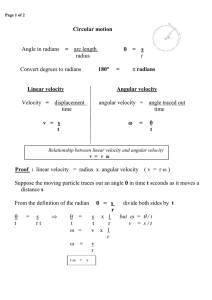
... Acceleration and Circular Motion What keeps the body in the circle? An object moving at a constant speed in a circle must have a force acting on it; otherwise it would move in a straight line. It’s a constant acceleration a toward the center of the circle: the centripetal acceleration ...
... Acceleration and Circular Motion What keeps the body in the circle? An object moving at a constant speed in a circle must have a force acting on it; otherwise it would move in a straight line. It’s a constant acceleration a toward the center of the circle: the centripetal acceleration ...
Ch. 12 Test Review Write the complete definition for the following
... 14. As the ____________________ of the objects increase, the ___________________ ____________________ of the objects also increase. 15. As the _______________________ between the objects increases, the ___________________ ______________________ of the objects decreases. 16. Mass x Acceleration = __ ...
... 14. As the ____________________ of the objects increase, the ___________________ ____________________ of the objects also increase. 15. As the _______________________ between the objects increases, the ___________________ ______________________ of the objects decreases. 16. Mass x Acceleration = __ ...
Newton`s Three Laws of Motion
... II. The relationship between an object's mass m, its acceleration a, and the applied force F is F = ma. Acceleration and force are vectors (as indicated by their symbols being displayed in slant bold font); in this law the direction of the force vector is the same as the direction of the acceleratio ...
... II. The relationship between an object's mass m, its acceleration a, and the applied force F is F = ma. Acceleration and force are vectors (as indicated by their symbols being displayed in slant bold font); in this law the direction of the force vector is the same as the direction of the acceleratio ...
Unit 4 Objectives: Circular Motion Standard: SP1. Students will
... 3. What is the number of rotations per unit of time called? RPM 4. What is the unit that rotational speed is commonly expressed in? RPM 5. What happens to the rotational speed of an object as it moves away from the axis of rotation toward the outer edge of a rotating system? Rotational speed stays c ...
... 3. What is the number of rotations per unit of time called? RPM 4. What is the unit that rotational speed is commonly expressed in? RPM 5. What happens to the rotational speed of an object as it moves away from the axis of rotation toward the outer edge of a rotating system? Rotational speed stays c ...
Sci_ch9_lesson_2_notes
... still, the forces acting on it are balanced. Forces are also balanced when objects’ velocity does not change. Like a bus traveling straight at a constant speed. Unbalanced forces are forces that change an objects motion. Newton’s Second Law of Motion The unbalanced force on an object is equal to the ...
... still, the forces acting on it are balanced. Forces are also balanced when objects’ velocity does not change. Like a bus traveling straight at a constant speed. Unbalanced forces are forces that change an objects motion. Newton’s Second Law of Motion The unbalanced force on an object is equal to the ...