Newton`s First Law of Motion Friction and Newton`s First Law
... The acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied. • Newton’s second law describes the motion of an object when an unbalanced force acts on the object. ...
... The acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied. • Newton’s second law describes the motion of an object when an unbalanced force acts on the object. ...
12.1 Forces
... Unbalanced force When an unbalanced force acts on an object, the object accelerates ...
... Unbalanced force When an unbalanced force acts on an object, the object accelerates ...
Chapter 10: Energy, Work and Simple Machines
... If F ll d, then W = Fd or W = -Fd W = Fd, Force in same direction as displacement ( = 0o: cos = 1, Positive Work) W = -Fd, Force is in the opposite direction as the displacement ( = 180o: cos = -1, Negative Work) ...
... If F ll d, then W = Fd or W = -Fd W = Fd, Force in same direction as displacement ( = 0o: cos = 1, Positive Work) W = -Fd, Force is in the opposite direction as the displacement ( = 180o: cos = -1, Negative Work) ...
Forces 12.1 Pg 356-362 - Physical Science 2014-2015
... Unbalanced force When an unbalanced force acts on an object, the object accelerates ...
... Unbalanced force When an unbalanced force acts on an object, the object accelerates ...
chapter 04
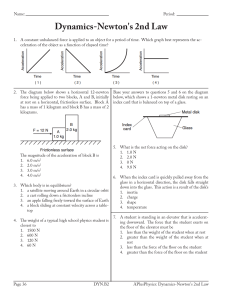
... • A diagram of the forces acting on an object • Must identify all the forces acting on the object of interest • Choose an appropriate coordinate system • If the free body diagram is incorrect, the solution will likely be incorrect ...
... • A diagram of the forces acting on an object • Must identify all the forces acting on the object of interest • Choose an appropriate coordinate system • If the free body diagram is incorrect, the solution will likely be incorrect ...
Motion - Portland Jewish Academy
... _______________________ - there would be nothing to slow them down. (Forever) 6. When an object is at rest, or sitting still, it __________________ sitting still unless acted on by an ______________________ force. Something that is moving will keep ______________________ unless acted on by an outsid ...
... _______________________ - there would be nothing to slow them down. (Forever) 6. When an object is at rest, or sitting still, it __________________ sitting still unless acted on by an ______________________ force. Something that is moving will keep ______________________ unless acted on by an outsid ...
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics continued
... ω : angular velocity of rotation (same for entire object) α : angular acceleration (same for entire object) vT = ω r : tangential velocity aT = α r : tangential acceleration According to Newton’s second law, a net force causes an object to have a linear acceleration. What causes an object to have an ...
... ω : angular velocity of rotation (same for entire object) α : angular acceleration (same for entire object) vT = ω r : tangential velocity aT = α r : tangential acceleration According to Newton’s second law, a net force causes an object to have a linear acceleration. What causes an object to have an ...
PHY_101_NOTE_-REVISED
... Kinematics is the study of the motion of objects without referring to what causes the motion. Motion is a change in position in a time interval. ...
... Kinematics is the study of the motion of objects without referring to what causes the motion. Motion is a change in position in a time interval. ...
Simple Harmonic Moti.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... The minus sign shows that the force is a restoring force, tending to move the object back toward its resting position. "Linear" means that the force required to hold the object a distance x from its equilibrium point is linearly proportional to the distance x, with k the constant of proportionality. ...
... The minus sign shows that the force is a restoring force, tending to move the object back toward its resting position. "Linear" means that the force required to hold the object a distance x from its equilibrium point is linearly proportional to the distance x, with k the constant of proportionality. ...
Symbols a = acceleration t = time d = distance s = speed Ѵ = velocity
... regardless of their weight. constant Definition: always the same; unchanging Context: Acceleration in freefall or rate of speed (gravity) is constant. g=9.8m/sec2 friction Definition: The force of one surface rubbing against another, with the total effect being to decrease motion Context: If you wan ...
... regardless of their weight. constant Definition: always the same; unchanging Context: Acceleration in freefall or rate of speed (gravity) is constant. g=9.8m/sec2 friction Definition: The force of one surface rubbing against another, with the total effect being to decrease motion Context: If you wan ...
unit 2 universal gravitation and circular motion
... Satellites are objects that are projected into space They are at a constant height above the planet and are in uniform circular motion The force of gravity keeps the satellite in orbit around the earth (or any other planet) ...
... Satellites are objects that are projected into space They are at a constant height above the planet and are in uniform circular motion The force of gravity keeps the satellite in orbit around the earth (or any other planet) ...
Ch13 Powerpoint
... 6. Explain the cause and effect relationship between the forces responsible for rotary motion and the objects experiencing the motion. 7. Define centripetal and centrifugal force, and explain the relationships between these forces and the factors ...
... 6. Explain the cause and effect relationship between the forces responsible for rotary motion and the objects experiencing the motion. 7. Define centripetal and centrifugal force, and explain the relationships between these forces and the factors ...
Force - TeacherWeb
... NEWTON- SI unit of force. WEIGHT- Measure of the force of gravity acting on an object. ...
... NEWTON- SI unit of force. WEIGHT- Measure of the force of gravity acting on an object. ...
File
... displacement, or both, yet no work is done on the object. Example: Holding a box in your hands. The box is not moving so no work is done so the displacement is zero. A puck on an air hockey table is moving but it does not have ...
... displacement, or both, yet no work is done on the object. Example: Holding a box in your hands. The box is not moving so no work is done so the displacement is zero. A puck on an air hockey table is moving but it does not have ...