Forces and Motion
... greatest English mathematician. Do you believe an apple caused all his theories, he made his 3 laws of motion. His first law is, if something is moving it will keep moving or if the object is at rest it will remain still. His second law of motion is, that when force is acting on an object, it will c ...
... greatest English mathematician. Do you believe an apple caused all his theories, he made his 3 laws of motion. His first law is, if something is moving it will keep moving or if the object is at rest it will remain still. His second law of motion is, that when force is acting on an object, it will c ...
3_Newton_s_Laws_1_2
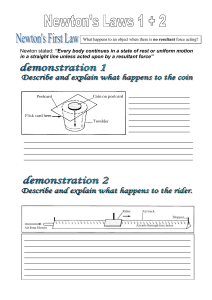
... _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ...
... _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ...
Conceptual Physics 2.2 PP
... An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will continue in motion with the same speed and direction UNLESS acted on by a force. ...
... An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will continue in motion with the same speed and direction UNLESS acted on by a force. ...
Chapter 10
... If a force F acts at a point having relative position r from axis of rotation , then Torque = r F sin=rFt= rF, where ( is angle between r and F) Ft is component of F to r, while r is distance between the rotation axis and extended line running through F. ris called moment arm of F. Unit o ...
... If a force F acts at a point having relative position r from axis of rotation , then Torque = r F sin=rFt= rF, where ( is angle between r and F) Ft is component of F to r, while r is distance between the rotation axis and extended line running through F. ris called moment arm of F. Unit o ...
N - Youngstown State University
... Vectors are physical quantities that have both magnitude and direction. Magnitude = amount and units. Direction can be stated as up/down, left/right, N/E/S/W or 35o S of E. Eg. of vectors: displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, and momentum. ...
... Vectors are physical quantities that have both magnitude and direction. Magnitude = amount and units. Direction can be stated as up/down, left/right, N/E/S/W or 35o S of E. Eg. of vectors: displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, and momentum. ...
Newton`s 1st Law
... But can you believe it when the starting velocity is some value like 8 mps rightwards? ...
... But can you believe it when the starting velocity is some value like 8 mps rightwards? ...
Newton`s Laws Discussion Questions
... it will fall behind the chimney instead of into it. c. If the train continues to slow down (deccelerate) while the ball is in the air, the ball will not be deccelerating with the train, so it will continue moving at the same horizontal speed and direction it had when it was shot from the train. Beca ...
... it will fall behind the chimney instead of into it. c. If the train continues to slow down (deccelerate) while the ball is in the air, the ball will not be deccelerating with the train, so it will continue moving at the same horizontal speed and direction it had when it was shot from the train. Beca ...
hw3,4
... of 9.8 meters per second per second. If you instead throw it downwards, its acceleration (ignore air resistance) will be A) less than 9.8 meters per second per second. B) 9.8 meters per second per second. C) greater than 9.8 meters per second per second. 5) A car accelerates at 2 meters per second p ...
... of 9.8 meters per second per second. If you instead throw it downwards, its acceleration (ignore air resistance) will be A) less than 9.8 meters per second per second. B) 9.8 meters per second per second. C) greater than 9.8 meters per second per second. 5) A car accelerates at 2 meters per second p ...
No Slide Title
... t is the amount of time the package takes to go from the height of the plane to the ground, accelerating at g but starting from rest. 2000 = 10 t2 200 = t = 14.1 seconds Therefore x = 200 (14.1) = 2820 meters ...
... t is the amount of time the package takes to go from the height of the plane to the ground, accelerating at g but starting from rest. 2000 = 10 t2 200 = t = 14.1 seconds Therefore x = 200 (14.1) = 2820 meters ...
PPT
... Consider the following situation: You are driving a car with constant speed around a horizontal circular track. On a piece of paper, draw a Free Body Diagram (FBD) for the car. How many forces are acting on the car? ...
... Consider the following situation: You are driving a car with constant speed around a horizontal circular track. On a piece of paper, draw a Free Body Diagram (FBD) for the car. How many forces are acting on the car? ...
Impulse and Momentum
... A. What was the average force applied to object? B. If the impulse was triangular, rather than constant, what was the maximum force applied to the object? (see the F vs. t graph below) Force Fmax ...
... A. What was the average force applied to object? B. If the impulse was triangular, rather than constant, what was the maximum force applied to the object? (see the F vs. t graph below) Force Fmax ...
SPH3U Forces-and-Motion-Exam
... 10. Object A of mass 2 kg is attached to Object B of mass 4 kg by a string suspended over a pulley. The tension in the part of the string attached to Object A is __________ the tension in the part of the string attached to Object B. *A. the same as B. less than C. greater than D. It cannot be deter ...
... 10. Object A of mass 2 kg is attached to Object B of mass 4 kg by a string suspended over a pulley. The tension in the part of the string attached to Object A is __________ the tension in the part of the string attached to Object B. *A. the same as B. less than C. greater than D. It cannot be deter ...