Ch4 Gravit Force
... gravitational constant. Its value in the SI system of units is, G = 6.67 10-11N.m2/Kg2. The law of gravitation is universal and very fundamental. It can be used to understand the motions of planets and moons, determine the surface gravity of planets, and the orbital motion of artificial satellites ...
... gravitational constant. Its value in the SI system of units is, G = 6.67 10-11N.m2/Kg2. The law of gravitation is universal and very fundamental. It can be used to understand the motions of planets and moons, determine the surface gravity of planets, and the orbital motion of artificial satellites ...
phys1443-fall07-091907
... Results of physical measurements in different reference frames could be different Observations of the same motion in a stationary frame would be different than the ones made in the frame moving together with the moving object. Consider that you are driving a car. To you, the objects in the car do no ...
... Results of physical measurements in different reference frames could be different Observations of the same motion in a stationary frame would be different than the ones made in the frame moving together with the moving object. Consider that you are driving a car. To you, the objects in the car do no ...
8.5
... Find the decomposition of v into two vectors that are perpendicular to each other. v1 = ( v • w / ll w ll2) * (w) v1 = 12 / 13 (w) = (-24/13) i + (36/13)j v2 = v – v1 = (51/13) i + (42/13) j ...
... Find the decomposition of v into two vectors that are perpendicular to each other. v1 = ( v • w / ll w ll2) * (w) v1 = 12 / 13 (w) = (-24/13) i + (36/13)j v2 = v – v1 = (51/13) i + (42/13) j ...
Motion Review Notes - Ms. Guggenheimer`s Education Connection
... An object will remain at rest or move at a constant speed in a straight line unless it is acted on by an unbalanced force. Inertia - the tendency of an object to remain at rest or in motion Newton's Second Law of Motion: The acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the size an ...
... An object will remain at rest or move at a constant speed in a straight line unless it is acted on by an unbalanced force. Inertia - the tendency of an object to remain at rest or in motion Newton's Second Law of Motion: The acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the size an ...
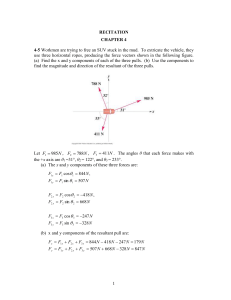
Recitation Ch 4-1
... 4-52. You leave the doctor’s office after your annual checkup and recall that you weighted 683 N in her office. You then get into an elevator that, conveniently, has a scale. Find the magnitude and direction of the elevator’s acceleration if the scale reads (a) 725 N, (b) 595 N. w 683 N is the for ...
... 4-52. You leave the doctor’s office after your annual checkup and recall that you weighted 683 N in her office. You then get into an elevator that, conveniently, has a scale. Find the magnitude and direction of the elevator’s acceleration if the scale reads (a) 725 N, (b) 595 N. w 683 N is the for ...
Chapter 4
... Rotating Coordinate Systems and the Equations of Motion 1. Rates of change of vectors We have derived the Navier Stokes equations in an inertial (non accelerating frame of reference) for which Newton’s third law is valid. However, in oceanography and meteorology it is more natural to put ourselves i ...
... Rotating Coordinate Systems and the Equations of Motion 1. Rates of change of vectors We have derived the Navier Stokes equations in an inertial (non accelerating frame of reference) for which Newton’s third law is valid. However, in oceanography and meteorology it is more natural to put ourselves i ...
patterns of motion and equilibrium - SCIENCE
... always changing its direction. Therefore, its velocity is always changing, so it is accelerating. • The acceleration that occurs in circular motion is known as centripetal acceleration. ...
... always changing its direction. Therefore, its velocity is always changing, so it is accelerating. • The acceleration that occurs in circular motion is known as centripetal acceleration. ...
Newton`s First and Second Laws
... In an effort to reduce the number of fundamental forces, in 1967 physicists predicted that the electromagnetic and weak forces were different manifestations of the same force, called the electroweak force The prediction was confirmed experimentally in 1984 ...
... In an effort to reduce the number of fundamental forces, in 1967 physicists predicted that the electromagnetic and weak forces were different manifestations of the same force, called the electroweak force The prediction was confirmed experimentally in 1984 ...
UCM HONORS PHYSICS 2016 2017
... Centrifugal Force (not real!) • Let’s say you are in a car and you go around this corner to the left too fast. The passenger on the right side might get thrown against the right (or outer) door. • Is there an outward force on the passenger? Some people say it is centrifugal force, pushing you outwa ...
... Centrifugal Force (not real!) • Let’s say you are in a car and you go around this corner to the left too fast. The passenger on the right side might get thrown against the right (or outer) door. • Is there an outward force on the passenger? Some people say it is centrifugal force, pushing you outwa ...
Lecture 6
... Newton’s Laws of Motion • The ancient (& wrong!) view (of Aristotle): – A force is needed to keep an object in motion. In the 21st Century, this is still a common – The “natural” state of an object is at rest. ...
... Newton’s Laws of Motion • The ancient (& wrong!) view (of Aristotle): – A force is needed to keep an object in motion. In the 21st Century, this is still a common – The “natural” state of an object is at rest. ...
reviewmtnoanswers1
... direction of the friction force on the block? A. 9.8 newtons down B. 10 newtons backward C. 2 newtons backward D. 2 newtons forward ...
... direction of the friction force on the block? A. 9.8 newtons down B. 10 newtons backward C. 2 newtons backward D. 2 newtons forward ...
Force and Motion
... • The symbol F is a vector and represents the size and direction of a force, while F represents only the magnitude. ...
... • The symbol F is a vector and represents the size and direction of a force, while F represents only the magnitude. ...
Forces and Newton`s Laws
... 3. FRICTION– is a force that appears whenever two things are in contact. • No matter which direction • something moves in, • friction pulls it the other way. ...
... 3. FRICTION– is a force that appears whenever two things are in contact. • No matter which direction • something moves in, • friction pulls it the other way. ...
PHYS 243, Exam 1
... Problem 1. A block of mass m = 2 kg resting on a rough horizontal surface is pushed by a force F = 10 Newtons that acts along a direction 37 degrees below the horizontal as shown. The block moves at a constant velocity v = 5 m/s. (a) (8 pts) What is the net force on the block? ANSWER: F_net = 0, sin ...
... Problem 1. A block of mass m = 2 kg resting on a rough horizontal surface is pushed by a force F = 10 Newtons that acts along a direction 37 degrees below the horizontal as shown. The block moves at a constant velocity v = 5 m/s. (a) (8 pts) What is the net force on the block? ANSWER: F_net = 0, sin ...
Wikipedia and Coriolis Force
... transverse forces from the perspective of any arbitrarily chosen polar origin. When Newton’s first law of motion is expressed in polar coordinates, relative to any arbitrarily chosen polar origin, radial and transverse inertial forces are revealed. See the derivation in the appendix in section VII a ...
... transverse forces from the perspective of any arbitrarily chosen polar origin. When Newton’s first law of motion is expressed in polar coordinates, relative to any arbitrarily chosen polar origin, radial and transverse inertial forces are revealed. See the derivation in the appendix in section VII a ...