Chapter 12: Forces in Motion
... • Why does a projectile follow a curved path? What Is a Force? • A force can cause a resting object to _________, or it can accelerate a moving object by changing the object’s speed or direction. • A __________ or a ___________ ...
... • Why does a projectile follow a curved path? What Is a Force? • A force can cause a resting object to _________, or it can accelerate a moving object by changing the object’s speed or direction. • A __________ or a ___________ ...
Physics I - Rose
... could be kept moving up the ramp. However, if you stop on the ramp and want to start the box from rest, the model of static friction applies. The analysis is the same except that the coefficient of static friction is used and we use the maximum value of the force of static friction. Therefore, we ha ...
... could be kept moving up the ramp. However, if you stop on the ramp and want to start the box from rest, the model of static friction applies. The analysis is the same except that the coefficient of static friction is used and we use the maximum value of the force of static friction. Therefore, we ha ...
Conservation Laws
... That is to say, the second sum will vanish if the force between any two particles acts along a line which is parallel to the displacement vector between them. In the vast majority of inter-particle forces we will consider, this will indeed be the case. It is the case for Newton’s law of gravitation, ...
... That is to say, the second sum will vanish if the force between any two particles acts along a line which is parallel to the displacement vector between them. In the vast majority of inter-particle forces we will consider, this will indeed be the case. It is the case for Newton’s law of gravitation, ...
Powerpoint for today
... held by the parking brake, what is the magnitude of the frictional force that holds your car in place? B. The coefficient of static friction between your car's wheels and the road when wet is 0.30. What is the largest angle slope on which you can park your car in the rain so that it will not slide d ...
... held by the parking brake, what is the magnitude of the frictional force that holds your car in place? B. The coefficient of static friction between your car's wheels and the road when wet is 0.30. What is the largest angle slope on which you can park your car in the rain so that it will not slide d ...
The Cause of Centrifugal Force
... pervades all space and which gives the familiar physical characteristics to a fluid on the atomic and molecular scale. Although we can identify a rotating electron-positron dipole with an Archimedes’ screw, the ultimate mechanism whereby the aether is pumped in through a positron source and pulled ...
... pervades all space and which gives the familiar physical characteristics to a fluid on the atomic and molecular scale. Although we can identify a rotating electron-positron dipole with an Archimedes’ screw, the ultimate mechanism whereby the aether is pumped in through a positron source and pulled ...
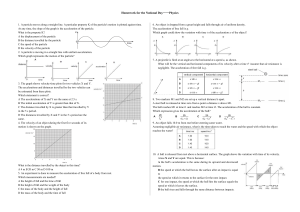
Homework for the National Day——Physics 1. A particle moves
... 3. The graph shows velocity-time plots for two vehicles X and Y. The accelerations and distances travelled by the two vehicles can be estimated from these plots. Which statement is correct? A The accelerations of X and Y are the same at 2.5 s. B The initial acceleration of Y is greater than that of ...
... 3. The graph shows velocity-time plots for two vehicles X and Y. The accelerations and distances travelled by the two vehicles can be estimated from these plots. Which statement is correct? A The accelerations of X and Y are the same at 2.5 s. B The initial acceleration of Y is greater than that of ...
procedure - Homework Market
... relationship is used later in the derivation of an expression for the period T of the conical pendulum. The cosine of theta is h /L, which can be solved for the letter “ h ” as shown. h = L (Cosine theta). This equation is used to solve for the height “ h ” from our data later in the experiment. The ...
... relationship is used later in the derivation of an expression for the period T of the conical pendulum. The cosine of theta is h /L, which can be solved for the letter “ h ” as shown. h = L (Cosine theta). This equation is used to solve for the height “ h ” from our data later in the experiment. The ...
1 Section 1.1: Vectors Definition: A Vector is a quantity that has both
... Applications to Physics and Engineering: A force is represented by a vector because it has both magnitude (measured in pounds or newtons) and direction. If several forces are acting on an object, the resultant force experienced by the object is the vector sum of the forces. EXAMPLE 5: Ben walks due ...
