Modified True/False
... is equivalent to the force of gravity acting on the object all of the above With respect to Newton’s third law, the action and reaction forces being equal, imply a “balanced” force situation act on different objects are equal provided the object is at rest are equal provided the object is moving wit ...
... is equivalent to the force of gravity acting on the object all of the above With respect to Newton’s third law, the action and reaction forces being equal, imply a “balanced” force situation act on different objects are equal provided the object is at rest are equal provided the object is moving wit ...
Holt Physics Chapter 8
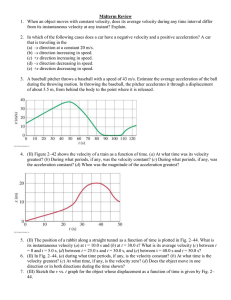
... the right side of a meter stick 0.30 m from the axis of rotation at an angle of 35 degrees. A second downward force of 67N is exerted at an angle of 49 degrees to the meter stick 0.40m to the left of the axis of rotation. What is the net torque? ...
... the right side of a meter stick 0.30 m from the axis of rotation at an angle of 35 degrees. A second downward force of 67N is exerted at an angle of 49 degrees to the meter stick 0.40m to the left of the axis of rotation. What is the net torque? ...
Work and Kinetic Energy - University of Utah Physics
... the space telescope? (b) if the telescope's mass were to increase, what would need to happen to its speed in order to maintain the same orbit? ...
... the space telescope? (b) if the telescope's mass were to increase, what would need to happen to its speed in order to maintain the same orbit? ...
Newton`s Laws on an Elevator (print version)
... Since the elevator and the rider are accelerating downward, the net force must act downward How would you feel? Heavier, lighter or normal? Lighter! You don’t feel the force of gravity, rather you feel how much the floor is supporting you! ...
... Since the elevator and the rider are accelerating downward, the net force must act downward How would you feel? Heavier, lighter or normal? Lighter! You don’t feel the force of gravity, rather you feel how much the floor is supporting you! ...
Forces and Newtons Laws
... Inertia – the tendency of an object at rest to remain at rest; or, if moving, to continue moving with a constant velocity, until acted upon by an unbalanced force. All objects have inertia because they resist changes in motion. An object with very little mass, such as a baseball, can be accelerated ...
... Inertia – the tendency of an object at rest to remain at rest; or, if moving, to continue moving with a constant velocity, until acted upon by an unbalanced force. All objects have inertia because they resist changes in motion. An object with very little mass, such as a baseball, can be accelerated ...
L14_RigidBody
... Object under Linear Force Given: force, f(t), gives rise to acceleration, a(t), or x(ti ) Use a(t) to update current state of point mass: x(t), v(t) ...
... Object under Linear Force Given: force, f(t), gives rise to acceleration, a(t), or x(ti ) Use a(t) to update current state of point mass: x(t), v(t) ...
homework assignments solutions to chapter 1 solutions to chapter 2
... force is necessary to accelerate the book. 16. The forces must be equal and opposite because they are the only forces acting on the person, who obviously is not accelerating. Note that the pair of forces do not comprise an action-reaction pair, however, for they act on the same body. The downward fo ...
... force is necessary to accelerate the book. 16. The forces must be equal and opposite because they are the only forces acting on the person, who obviously is not accelerating. Note that the pair of forces do not comprise an action-reaction pair, however, for they act on the same body. The downward fo ...
8.012 Physics I: Classical Mechanics MIT OpenCourseWare rms of Use, visit: .
... A cylinder of mass M, length L and radius R is spinning about its long axis with angular velocity on a frictionless horizontal surface. The cylinder is given a sharp, horizontal strike with impulse Δp at a distance r from its center of mass (COM). Assume that constant gravitational acceleration acts ...
... A cylinder of mass M, length L and radius R is spinning about its long axis with angular velocity on a frictionless horizontal surface. The cylinder is given a sharp, horizontal strike with impulse Δp at a distance r from its center of mass (COM). Assume that constant gravitational acceleration acts ...
Newton`s Laws II - Rutgers Physics
... 0. First, test the four wheels on the Pasco cart by spinning each one by hand to see if it spins for at least 3 seconds before stopping. If it stops quickly, try pushing the wheels (along their axes) away from the side walls of the cart since rubbing up against the side internally could be causing f ...
... 0. First, test the four wheels on the Pasco cart by spinning each one by hand to see if it spins for at least 3 seconds before stopping. If it stops quickly, try pushing the wheels (along their axes) away from the side walls of the cart since rubbing up against the side internally could be causing f ...
Appendix B: Simple Harmonic Motion
... where k is the spring constant. The negative sign means that when x is positive (spring is stretched), the force is negative and thus the direction of the force is opposite to the direction the spring was stretched. For example, in Figure B.1, pulling the mass down, produces a force which is up. Now ...
... where k is the spring constant. The negative sign means that when x is positive (spring is stretched), the force is negative and thus the direction of the force is opposite to the direction the spring was stretched. For example, in Figure B.1, pulling the mass down, produces a force which is up. Now ...
What is a force? - iGCSE Science Courses
... • Find the resultant of two or more forces acting along the same line • Recognise that if there is no resultant force on a body it either remains at rest or continues at constant speed in a straight line • Understand friction as the force between two surfaces which impedes motion and results in heat ...
... • Find the resultant of two or more forces acting along the same line • Recognise that if there is no resultant force on a body it either remains at rest or continues at constant speed in a straight line • Understand friction as the force between two surfaces which impedes motion and results in heat ...