Newton`s 3rd Law
... A common misconception is that a rocket is propelled by the impact of exhaust gases against the atmosphere. In fact, in the early 1900s before the advent of rockets, many people thought that sending a rocket to the moon was impossible because of the absence of an atmosphere for the rocket to push a ...
... A common misconception is that a rocket is propelled by the impact of exhaust gases against the atmosphere. In fact, in the early 1900s before the advent of rockets, many people thought that sending a rocket to the moon was impossible because of the absence of an atmosphere for the rocket to push a ...
AAAAA
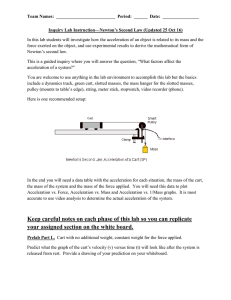
... Inquiry Lab Instruction—Newton’s Second Law (Updated 25 Oct 16) In this lab students will investigate how the acceleration of an object is related to its mass and the force exerted on the object, and use experimental results to derive the mathematical form of Newton’s second law. This is a guided in ...
... Inquiry Lab Instruction—Newton’s Second Law (Updated 25 Oct 16) In this lab students will investigate how the acceleration of an object is related to its mass and the force exerted on the object, and use experimental results to derive the mathematical form of Newton’s second law. This is a guided in ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion Powerpoint
... • Another way to increase acceleration is to change the mass. • According to the equation, acceleration and mass change in opposite ways. • If the force is constant, an increase in mass causes a decrease in acceleration. • The opposite is also true: A decrease in mass causes an increase in accelera ...
... • Another way to increase acceleration is to change the mass. • According to the equation, acceleration and mass change in opposite ways. • If the force is constant, an increase in mass causes a decrease in acceleration. • The opposite is also true: A decrease in mass causes an increase in accelera ...
Ch_04
... An object sliding down an incline has three forces acting on it: the normal force, gravity, and the frictional force. • The normal force is always perpendicular to the surface. • The friction force is parallel to it. • The gravitational force points down. If the object is at rest, the forces are the ...
... An object sliding down an incline has three forces acting on it: the normal force, gravity, and the frictional force. • The normal force is always perpendicular to the surface. • The friction force is parallel to it. • The gravitational force points down. If the object is at rest, the forces are the ...
COURSE EXPECTATIONS COURSE CODE: PHYS
... CALENDAR COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course, specializing to students in Bachelor of Science, Bachelor of Science and Technology, Bachelor of General and Liberal Science programs, introduces fundamental concepts and physical laws in classical mechanics and their applications in modern science and techn ...
... CALENDAR COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course, specializing to students in Bachelor of Science, Bachelor of Science and Technology, Bachelor of General and Liberal Science programs, introduces fundamental concepts and physical laws in classical mechanics and their applications in modern science and techn ...
U9 WS 2 - Rollercoasters
... 7. At what constant speed would the 80 kg driver pictured below have to be traveling in order to feel twice his normal body weight as he drives into a depression in the road with a radius of curvature of 20 meters. Be sure to draw a force diagram to represent the situation before you even attempt to ...
... 7. At what constant speed would the 80 kg driver pictured below have to be traveling in order to feel twice his normal body weight as he drives into a depression in the road with a radius of curvature of 20 meters. Be sure to draw a force diagram to represent the situation before you even attempt to ...
force
... 5.3 Equilibrium and normal forces A normal force is created whenever an object is in contact with a surface. ► The normal force has equal strength to the force pressing the object into the surface, which is often the object’s weight. ...
... 5.3 Equilibrium and normal forces A normal force is created whenever an object is in contact with a surface. ► The normal force has equal strength to the force pressing the object into the surface, which is often the object’s weight. ...
Chapter 3-
... wheels of a train rotate when they come into contact with the track, rather than sliding over it. ...
... wheels of a train rotate when they come into contact with the track, rather than sliding over it. ...
gravity notes - mrkearsley.com
... Terminal Velocity: The fastest an object can fall. This occurs when the air resistance is equal to the force of gravity ...
... Terminal Velocity: The fastest an object can fall. This occurs when the air resistance is equal to the force of gravity ...
Circular motion and rotation Uniform circular motion
... Recall Newton’s Second Law Thus, in uniform circular motion there must be a net force to produce the centripetal acceleration. The centripetal force is the name given to the net force required to keep an object moving on a circular path. The direction of the centripetal force always points to ...
... Recall Newton’s Second Law Thus, in uniform circular motion there must be a net force to produce the centripetal acceleration. The centripetal force is the name given to the net force required to keep an object moving on a circular path. The direction of the centripetal force always points to ...
Lecture06-09
... A 71-kg parent and a 19-kg child meet at the center of an ice rink. They place their hands together and push. (a) Is the force experienced by the child more than, less than, or the same as the force experienced by the parent? (b) Is the acceleration of the child more than, less than, or the same as ...
... A 71-kg parent and a 19-kg child meet at the center of an ice rink. They place their hands together and push. (a) Is the force experienced by the child more than, less than, or the same as the force experienced by the parent? (b) Is the acceleration of the child more than, less than, or the same as ...
document
... there will be a drag force opposing the motion. Here the drag force is proportional to - kv. Viscous drag. Stokes Law: terminal velocity is proportional to mass A 1000 km boat in the water shuts off its engine at 90 km/hr. Find the time required to slow down to 45 km/hr due to a water drag force equ ...
... there will be a drag force opposing the motion. Here the drag force is proportional to - kv. Viscous drag. Stokes Law: terminal velocity is proportional to mass A 1000 km boat in the water shuts off its engine at 90 km/hr. Find the time required to slow down to 45 km/hr due to a water drag force equ ...
ISChpt3-local-local
... The motion of an object depends on the total of all forces action on the object. We call the total of all forces the net force When forces on an object are balanced, the net force is zero and we say that the object is at equilibrium. ...
... The motion of an object depends on the total of all forces action on the object. We call the total of all forces the net force When forces on an object are balanced, the net force is zero and we say that the object is at equilibrium. ...
Physics Semester Exam Study Guide January 2014
... 57. Which of the following is an area of physics that studies motion and its causes? 58. What is a term for the quantity Ft, where F is an applied force and t is the time interval over which the force is applied? ...
... 57. Which of the following is an area of physics that studies motion and its causes? 58. What is a term for the quantity Ft, where F is an applied force and t is the time interval over which the force is applied? ...
Chapter 7
... We have found two different velocities at two different times so we can find the acceleration. But we want to know the acceleration the instant the string would break, that way we can use our tangential velocity concept. ...
... We have found two different velocities at two different times so we can find the acceleration. But we want to know the acceleration the instant the string would break, that way we can use our tangential velocity concept. ...
Chapters Two and Three
... “Whenever two objects interact, the force exerted on one object is equal in size and opposite in direction to the force exerted on the other object” Example: Standing on the Floor FAB = FBA ...
... “Whenever two objects interact, the force exerted on one object is equal in size and opposite in direction to the force exerted on the other object” Example: Standing on the Floor FAB = FBA ...