... Applications to Physics and Engineering: A force is represented by a vector because it has both magnitude (measured in pounds or newtons) and direction. If several forces are acting on an object, the resultant force experienced by the object is the vector sum of the forces. EXAMPLE 5: Ben walks due ...
Physics 11 Final Exam Outline
... -Recognize the main forms of energy and be able to perform calculations involving the law of conservation of energy define work in terms of force and displacement solve a variety of problems involving work force displacement determine graphically the amount of work done on objects by con ...
... -Recognize the main forms of energy and be able to perform calculations involving the law of conservation of energy define work in terms of force and displacement solve a variety of problems involving work force displacement determine graphically the amount of work done on objects by con ...
Overheads - Physics 420 UBC Physics Demonstrations
... • The friction between the road and a car’s wheels is called traction. • Traction allows cars to accelerate and to change direction. • What happens when the surface the wheels contact changes (the coefficient of friction is ...
... • The friction between the road and a car’s wheels is called traction. • Traction allows cars to accelerate and to change direction. • What happens when the surface the wheels contact changes (the coefficient of friction is ...
Part I
... • Energy: Traditionally defined as the ability to do work. We now know that not all forces are able to do work; however, we are dealing in these chapters with mechanical energy, which does follow this definition. • Kinetic Energy The energy of motion “Kinetic” Greek word for motion An object in ...
... • Energy: Traditionally defined as the ability to do work. We now know that not all forces are able to do work; however, we are dealing in these chapters with mechanical energy, which does follow this definition. • Kinetic Energy The energy of motion “Kinetic” Greek word for motion An object in ...
Physics Department Physics 101 - Physics Department ,Kuwait
... building observes its motion. On which of the following will the two observers disagree? (Neglect air resistance) a. the change in the ball’s potential energy. b. the ball’s kinetic energy at some point during its motion. ...
... building observes its motion. On which of the following will the two observers disagree? (Neglect air resistance) a. the change in the ball’s potential energy. b. the ball’s kinetic energy at some point during its motion. ...
Lecture 13.Work
... •Work is a scalar, not a vector. •Work can be positive, negative, or zero. •The angle is always the angle between F and d . Be careful about this. •There is often more than one force acting on an object. The total net work is the sum of the work done by all the forces. ...
... •Work is a scalar, not a vector. •Work can be positive, negative, or zero. •The angle is always the angle between F and d . Be careful about this. •There is often more than one force acting on an object. The total net work is the sum of the work done by all the forces. ...
Document
... • Velocity refers to both speed and direction • Acceleration means a change in velocity • Mass is a property of objects that represents their reluctance to accelerate • If an object is accelerating, it’s being acted on by an unbalanced force, and F = ma • Gravity causes all objects to suffer the sam ...
... • Velocity refers to both speed and direction • Acceleration means a change in velocity • Mass is a property of objects that represents their reluctance to accelerate • If an object is accelerating, it’s being acted on by an unbalanced force, and F = ma • Gravity causes all objects to suffer the sam ...
Chapter 12 Section 1 Notes - School District of La Crosse
... through the air is known as air resistance. ...
... through the air is known as air resistance. ...
Combining Forces
... moving, it continues to move in a straight line with constant speed. Newton’s Laws of Motion ...
... moving, it continues to move in a straight line with constant speed. Newton’s Laws of Motion ...
Lecture 18
... Procedure of analysis (17.5) Problems involving the kinetics of a rigid body undergoing general plane motion can be solved using the following procedure. 1. Establish the x-y inertial coordinate system. Draw both the free body diagram and kinetic diagram for the body. 2. Specify the direction and s ...
... Procedure of analysis (17.5) Problems involving the kinetics of a rigid body undergoing general plane motion can be solved using the following procedure. 1. Establish the x-y inertial coordinate system. Draw both the free body diagram and kinetic diagram for the body. 2. Specify the direction and s ...