
Revision Semester 2 Physics test File
... 2. As a rocket takes off to the sky, it’s speed increases. Explain why. F = m × a; Newton second law states that acceleration of an object is directly proportional and in the same direction as the applied force, and inversely proportional to its mass. Therefore, as the rocket takes off to the sky, i ...
... 2. As a rocket takes off to the sky, it’s speed increases. Explain why. F = m × a; Newton second law states that acceleration of an object is directly proportional and in the same direction as the applied force, and inversely proportional to its mass. Therefore, as the rocket takes off to the sky, i ...
investigating newton`s second law of motion
... Analysis of the area under a given graph also provides useful information. In fact, the area under a velocity/time graph yields displacement while the area under an acceleration/time graph yields velocity. Motion can not only be represented by graphs, but additionally, it can be described by Newton’ ...
... Analysis of the area under a given graph also provides useful information. In fact, the area under a velocity/time graph yields displacement while the area under an acceleration/time graph yields velocity. Motion can not only be represented by graphs, but additionally, it can be described by Newton’ ...
3 rd CLASS - MissCalnan
... 3. Newton’s 1st law is the law of INERTIA 4. Give an example of Newton’s 2nd law? BOUNCING A BALL, JUMPING 5. What type of joint is the elbow joint? And what muscle causes elbow flexion ...
... 3. Newton’s 1st law is the law of INERTIA 4. Give an example of Newton’s 2nd law? BOUNCING A BALL, JUMPING 5. What type of joint is the elbow joint? And what muscle causes elbow flexion ...
Chapter 4 - Newton`s Laws of motion
... start moving backward relative to the bus as the bus gains speed. If instead the bus was slowing to a stop, you would start moving forward down the aisle. In either case, it looks as though Newton’s first law is not obeyed; there is no net force acting on you, yet your velocity change. What wrong? ...
... start moving backward relative to the bus as the bus gains speed. If instead the bus was slowing to a stop, you would start moving forward down the aisle. In either case, it looks as though Newton’s first law is not obeyed; there is no net force acting on you, yet your velocity change. What wrong? ...
Force due to gravity: A field force (a vector quantity) that always is
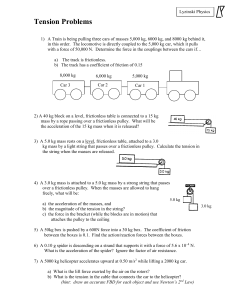
... What is the acceleration of the spider? Ignore the factor of air resistance. 7) A 5000 kg helicopter accelerates upward at 0.50 m/s2 while lifting a 2000 kg car. a) What is the lift force exerted by the air on the rotors? b) What is the tension in the cable that connects the car to the helicopter? ( ...
... What is the acceleration of the spider? Ignore the factor of air resistance. 7) A 5000 kg helicopter accelerates upward at 0.50 m/s2 while lifting a 2000 kg car. a) What is the lift force exerted by the air on the rotors? b) What is the tension in the cable that connects the car to the helicopter? ( ...
WORD - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... if it could be slowed down and pulled into Earth’s atmosphere. 12. The passengers, as seen in the diagram, are standing on the floor. (a) If a passenger held an object beside their waist and then released it, the object would move in a straight line, tangential to the circle in which the passenger’s ...
... if it could be slowed down and pulled into Earth’s atmosphere. 12. The passengers, as seen in the diagram, are standing on the floor. (a) If a passenger held an object beside their waist and then released it, the object would move in a straight line, tangential to the circle in which the passenger’s ...
Concept Summary
... o Acceleration changes the velocity (in magnitude, direction, or both). o Acceleration can speed you up or slow you down (often called deceleration). o Constant velocity means the acceleration is zero and visa versa. o Average acceleration = change in velocity/elapsed time vector quantity = magnit ...
... o Acceleration changes the velocity (in magnitude, direction, or both). o Acceleration can speed you up or slow you down (often called deceleration). o Constant velocity means the acceleration is zero and visa versa. o Average acceleration = change in velocity/elapsed time vector quantity = magnit ...
Lecture 7: Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity
... • Using accumulated data on the motions of the Moon and planets, and his first law, Newton deduced the existence of the gravitational force that is responsible for the movement of the Moon and planets and this force acts between any two objects. If two particles with mass m1 and m2 are separated by ...
... • Using accumulated data on the motions of the Moon and planets, and his first law, Newton deduced the existence of the gravitational force that is responsible for the movement of the Moon and planets and this force acts between any two objects. If two particles with mass m1 and m2 are separated by ...
