template
... engineers assume the mass of the average rider is 75 kg. The elevator itself has a mass of 500 kg. The cable supporting the elevator can tolerate a maximum force of 30, 000 N. What is the greatest acceleration that the elevator's motor can produce without snapping the cable? For these problems, you ...
... engineers assume the mass of the average rider is 75 kg. The elevator itself has a mass of 500 kg. The cable supporting the elevator can tolerate a maximum force of 30, 000 N. What is the greatest acceleration that the elevator's motor can produce without snapping the cable? For these problems, you ...
Force Diagrams
... Big mass = small acceleration An object’s motion is constant UNLESS a force is applied. – Constant velocity = NO NET FORCE! ...
... Big mass = small acceleration An object’s motion is constant UNLESS a force is applied. – Constant velocity = NO NET FORCE! ...
AcaDec - University of Arizona
... whose moment of inertia is 2.5 kg*m spinning with an angular velocity of 5 m/s? ...
... whose moment of inertia is 2.5 kg*m spinning with an angular velocity of 5 m/s? ...
1. newton`s laws
... Forces are balanced when they are equal in size but opposite in direction. If everyone pulls with the same strength there will be no movement. pull ...
... Forces are balanced when they are equal in size but opposite in direction. If everyone pulls with the same strength there will be no movement. pull ...
Chapter 6 - SFSU Physics & Astronomy
... the same force that keeps the Moon in its orbit. Hence, Universal Gravitation. ...
... the same force that keeps the Moon in its orbit. Hence, Universal Gravitation. ...
Forces
... • Newton’s 1st law of motion deals with inertia • An object at rest remains at rest, an object in motion maintains its velocity, unless acted upon by an outside force • Objects change their state of motion only when a net force is applied to the object • Inertia: the tendency of an object to maintai ...
... • Newton’s 1st law of motion deals with inertia • An object at rest remains at rest, an object in motion maintains its velocity, unless acted upon by an outside force • Objects change their state of motion only when a net force is applied to the object • Inertia: the tendency of an object to maintai ...
8th PS 9-Weeks 3 Exam
... d. 150 m/s2 The size of the gravitational force between two objects depends on their ____. a. frictional forces b. inertia c. masses and the distance between them d. speed and direction A feather will fall through the air more slowly than a brick because of ____. a. air resistance c. inertia b. grav ...
... d. 150 m/s2 The size of the gravitational force between two objects depends on their ____. a. frictional forces b. inertia c. masses and the distance between them d. speed and direction A feather will fall through the air more slowly than a brick because of ____. a. air resistance c. inertia b. grav ...
Chapter 3 Notes File
... III. Friction-the force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching each other. A. Depends on two factors 1. Kind of surface 2. Force pressing the surfaces together B. What causes friction? 1. Microwelds form between two surfaces a. Where two surfaces stick together 2. The stronger t ...
... III. Friction-the force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching each other. A. Depends on two factors 1. Kind of surface 2. Force pressing the surfaces together B. What causes friction? 1. Microwelds form between two surfaces a. Where two surfaces stick together 2. The stronger t ...
Sliding Mass Problems
... Draw a force diagram and label the known information for each problem. Use your diagrams to write a valid equation for Newton’s Second Law and solve for the unknowns. You will need to use other equations (form Chapter 5) to solve. 1. A loaded snow sled is pulled by six huskies with a force of 1,250 ...
... Draw a force diagram and label the known information for each problem. Use your diagrams to write a valid equation for Newton’s Second Law and solve for the unknowns. You will need to use other equations (form Chapter 5) to solve. 1. A loaded snow sled is pulled by six huskies with a force of 1,250 ...
Motion, Forces, and Simple Machines
... 1. Average speed is defined as the total distance traveled divided by the travel time. *The formula used to calculate average speed is: s=d/t *To find the distance (d), the formula changes to: d=s x t 2. instantaneous speed is the speed of an object at any instant of time. 3. Velocity is the speed ...
... 1. Average speed is defined as the total distance traveled divided by the travel time. *The formula used to calculate average speed is: s=d/t *To find the distance (d), the formula changes to: d=s x t 2. instantaneous speed is the speed of an object at any instant of time. 3. Velocity is the speed ...
Free Body Diagrams and Newton`s Laws
... Notice that while the normal force and gravitation forces are balanced (each are 50 N) the force of friction results in unbalanced force on the horizontal axis. The net force is 20 N left or Fnet = -20N and the acceleration is negative. (in the direction of the net Force ...
... Notice that while the normal force and gravitation forces are balanced (each are 50 N) the force of friction results in unbalanced force on the horizontal axis. The net force is 20 N left or Fnet = -20N and the acceleration is negative. (in the direction of the net Force ...
Forces with acceleration homework
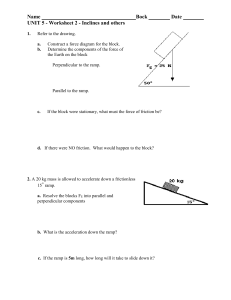
... Construct a force diagram for the block. Determine the components of the force of the Earth on the block Perpendicular to the ramp. ...
... Construct a force diagram for the block. Determine the components of the force of the Earth on the block Perpendicular to the ramp. ...
Centripetal and Gravitational Forces
... • The smaller the length of rope (radius), the more centripetal force you will have to apply to the rope. • Notice that the centripetal force and the centripetal acceleration are always pointing in the same direction. http://regentsprep.org ...
... • The smaller the length of rope (radius), the more centripetal force you will have to apply to the rope. • Notice that the centripetal force and the centripetal acceleration are always pointing in the same direction. http://regentsprep.org ...
Newton`s First Law
... Inertia a property of matter that causes an object to resist changes in its state of motion it is directly proportional to the mass of the object ...
... Inertia a property of matter that causes an object to resist changes in its state of motion it is directly proportional to the mass of the object ...
Chapter 7
... circular motion about the point O All parts of the object of the body rotate through the same angle during the same time The object is considered to be a rigid ...
... circular motion about the point O All parts of the object of the body rotate through the same angle during the same time The object is considered to be a rigid ...
newtons-2nd-3rd-law
... • Net force refers to what you get when you consider the total effect of all the forces acting on an object. • If the forces on an object are equal and opposite, they are said to be balanced, and the object experiences no change in motion. • If the forces are not equal and opposite, then the forces ...
... • Net force refers to what you get when you consider the total effect of all the forces acting on an object. • If the forces on an object are equal and opposite, they are said to be balanced, and the object experiences no change in motion. • If the forces are not equal and opposite, then the forces ...