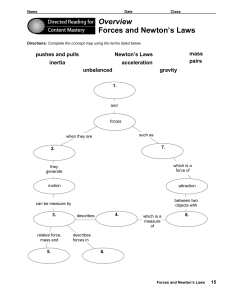
Force, mass, and acceleration
... force on another, the second object exerts and equal and opposite force on the first –For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction –If you push on a wall, you feel the wall pushing back on your ...
... force on another, the second object exerts and equal and opposite force on the first –For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction –If you push on a wall, you feel the wall pushing back on your ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Objects with more mass will have more inertia than objects with less mass. Have you ever been forced against the side of a car as it turns? When the car is changing direction, your body tends to keep moving straight. The car is pushing on you during a turn. ...
... Objects with more mass will have more inertia than objects with less mass. Have you ever been forced against the side of a car as it turns? When the car is changing direction, your body tends to keep moving straight. The car is pushing on you during a turn. ...
Weight is expressed in A push or a pull Force exerted when only
... A car is turning while moving at a constant speed. Are the forces acting on the car balanced or unbalanced? ...
... A car is turning while moving at a constant speed. Are the forces acting on the car balanced or unbalanced? ...
Speed and Velocity
... traveling in the same direction but at different speeds – the only way to have the same velocity is if 2 objects are traveling at the same speed in the same direction ...
... traveling in the same direction but at different speeds – the only way to have the same velocity is if 2 objects are traveling at the same speed in the same direction ...
Class 11, 3 July
... – Always act at right angles to surface – Force of electron clouds repelling each other – Friction always normal to normal force, so friction is always parallel to surface ...
... – Always act at right angles to surface – Force of electron clouds repelling each other – Friction always normal to normal force, so friction is always parallel to surface ...
Newton`s 2nd Law Note
... move (or don't move) as they do. These three laws have become known as Newton's three laws of motion ...
... move (or don't move) as they do. These three laws have become known as Newton's three laws of motion ...
Unit 3 Notes
... Examples of Newton’s 3 Law Newton’s third law: "For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction." When you fire a gun you feel the recoil. Some of the funniest things in cartoons follow physics that have been exaggerated or just plain ignored. Wyle Coyote hangs suspended in space over that ...
... Examples of Newton’s 3 Law Newton’s third law: "For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction." When you fire a gun you feel the recoil. Some of the funniest things in cartoons follow physics that have been exaggerated or just plain ignored. Wyle Coyote hangs suspended in space over that ...
Gravity PP
... G is the “Universal Gravitational Constant” – 6.67 x 10-11 (N x m2)/kg2 – Gravitational force measured between two 1-kg objects ...
... G is the “Universal Gravitational Constant” – 6.67 x 10-11 (N x m2)/kg2 – Gravitational force measured between two 1-kg objects ...
4-2 Force, Mass and Newton`s 2nd Law
... Q: Are astronauts in an orbiting satellite in free-fall? A: Yep. The only force acting on them is their own weight, which produces an acceleration of g. Since there is no force balancing the force of gravity, their apparent weight is zero (unless you consider the weight of the diaper acting against ...
... Q: Are astronauts in an orbiting satellite in free-fall? A: Yep. The only force acting on them is their own weight, which produces an acceleration of g. Since there is no force balancing the force of gravity, their apparent weight is zero (unless you consider the weight of the diaper acting against ...
Document
... Match the correct definition with the correct term. Write the letter in the space provided. Some terms will not be used. ______ 1. a push or a pull that always acts on an object ...
... Match the correct definition with the correct term. Write the letter in the space provided. Some terms will not be used. ______ 1. a push or a pull that always acts on an object ...
Newton`s Second Law
... A tennis ball undergoes an acceleration of 5,500m/s2. How much force would the tennis racket have to exert to give the ball this acceleration? The ball has a mass of .06kg. ...
... A tennis ball undergoes an acceleration of 5,500m/s2. How much force would the tennis racket have to exert to give the ball this acceleration? The ball has a mass of .06kg. ...