Centripetal Force / Gravity (very good practice)
... 5. The acceleration of gravity on the moon is one-sixth what it is on Earth. The radius of the moon is one-fourth that of the Earth. Determine the moon’s mass. 6. Two objects, with masses m1 and m2, are originally a distance r apart. The magnitude of the force between them is F. If the masses are ch ...
... 5. The acceleration of gravity on the moon is one-sixth what it is on Earth. The radius of the moon is one-fourth that of the Earth. Determine the moon’s mass. 6. Two objects, with masses m1 and m2, are originally a distance r apart. The magnitude of the force between them is F. If the masses are ch ...
1 - ActiveClassroom!
... 36. The driver of a 2000 kg car moving at 30 m/s presses on the break pedal. If the braking force is 10,000 N, how far does the car travel before stopping? a. 45 m b. 90 m c. 135 m d. 180 m 37. A 2 kg ball moving at 3 m/s hits a wall and bounces off. Immediately after the collision, it moves at 3 m ...
... 36. The driver of a 2000 kg car moving at 30 m/s presses on the break pedal. If the braking force is 10,000 N, how far does the car travel before stopping? a. 45 m b. 90 m c. 135 m d. 180 m 37. A 2 kg ball moving at 3 m/s hits a wall and bounces off. Immediately after the collision, it moves at 3 m ...
Document
... 4. An airplane travels at a constant speed, relative to the ground, of 900.0 km/h. How far has the airplane traveled after 2.0 h in the air? 5. A straight line on a graph shows that there is a(n) ____________ between the two variables. 6. The area under a velocity-time graph is equal to the object’s ...
... 4. An airplane travels at a constant speed, relative to the ground, of 900.0 km/h. How far has the airplane traveled after 2.0 h in the air? 5. A straight line on a graph shows that there is a(n) ____________ between the two variables. 6. The area under a velocity-time graph is equal to the object’s ...
Newton*s Laws of Motion
... A car is set on cruise control and moving at a constant 50 m/s headed east. If the car’s mass is 1000 kg, what is its acceleration? Because the car is not CHANGING its velocity, the acceleration ...
... A car is set on cruise control and moving at a constant 50 m/s headed east. If the car’s mass is 1000 kg, what is its acceleration? Because the car is not CHANGING its velocity, the acceleration ...
File
... Apply Newton's First Law of Motion to an object that is moving at a constant speed and is experiencing either sliding or rolling friction. Compare the size of static friction to sliding or rolling friction when an object is not moving, has just started moving, is accelerating and is moving at a cons ...
... Apply Newton's First Law of Motion to an object that is moving at a constant speed and is experiencing either sliding or rolling friction. Compare the size of static friction to sliding or rolling friction when an object is not moving, has just started moving, is accelerating and is moving at a cons ...
+ B
... Discuss what the driver experiences when a car accelerates from rest and then applies the brakes. (a) The driver is forced to move forward. An object at rest tends to remain at rest. ...
... Discuss what the driver experiences when a car accelerates from rest and then applies the brakes. (a) The driver is forced to move forward. An object at rest tends to remain at rest. ...
Physics Quiz II
... as they move past each other c. an attracting force that acts between any two masses d. the product of an object’s velocity and mass; an object with lots of this is difficult to stop e. a push or pull that acts on an object f. the speed and direction an object is moving g. fluid friction acting on a ...
... as they move past each other c. an attracting force that acts between any two masses d. the product of an object’s velocity and mass; an object with lots of this is difficult to stop e. a push or pull that acts on an object f. the speed and direction an object is moving g. fluid friction acting on a ...
Document
... The dimensions of moment of inertia are ML2 and its SI units are kg.m2 We can calculate the moment of inertia of an object more easily by assuming it is divided into many small volume elements, each of mass Dmi ...
... The dimensions of moment of inertia are ML2 and its SI units are kg.m2 We can calculate the moment of inertia of an object more easily by assuming it is divided into many small volume elements, each of mass Dmi ...
Chapter 11 Reference Frames
... Suppose the object in Figure 11.1 is moving; then observers in different reference frames will measure different velocities. Denote the velocity of the object in frame S by ...
... Suppose the object in Figure 11.1 is moving; then observers in different reference frames will measure different velocities. Denote the velocity of the object in frame S by ...








![Unit 3 Test [23291]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015152085_1-4422a9acf541d0ae577d3837c91dd891-300x300.png)













